- Introduction
- Definition of Data Science
- Definition of Artificial Intelligence
- Overlap Between the Two
- Scope and Applications
- Educational Pathways
- Required Skill Sets
- Conclusion
Introduction
In today’s fast-paced technological landscape, Data Science and Artificial Intelligence (AI) stand out as two of the most influential and rapidly advancing fields. Both play crucial roles in driving digital transformation across industries, revolutionizing how businesses make decisions, streamline operations, and innovate new products and services. Despite their frequent overlap in real-world applications, Data Science and AI have distinct goals and approaches that complement each other. Data Science focuses on extracting valuable insights from vast amounts of data using statistical analysis, machine learning, data visualization, and Data Science Training. It helps organizations understand patterns, predict trends, and make data-driven decisions. AI, on the other hand, aims to create intelligent systems that can perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, and problem-solving. Machine learning, a key subset of AI, heavily relies on data science techniques for training models. This article delves into the definitions of both fields, highlights their similarities and differences, and discusses educational pathways and career opportunities. It also explores emerging trends shaping their futures. Understanding these aspects is essential for professionals looking to build a career in either field and for businesses aiming to leverage the power of data and intelligent automation in a competitive world.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Data Science? Sign Up For Our Data Science Course Training Today!
Definition of Data Science
Data Science is an interdisciplinary field that focuses on extracting, analyzing, and interpreting large volumes of data to reveal hidden patterns, insights, and trends that support informed decision-making. It blends knowledge from computer science, statistics, and specific domain expertise to transform raw data into actionable information. This process often involves techniques such as data mining, machine learning, and statistical analysis, which enable organizations to solve complex problems or predict future outcomes, illustrating Data Mining Vs. Machine Learning. At its core, Data Science is about discovering meaningful insights within data. It requires not only collecting and processing data but also interpreting it in ways that can drive progress in business, science, and technology. For example, data scientists analyze customer behavior to optimize marketing strategies, helping businesses target their audiences more effectively.
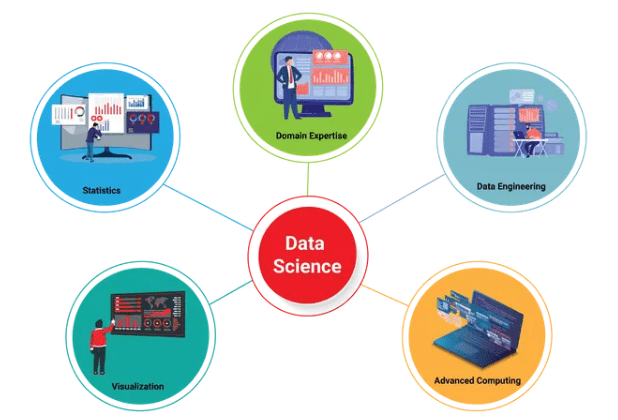
In healthcare, they study patient records to forecast disease outbreaks, personalize treatments, and improve patient outcomes. By combining advanced algorithms, statistical methods, and domain knowledge, Data Science empowers organizations to make data-driven decisions, enhance operational efficiency, and innovate. Its ability to turn vast and complex datasets into clear, actionable insights makes Data Science a critical tool in today’s data-rich world, impacting industries from finance and retail to healthcare and beyond.
Definition of Artificial Intelligence
- Machine Learning: A core component of AI where machines learn from data and improve their performance without being explicitly programmed for every task.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): AI enables computers to understand, interpret, and respond to human language in a meaningful way.
- Computer Vision: AI allows machines to interpret and analyze visual information from the world, such as recognizing objects, faces, and scenes.
- Automation of Tasks: AI systems can automate tasks, boosting efficiency and reducing errors, highlighting Advantages & Disadvantages of Python programming language.
- Decision Making and Problem Solving: AI systems use algorithms and models to analyze data, make predictions, and support decision-making processes.
- Broad Applications: AI is applied in diverse fields including healthcare, finance, robotics, customer service, and autonomous vehicles, transforming how we interact with technology.
- Simulation of Human Intelligence: AI refers to the creation of computer systems that can perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence, such as reasoning, learning, and problem-solving.
- Distinct but Overlapping Fields: Data Science and AI are separate disciplines but overlap significantly, particularly in machine learning applications.
- Data Science as a Precursor: Data Science lays the foundation for AI by gathering, cleaning, and preparing data that AI systems require to learn effectively.
- Role of Data Scientists: Data scientists handle collecting and processing raw data through Data Science Training to ensure AI models are trained with high-quality, reliable datasets.
- Machine Learning as a Subset of AI: Machine learning, a core part of AI, depends heavily on data science techniques like data preprocessing, statistical analysis, and feature engineering.
- Importance of Data: Without well-processed data, AI algorithms cannot identify patterns or make accurate predictions, highlighting the critical role of data science.
- Shared Tools and Technologies: Both fields commonly use programming languages like Python and R, and machine learning libraries such as TensorFlow and PyTorch.
- Interdisciplinary Knowledge: Given the overlap, professionals in AI and data science benefit greatly from understanding each other’s domains to develop better, more efficient solutions.
- Bootcamps: Intensive data science and AI bootcamps offer practical, project-based learning in a short time frame, focusing on real-world tools and applications.
- Undergraduate Degrees: Many start with bachelor’s degrees in fields like computer science, statistics, mathematics, or engineering, which provide foundational knowledge in programming and analytical thinking.
