
- Footprinting Overview
- Types of Footprinting
- Tools for Footprinting
- DNS Footprinting
- Whois Lookup
- Social Engineering in Footprinting
- Website Footprinting
- Email Footprinting
- Tools & Techniques Demo
- Countermeasures
- Role in Ethical Hacking Phases
- Conclusion
Footprinting Overview
Footprinting is one of the most crucial stages in the ethical hacking process. It refers to the method of gathering as much information as possible about a target system, network, or organization before attempting penetration. The main objective is to create a blueprint of the target’s security posture useful for Cyber security training by identifying key details such as domain names, IP addresses, operating systems, and technologies used. Ethical hackers perform footprinting to think like attackers while staying within legal boundaries. This preparatory phase allows them to better plan simulated attacks and discover vulnerabilities without causing harm. Since information is one of the most valuable assets in cybersecurity, footprinting provides the foundation for all other phases of hacking like scanning, enumeration, and exploitation.
Types of Footprinting
Footprinting can be categorized broadly into two main types: passive and active footprinting.
Passive Footprinting – This involves gathering publicly available information without directly interacting with the target system. Examples include searching Google, scanning social media profiles, checking online forums, reading press releases, and analyzing public records. Since the hacker does not touch the target’s systems, passive methods are harder to detect.
Active Footprinting – This type involves directly interacting with the target to extract information (often evaluated with Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curves). Examples include ping sweeps, traceroute, port scanning, and banner grabbing. Active methods provide more precise details but come with the risk of detection since the target system may log suspicious activities.
Both types are equally important. Passive footprinting helps build a background, while active footprinting provides technical insights for deeper penetration.
Interested in Obtaining Your Cybercrime Certificate? View The Cyber Security Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Tools for Footprinting
Various tools assist ethical hackers in collecting target information efficiently. Some of the most common include:
- Nmap – Used for network scanning, detecting live hosts, and discovering open ports.
- Traceroute – Maps the path packets take to reach a target, revealing intermediate devices.
- Maltego – A powerful tool for data mining and link analysis, especially useful in OSINT (Open Source Intelligence) and Fraud Detection Using Machine Learning .
- Google Hacking (Dorks) – Uses advanced search operators to uncover sensitive data exposed unintentionally.
- Recon-ng – A web reconnaissance framework to gather information through automation.
- Shodan – A search engine for internet-connected devices that reveals exposed servers, IoT devices, and systems.
Ethical hackers often combine multiple tools to ensure they collect comprehensive data without missing critical details.
To Explore Cybersecurity in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Cyber Security Online Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Whois Lookup
Whois is another widely used footprinting technique that reveals registration details of a domain. Ethical hackers use Whois lookup services to find domain ownership, registrar details, email addresses of administrators, contact numbers, and sometimes even the physical address of the organization. This information may seem harmless but can be used in social engineering attacks, where Tree Algorithm in ML techniques can help analyze and predict vulnerable targets. For example, attackers can impersonate domain administrators or exploit expired domains. Ethical hackers, on the other hand, use Whois data responsibly to highlight risks and recommend the use of privacy protection services to conceal sensitive information.
DNS Footprinting
DNS (Domain Name System) footprinting is a technique that provides valuable insights into the target’s online infrastructure. It helps hackers gather domain-related information like IP addresses, mail servers, subdomains, and hostnames. Ethical hackers use DNS queries to understand What is DOS And DDOS Attack and how the target manages internet communication. For instance, using tools like Nslookup or Dig, one can extract DNS records (A, MX, NS, CNAME). This information may highlight misconfigured DNS servers or exposed subdomains, which could serve as entry points for attackers. Moreover, zone transfer misconfigurations can accidentally leak entire domain structures.
Social Engineering in Footprinting
Footprinting is not limited to technical reconnaissance. Social engineering plays a powerful role in this phase. Ethical hackers attempt to collect information from employees, business associates, or partners through non-technical means. This could include pretexting, where the hacker pretends to be a legitimate person to extract details, or phishing emails that trick employees into revealing confidential information, which can be followed by Enumeration in Ethical Hacking to discover further targets.
