
- What is Ethical Hacking
- Ethical Hacking with Python
- Why Python for Ethical Hacking?
- Setting Up Python for Ethical Hacking
- Must-Have Python Libraries for Ethical Hacking
- Common Ethical Hacking Tasks with Python
- Building Custom Ethical Hacking Tools with Python
- Best Practices for Ethical Hacking with Python
- Popular Python-Based Frameworks for Ethical Hacking
- Conclusion
What is Ethical Hacking
Ethical hacking, or penetration testing is the attempt at taking advantage of the system defenses lawfully and with the intent of determining how those weaknesses would be taken advantage of by malicious actors. While black-hat hackers employ such tactics for personal evil purposes, ethical hackers work with organizations to strengthen the Cyber Security Training of those weaknesses before they become exploited. The penetration testing task involves a series of steps, from gathering information to exploiting any vulnerability, if any. Throughout the entire process, there are hackers known as the good guys using many python tools and techniques, as the use of Python is an apolitical tool because it’s easy to use and even to automate complex tasks.
Ethical Hacking with Python
Among the programming languages used widely in ethical hacking, one of the most commonly used and selected programming languages is Python. The simplicity and flexibility of this tool, with a high-level library that has comprehensive outreach, have made it something that no information security professional can do away with. To explore how such tools empower ethical hackers in reconnaissance, exploitation, and automation, check out Hacking Tools and Software a curated guide that highlights essential utilities, scripting frameworks, and advanced toolkits used across penetration testing and cybersecurity operations. Whether streamlining tasks, automating processes, or creating customized security python tools has proven to be an indispensable language for ethical hackers. From penetration testing and automatic vulnerability scanning to building exploitation python tools capabilities are vast. This blog post will describe the function of ethical hacking by python and explore some of the key libraries, essential tools, and typical uses of Python in cybersecurity. By the end of this tutorial, you’ll clearly understand howEthical Hacking with Python can make your penetration testing and vulnerability assessments more efficient and effective.
Interested in Obtaining Your Cyber Security Certificate? View The Cyber Security Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Why Python for Ethical Hacking?
Python is best suited for ethical hacking due to a host of reasons.
- Ease and Readability: It is very easy to learn and work with, making it the best choice for beginners and experienced hackers alike. Its clean syntax translates well into putting together effective code when working under the pressure of security assessment.
- Advanced Libraries: Python boasts of having all the advanced libraries that can be used directly, especially in most security work like network scanning, web scraping, and even cryptography. This reduces almost all the hassle and demands that would have gone into writing custom code from scratch.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: This feature makes Python perfect for ethical hackers. It works fluently on Windows, macOS, and Linux. Since ethical hackers often work across different environments, this cross-platform compatibility ensures python tools and scripts can be used universally, even when dealing with attacks like Session Hijacking.
- Automation: Python is primarily utilized to develop auto-scripts, which scan the network for repetitions or review security measures. This saves time and exposes ethical hackers to the complexity and intricacy associated with penetration testing.
- Active Community: The developers are pretty active, and you will find libraries, tools, tutorials, and even frameworks customized specifically for hacking and cybersecurity challenges.
- Install Python: Go to the Python website and download the latest version. Installing Python 3.x is preferred since it tends to support the most recent libraries and cybersecurity patches.
- Creating a Virtual Environment: A virtual environment isolates your project’s dependencies from the possibility of conflict with system-wide installations. The development of a virtual world can be done.
- Install Essential Libraries: Ethical hackers typically use a set of libraries to perform tasks like network scanning, data manipulation, and web scraping. You can install some useful libraries using ‘pip’:
- Requests: The ‘requests’ library is paramount for making HTTP requests that interact with web servers. This is generally used for testing the web application, interacting with APIs, and even logging in.
- Scapy: This library is powerful for network packet manipulation. It is commonly used for network sniffing, crafting packets, and exploiting protocol vulnerabilities, which are key areas in Cyber Awareness.
- BeautifulSoup: BeautifulSoup is an ethical hacking by python library used to parse and scrape HTML and XML content. It is heavily used to extract data from the web, which is a key step in any penetration test’s ‘information gathering’ step.
- Nmap: Nmap is an open-source tool widely used for network discovery and vulnerability scanning. Python’s ‘python-nmap’ wrapper lets you integrate Nmap’s functionalities into your Python scripts for automated scanning.
- Paramiko: This is a library used for creating SSH connections and automating remote interactions on servers. It helps penetration testers execute commands and transfer files remotely.
- Cryptography: Cryptography from the cyber Python ‘cryptography’ library is important for any work requiring encryption and decryption. Ethical hackers test it to ensure that communications are safe from vulnerabilities.
- Always Get Permission: Never do Network Penetration Testing or ethical hacking by python on any system without writing permission. Unapplied testing is illegal and unethical.
- Keep Documentation: Keep an updated record of all the tools and techniques used, the results, and your findings. You will need this documentation to write reports and analyze.
- Test in Isolation: Test your tools and scripts in isolation environments to prevent unintended harm to live systems and data.
- Respect Privacy and Confidentiality: Ethical hackers ought to always respect Privacy policies and maintain confidentiality of the data they come across while testing.
- Pwntools: The complete framework for exploitation, payloads, and all kinds of security software created to participate in Capture the Flag challenges and penetration tests in the real world.
- Impacket: A library that will give you the tools to work with network protocols. It is a resource used widely to catch other endeavours: SMB exploitation, remote code execution, etc.
