
- Understanding Cryptography and the Fundamentals of Encryption
- What is Public Key?
- What is a Private Key?
- What’s the Difference between Public Keys and Private Keys?
- How to Generate a Public Key and a Private Key
- Conclusion
Cyber Security Training Courses thorough comprehension of them extends beyond technical expertise and aids in comprehending how intelligent systems enhance the safety of our online environment. The following information will assist you in understanding the principles of network security and how to share information while ensuring your safety online.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Public Key and a Private Key? Sign Up For Our Cyber Security Online Training Today!
Understanding Cryptography and the Fundamentals of Encryption
Cryptography is like network security guards that ensure our online chats and information remain private and safe. Here’s how it works: It transforms your messages into a secret code only the intended recipient can read. Do you remember sending a hidden note that only your friend can read? That’s exactly what data encryption does it scrambles your message so nobody else can read it. In the age of Cyber Media, where information spreads rapidly across multiple platforms, encryption is essential to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access and ensure privacy in online communications.
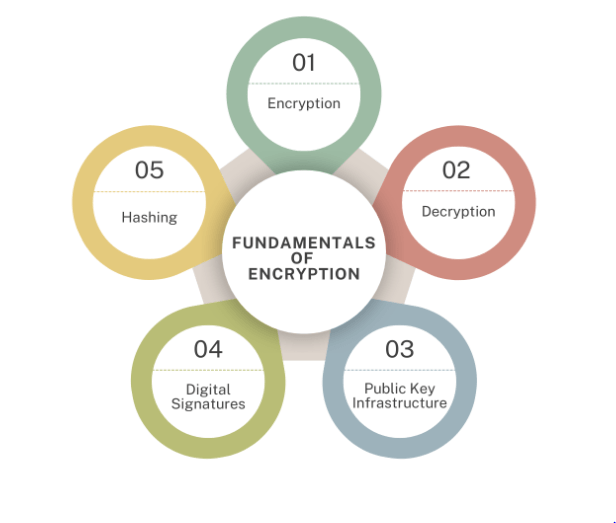
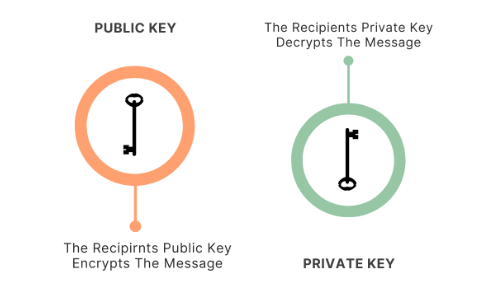
Decryption is when the secret encryption key can reconstruct the message and begin reading it again. All these processes keep our emails and shopping done via the internet secure. There are two kinds of key based processes private key and public key cryptography. In other words, imagine the public key encryption as a lock that anyone can close, but only the private key can unlock. The private key is a secret key only you have; it unlocks the scrambled messages. It’s a two key system: everybody knows your public key or the lock but you alone can see the message with your private key that unlocks it.
What Is Public Key?
A public key encryption would act like an electronic version of your address, something you’d distribute freely. Public key cryptography is applied to receive secure messages or transactions. It functions like your public email, where others can send you encrypted email security messages, but only you, using your private key, can decrypt and read them. However, without proper security, encrypted communications can be exploited for malicious purposes, such as Cyber Defamation. Besides securing communications, public key encryption is also significant in the generation of digital signatures. You can sign a message or a transaction using your private key; this will prove that the message or transaction truly originated from you and hasn’t been tampered with. The recipient can verify this signature by using your public key, hence ensuring integrity and authenticity in the message. This combination of encryption and digital signatures is crucial for protection of trust in online activities and secure email exchange, electronic commerce transactions, and digital contracts so that users can be protected from fraud and tampering.
To Explore Public Key and a Private Key in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Cyber Security Online Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
What is a Private Key?
A private key is a secret password for your digital address called the public key. In private key encryption, it is kept confidential to decrypt encrypted messages or permit secure transactions. For instance, attackers may use tools such as the Google Hacking Database to find exposed systems or vulnerabilities in poorly secured cryptographic implementations. For example, it’s just like the key to your mailbox: only you can open the mailbox and control the information addressed to you.
The private key in public key cryptography works together with a public key that can be shared with people publicly for use in encrypting messages. As such, this system ensures that even if somebody intercepts the encrypted message, they cannot access the contents without the corresponding private key. This two-key method provides a strong level of security so that there can be secure communication and transactions over the internet, protect sensitive information from others, and assure the authenticity of digital identity.
Looking to Master Cybersecurity? Discover the Cyber Security Expert Masters Program Training Course Available at ACTE Now!
What’s the Difference between Public Keys and Private Keys?
| Aspect | Public Key | Private Key |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership and Accessibility | Publicly available to anyone and can be shared openly | Kept confidential and accessible only by the individual or entity it belongs to |
| Primary Function | Mainly used to encrypt data intended for the private key holder and to verify digital signatures | Primarily used to decrypt data encrypted with the corresponding public key and to sign digital documents |
| Algorithm Used | Utilized in algorithms like RSA, DSS, etc. | Used in algorithms such as AES 128, AES 192, and AES 256, with AES standing for Advanced Encryption Standard |
| Data Transmission | Electrical Signal or Bits | Frame (L2 Switch), Frame and Packet (L3 Switch) | Distribution and Sharing | Freely shared and can be published in public directories or websites without compromising security | Must remain secret and never be shared to preserve security integrity, Cyber Awareness plays a key role in educating users about the importance of safeguarding such secrets |
| Security Concerns | Remains secure as long as the private key is kept confidential | Requires a high level of security; if compromised, it can result in significant security breaches |
| Pairing with Other Key | Always paired with a corresponding private key, forming a unique key pair | Always paired with a corresponding public key in a cryptographic system |
| Role in Digital Signatures | Verifies digital signatures created with the corresponding private key | Generates a digital signature that can be verified by anyone with the corresponding public key |
| Typical Use Cases | Encrypting emails or documents, securing online transactions, and verifying identity | Decrypting sensitive information, authenticating identity, and signing software or documents |
| Revocation and Replacement | Can be easily replaced or updated without needing a new key pair | If compromised, it requires complete revocation and the generation of a new key pair |
| Storage and Protection | Can be stored in less secure, more accessible environments | Stored in highly secure environments, often supported by hardware like HSM |
| Key Length and Complexity | Length and complexity balance security needs with computational efficiency | Generally long and complex for security, matching the length of the public key |
| Example Scenario | A sender encrypts an email using the recipient’s public key, ensuring that only the recipient can read it | A user decrypts an encrypted email sent to them using their private key |
How to Generate a Public Key and a Private Key
Several algorithms secure digital communication, with three currently being the most effective and widely used: RSA, DSS, and ECC.
Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA): RSA is one of the oldest methods in Cyber Security Training Courses. It’s mainly used to transmit shared keys with symmetric key cryptography securely. This method depends on the factoring challenge of large prime numbers, so it has been secured in many applications.
Preparing for a Cyber Security Job Interview? Check Out Our Blog on Cyber Security Interview Questions and Answers
Conclusion
We’ve explored how private key and public key cryptography functions in Cyber Security Training Courses. Think of this system as a duo: the public key serves as an open mailbox for anyone to send you messages, while the private key is a unique key only you possess, allowing you to unlock those messages. This illustrates the fundamental principles of how these keys work together for data encryption and decryption, enhancing the email security of your online information. Whether new to digital security or looking to deepen your understanding, it’s important to ask questions and seek knowledge. There’s always more to learn about private and public keys and how they protect your data in an increasingly connected world!