- Specialized Data Science Programs: Increasingly, universities offer dedicated undergraduate and graduate programs focused specifically on data science, combining courses in machine learning, big data, and statistics.
- Master’s Degrees: A master’s degree in data science, artificial intelligence, or related fields offers advanced training in algorithms, data mining, and predictive modeling, often including hands-on projects such as What is Normality Test in Minitab.
- Online Courses and Certifications: Platforms like Coursera, edX, and Udacity provide flexible learning options with certifications in data science, AI, and machine learning, accessible to professionals seeking skill upgrades.
- Interdisciplinary Learning: Combining knowledge from domains such as business, healthcare, or social sciences with data science skills can enhance one’s ability to solve domain-specific problems.
- Continuous Learning: Given the fast-evolving nature of data science and AI, professionals need to engage in lifelong learning through workshops, research papers, and new technologies to stay current.
To Explore Data Science in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Data Science Course Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
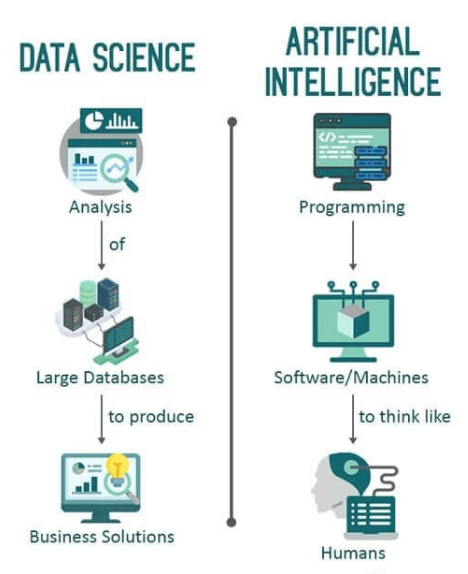
Overlap Between the Two
Scope and Applications
The scope of Data Science and Artificial Intelligence (AI) is vast and continues to expand rapidly across various industries. Data Science involves extracting valuable insights from large, complex datasets, making it crucial for decision-making in sectors such as finance, healthcare, marketing, and retail. By analyzing trends, customer behavior, and operational data, organizations can optimize strategies, improve services, and drive growth. AI extends this capability by enabling machines to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as image recognition, natural language processing, and autonomous decision-making. AI-powered applications are transforming industries by automating routine tasks, enhancing customer experiences through chatbots, improving diagnostics in healthcare, and enabling self-driving vehicles, as highlighted in Top Data Science Books for Beginners & Advanced Data Scientist. Together, Data Science and AI fuel innovation in emerging fields like personalized medicine, predictive maintenance, fraud detection, and smart cities. Their integration with big data technologies allows organizations to process and analyze enormous volumes of data in real-time, leading to faster and more accurate insights. As more businesses adopt these technologies, the demand for skilled professionals in Data Science and AI grows, creating abundant career opportunities. The combined power of data-driven analysis and intelligent automation promises to revolutionize how industries operate, making these fields integral to the future of technology and society.
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Data Science by Enrolling in Our Data Science Masters Course.
Educational Pathways
Required Skill Sets
Successful data scientists and AI professionals need a diverse set of skills that combine technical expertise, analytical thinking, and domain knowledge. At the core, strong programming skills are essential, with languages like Python, R, Java, and SQL commonly used for data manipulation, analysis, and building machine learning models. Proficiency in statistical analysis and a deep understanding of algorithms help professionals interpret data patterns and develop predictive models effectively. Data handling skills, including data cleaning, preprocessing, and feature engineering, are crucial for preparing raw data into usable formats, which are among the Reasons You Should Learn R, Python, & Hadoop. Familiarity with machine learning frameworks such as TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Scikit-learn allows for efficient model development and deployment. Visualization skills using tools like Matplotlib, Seaborn, or Tableau enable professionals to communicate insights clearly to stakeholders. Beyond technical skills, strong problem-solving abilities and critical thinking are vital for designing effective solutions. Domain expertise helps in understanding the context and relevance of data, ensuring that analyses address real-world problems. Collaboration and communication skills are equally important, as data professionals often work in multidisciplinary teams and must explain complex concepts to non-technical audiences. Finally, given the rapidly evolving nature of data science and AI, a commitment to continuous learning and adaptability is essential to stay updated with emerging tools, techniques, and best practices in the field.
Go Through These Data Science Interview Questions & Answer to Excel in Your Upcoming Interview.
Conclusion
Data Science and Artificial Intelligence (AI) are both essential pillars driving the future of technology and business innovation. Although these fields share some overlap, they serve distinct but complementary purposes. Data Science primarily focuses on extracting meaningful insights from large volumes of data through analysis, statistical methods, and visualization. By uncovering patterns and trends, data scientists help organizations make informed, data-driven decisions. In contrast, AI centers on creating intelligent systems capable of automating tasks, learning from data, and making decisions independently through Data Science Training. AI technologies, such as machine learning and natural language processing, enable machines to mimic human cognitive functions, leading to smarter applications in areas like robotics, healthcare, finance, and customer service. The demand for skilled professionals in both data science and AI continues to grow rapidly as companies seek to leverage data and intelligent systems to stay competitive. These fields are constantly evolving, with new tools, techniques, and applications emerging regularly. This dynamic landscape offers abundant opportunities for innovation, career growth, and impact. Choosing a career in either Data Science or AI opens doors to exciting roles that influence the future of technology. Together, these disciplines are shaping smarter, more efficient, and data-driven industries worldwide.