- Metasploit: This framework is entirely written in Ruby but integrates with Python; hackers can use it to control and automate different exploits and payloads within a cyber Python script.
To Explore Cybersecurity in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Cyber Security Online Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Setting Up Python for Ethical Hacking
It would help if you prepared your environment before starting to use Python for ethical hacking. This includes setting up the necessary cyber Python tools and ensuring proper Data Classification to handle sensitive information securely during your testing.
Must-Have Python Libraries for Ethical Hacking
Python has an outstanding collection of libraries that can help ethical hackers automate several operations. Below are some of the most used ones.
Looking to Master Cybersecurity? Discover the Cyber Security Expert Masters Program Training Course Available at ACTE Now!
Common Ethical Hacking Tasks with Python
Python has become an invaluable tool in the realm of penetration testing, facilitating a variety of activities that enhance the effectiveness of ethical hacking. One of the primary tasks it assists with is port scanning, a crucial technique for identifying open ports on a system. This process allows ethical hackers to audit these ports for vulnerabilities by utilizing relevant Python libraries, which is essential for determining potential attack surfaces during a penetration test. Vulnerability Exploitation Once those vulnerabilities have been determined, Python can offer different tools for taking advantage of the vulnerabilities. Examples include SQL injection attacks or buffer overflow exploits, among others you know. Such examples open the doors to various security risks against a system in Cyber Security Training. In addition to port scanning, Python is also adept at network sniffing, where it enables the capture and analysis of network traffic to uncover sensitive data or weaknesses in communication protocols. Libraries such as Scapy make it remarkably straightforward for ethical hackers to intercept and analyze network packets, providing insights into the security posture of the network. Another significant application of Python in ethical hacking is web scraping the process of extracting information from websites. This technique can be employed to gather valuable data, such as login forms, outdated software, or hidden endpoints, all of which may reveal vulnerabilities within web applications. Furthermore, Python plays a critical role in password cracking, where ethical hackers can automate the testing of passwords using dictionary or brute force attacks to assess their strength against potential breaches.
Preparing for Cyber Security Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Cyber Security Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Building Custom Ethical Hacking Tools using Python
Python’s greatest strength lies in its ability to create unique ethical hacking by python tools. Do you need a special vulnerability scanner, a brute-force password cracker, or an advanced network mapper? With Python, you can make bespoke solutions tailored to your needs. Building your tools using cyber Python is very efficient and helps ethical hackers address particular challenges more effectively. To understand how these custom tools fit into structured risk analysis and proactive defense planning, explore What is Threat Modeling a foundational guide that explains how to identify potential threats, assess vulnerabilities, and design countermeasures using both manual and automated approaches. With the versatility of Python, you can prototype security tools rapidly, addressing a new vulnerability or simply automating tasks unique to your testing environment.
Best Practices for Ethical Hacking with Python
To use Python in ethical hacking, best practices of responsible testing apply:
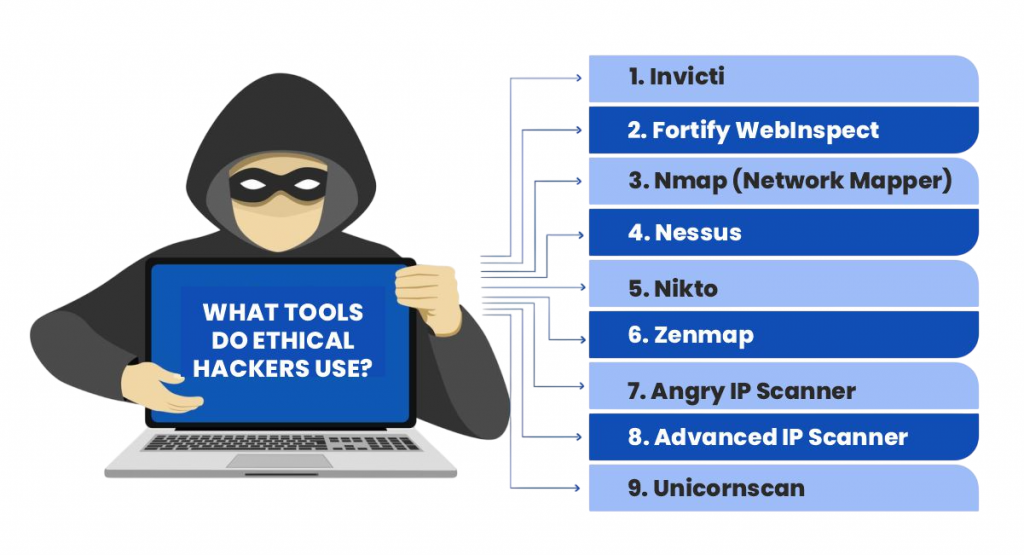
Popular Python-Based Frameworks for Ethical Hacking
Several open-source frameworks were invented with the specific goal of helping ethical hackers make their jobs easier. Some of the most commonly used Python-based frameworks include those that assist in testing and bypassing security measures like Multi-Factor Authentication .
Conclusion
Python is an important tool for ethical hackers since it is easy to use, flexible, and has many libraries that make it easy to automate, custom tool building, and penetration testing. It would be great to scan networks, web scrape information, or automate exploitation and find a weakness in Cyber Security Training more efficiently and effectively. Mastering Ethical Hacking with Python will make you a better beneficiary of technical skills and contribute to creating a safer digital world by making organizations more proactive and defensive against cyber threats. With Python now in your toolkit.




