
- What is an Ethical Hacker?
- The Core Principles of Hacking Ethics
- Understanding the Ethical Hacker’s Toolkit
- The Growing Impact of Cybercrime on Society
- Motivations behind Hacking
- Challenges in Ethical Hacking
- The Role of Ethical Hackers in Combating Cybercrime
- Conclusion
In today’s fast-paced digital world, hacking automatically refers to bad intent and cybercrime. However, there is a vital difference between bad hacking practices and what’s termed ethical hacking, which forms the basis of modern security efforts. This paper shall outline the Cybersecurity Training Courses and its role in boosting digital security and keeping sensitive information undercover. We discuss in this article the significance of hacking ethics and their contribution to the world of cybersecurity by ethical hackers.
To become a certified cyber security, have a look at our Cyber Security Online Training right now.
What is an Ethical Hacker?
Ethical hacking means testing and assessing the security of a computer system, network, or application with the permission of its legal owner. The approach is essentially that of a criminal hacker, but the motives are good to discover problems in the system before they can become exploited by a malicious operator. Thus, cybercrime prevention can be referred to as a term of ethical hacking which the black-hat hacker commonly mistakes. While the tools and techniques of an ethical hacker are similar to a black-hat hacker, they operate in a legal and moral context. Organizations sometimes retain ethical hackers for conducting penetration testing and vulnerability assessment among cyber crime security measures to protect the systems installed. In so doing, cyber related crimes prevention gives businesses and individuals a sense of proactive protection of their digital environment against Hacking in Cybersecurity .
The Core Principles of Hacking Ethics
- Authorization
- Confidentiality
- Transparency
- Minimizing Harm
- Accountability
- Reputation Damage: A cyberattack can harm an organization’s standing and seriously undermine consumer confidence.
- Privacy Violations: Cyber thieves often steal sensitive personal information, leading to identity theft and violations of privacy.
- National Security Risks: Cyber attacks on critical infrastructure, such as power grids and communication systems, pose a serious cyber security risks to national security. The demand for skilled, ethical hackers will increase with cybercrime’s evolution.
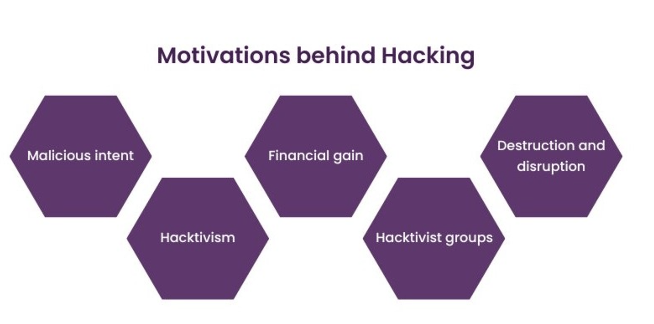
- Malicious intent: Hackers act maliciously motivated by retaliation, personal benefit, or ideological convictions. They have set motives that make them hack systems to perpetuate financial gains, get revenge against individuals or organizations, and further their agendas, spreading cyber threats .
- Hacktivism: Some hackers resort to hacktivism, which is hacking systems into situations that advance social, political, or environmental causes. They may deface websites or leak sensitive information to raise awareness on certain issues and, therefore, can be termed digital activists.
- Financial gain: The most common motivation for hacking is economic profit. Web Application Security might hack into banking systems, e-commerce sites, or cryptocurrency platforms to steal financial information, perform financial fraud, or ask for ransom in cryptocurrency. All of these are usually motivated by a monetary incentive.
- Hacktivist groups:There are also organized hacktivist groups that perform hacking activities. This is also organized in such that their groups, operating with social or political ideology, are generally attacking selected targets to make statements or protest particular injustices. Their attacks are usually high-profile and find publicity in the media.
- Destruction and disruption: Cause chaos and make some systems fall on their knees. Some hackers want to cause confusion and bring some systems down. Losses of reputational damage and operational disruptions for businesses and organizations are caused by launching distributed denial of cybercrime as a service attacks, defacing websites, or, worse, corrupting data.
- Legal Boundaries Ethical hackers have to operate within rather narrow legal boundaries. The differences between ethical and unethical hacking sometimes become rather obscure, especially in those countries with vague cyber crime security laws.
- Staying Ahead of Cybercriminals Cyberthieves’ technological know-how is constantly updating and developing. An ethical hacker should be aware of new hacking techniques and technologies to carry out productive vulnerability identification.
- Balancing Ethics with Efficiency An ethical hacker needs to balance aggressive testing with respect for the systems’ operational integrity that they are about to test. Over-testing or disruptive approaches can disrupt the organization’s regular functioning.
- Penetration Testing: Ethical hackers occasionally perform penetration tests to mimic live attacks in real-time so that systems become stronger and safer from cyber attacks. Vulnerability Assessments: Hackers identify and correct vulnerabilities so cyber related crimes prevention may not exploit them.
- Incident Response:They help organizations to respond to and contain the impact of security breaches.
- Security Audits:They conduct audits to ensure that organizations adhere to best security practices and regulatory compliance.
Ethical hackers only operate with direct permission from the system’s owner. Otherwise, hacking is illegal and unethical if done without explicit permission. Getting unauthorized access to a system attracts violations of laws concerning privacy and cyber crime security, which falls under malicious hacking.
Ethical hackers are accorded sensitive information in their assessments. As such, they are expected to keep confidentiality and ensure that the information accessed is protected. This entails not involving third parties with information they have harvested from the system or weaknesses of the system and not exploiting any accessed information for their advantage.
Ethical hackers are transparent about all their activities. They communicate their test methods, findings, and outcomes to the hiring organization, ensuring that the organization understands all the vulnerabilities found and how best to address cyber security risks.
Ethical hackers will look for weaknesses without harming the system or its users. They test security measures without interfering with the system’s functionality or performance. They strive to increase security without resulting in Harm or loss of information.
Ethical hackers are responsible for their actions. They also ensure that their work is within the limits set by the organization and the community of cybersecurity professionals, both from a legal and ethical perspective. If they identify a vulnerability, they report it in time and give actionable recommendations on how to be safe against it.
Enroll in ACTE’S Cybersecurity Online Training if you want to become an expert in Ethical Hacker’s Toolkit field and have a prosperous career.
Understanding the Ethical Hacker’s Toolkit
The toolkit of ethical hackers comprises a variety of tools and software that support an ethical hacker to perform penetration testing, vulnerability testing, and other cyber crime security activities. cyber security risks allow hackers to emulate attacks on computer systems and vulnerabilities cybercrime as a service a malicious attacker would use. There are several major categories of such tools.

Penetration Testing Tool:Ethical hackers engage in penetration testing, or “pen testing,” which refers to simulating a cyber attack to assess a system’s security. Penetration testing tools probe a system’s defenses and expose weaknesses.Kali Linux is an open-source operating system with more than 600 tools for penetration testing.Metasploit is a popular framework to exploit system vulnerabilities to test defenses.Burp Suite is one of the major tools used to test the security of web applications by intercepting and modifying HTTP requests.These tools help the ethical hacker simulate cyberattacks, system weaknesses, etc., and give recommendations to enhance security measures.
Network Analysis ToolsNetwork analysis tools are utilized to monitor and analyze network traffic for identifying security flaws and detecting potential intrusions.Wireshark package analyzer sniffs and catches live network traffic, inspecting it in detail.Network scanning that can scan what devices exist in the network, open ports, and cybercrime as a service that sit on top of them.Tcpdump Command-line utility for helping in packet capture and network traffic analysis. Cybersecurity Training Courses network traffic analysis, ethical hackers may deduce unauthorized access, data breaches, or vulnerabilities in network configurations.
Vulnerability Scanners:Vulnerability scanners identify known security flaws in systems, applications, or networks. The scanning is automated, making it easier for an ethical hacker to determine what really needs to be patched.Nessus is the most commonly used vulnerability scanner. It scans the largest possible number of network and application vulnerabilities.OpenVAS open-source tool is utilized for vulnerability scanning and management.Qualies is a cloud-based vulnerability scanner that aims to help organizations identify, prioritize, and manage the cyber security risks they are exposed to.
The Growing Impact of Cybercrime on Society
This has proven to be an epidemic worldwide since hackers continuously aim at people, corporations, and governments. Thus, cyber related crimes is more than monetary loss damage like reputational decline, data breaches, identity theft and national Database Security . Financial Losses: Cybercrime damages businesses with billions of dollars in lost revenue and legal fees each year.
Leverage Cyber Security to Unlock the Future! Enroll in the Cybersecurity Expert Masters Program Training Course Program at ACTE Right Away.
Motivations behind Hacking
Challenges in Ethical Hacking
Thus, while ethical hacking is a rather important requirement for the betterment of Ethical Hacking Techniques , it presents its own set of difficulties:
Get interview-ready with our collection of Cybersecurity Interview Questions and Answers Questions. Equip yourself with the knowledge to impress potential employers!
The Role of Ethical Hackers in Combating Cybercrime
Ethical hackers are a significant component of the fight against Web Security , as they identify and address any insecurity long before cybercrime preventionoccurs. As cybercriminals develop and make their sophisticated techniques more sophisticated every day, ethical hackers are overly busy developing new skills and more advanced tools to fight the advanced cyberthreats.
Ethical hackers reduce the ability of potential cyber related crimes to impact individuals and organizations to the barest minimum by identifying vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
Conclusion
The Cybersecurity Training is a rather significant collection of tools to help the ethical hacker combat the increasing cyberthreats that has engulfed the world in cybercrime. Penetration testing software, network analyzers, vulnerability scanners, and exploitation frameworks are what are put to use by ethical hackers to identify and correct vulnerabilities before those can be taken advantage of by cybercriminals. This proactive approach of hackers is crucial in protecting digital assets and preventing the destructive impact of cybercrime. More and more, as the digital landscape continues to evolve, cybercrime as a service becomes clear that in the battle against cybercrime, the future big players will be ethical hackers. Knowing such tools and techniques in ethical hacking can safeguard well-organized organizations and their customers against the increasingly rising tide of cyberthreats.