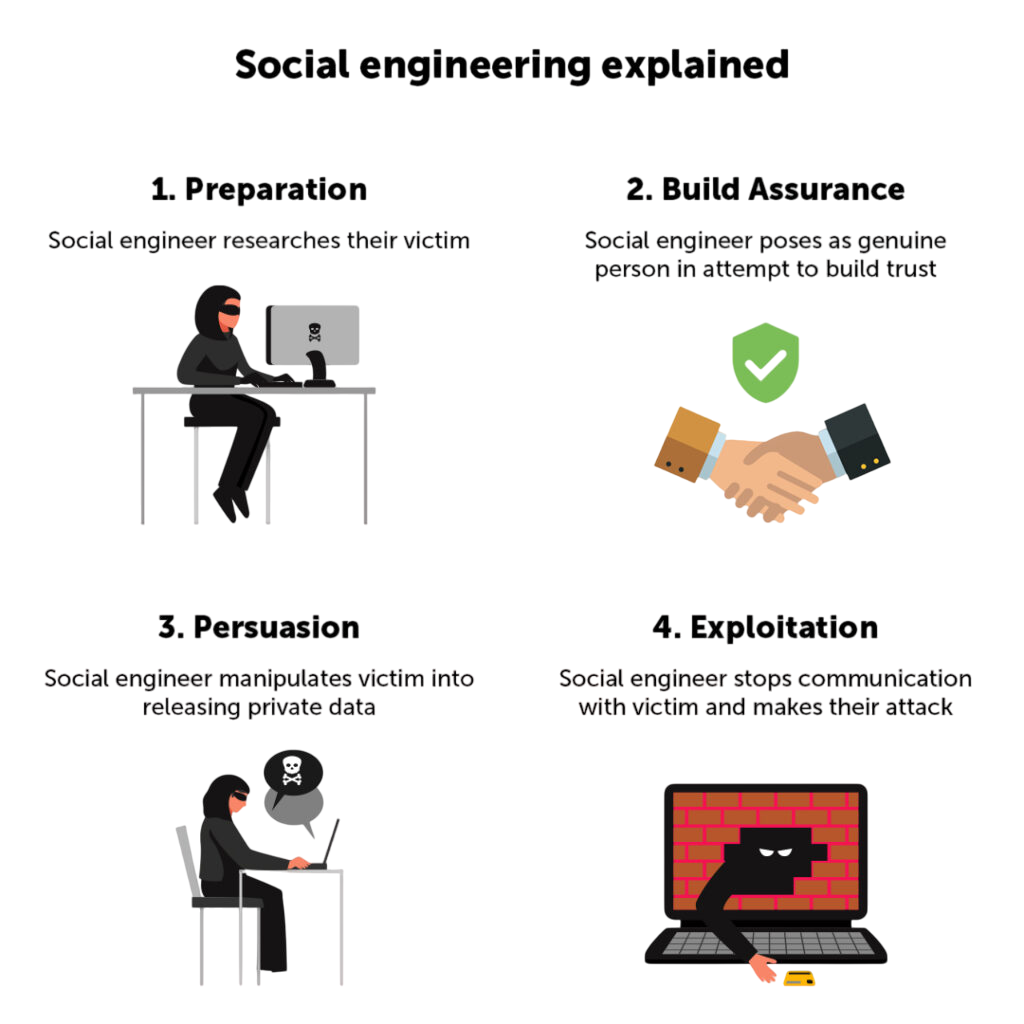
Even casual conversations at events or monitoring social media activity can reveal useful data about the target organization’s internal systems or employees. For example, a LinkedIn post mentioning “migration to Windows Server 2022” may inform an attacker about the company’s infrastructure.
Looking to Master Cybersecurity? Discover the Cyber Security Expert Masters Program Training Course Available at ACTE Now!
Website Footprinting
An organization’s website often holds a treasure trove of information. Ethical hackers analyze web pages to uncover hidden directories, backend technologies, CMS platforms, and sometimes even test or development environments. By examining the robots.txt file, they can discover restricted directories. Tools like Burp Suite or HTTrack help in mapping the site structure for Cyber security training purposes.Banner grabbing techniques also reveal server details, operating system versions, and scripting languages used. Additionally, error messages may accidentally expose database details or internal paths. Website footprinting is a critical step for understanding the online presence and security weaknesses of a target.
Email Footprinting
Email communications can also expose important data. Ethical hackers analyze email headers to track the origin of the message, mail server information, IP addresses, and routing paths. Using tools like EmailTrackerPro, one can determine the geographic location of the sender, and safeguard that information with Secret Key Cryptography Misconfigured email servers, if discovered, can allow attackers to spoof emails or conduct phishing campaigns. Furthermore, leaked employee email addresses often become the primary targets for spear-phishing campaigns. Ethical hackers highlight these risks and suggest implementing SPF, DKIM, and DMARC protocols to prevent spoofing.
Preparing for Cyber Security Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Cyber Security Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Tools & Techniques Demo
To better understand footprinting, let’s consider an example. Suppose an ethical hacker wants to assess the security of an organization called “examplecorp.com.”
- They start with Whois Lookup and discover the registrar, contact emails, and DNS servers.
- Using Nslookup, they extract DNS records, revealing subdomains like mail.examplecorp.com and vpn.examplecorp.com.
- With Traceroute, they analyze the network path, discovering intermediary hops.
- Using Google Dorks, they find PDF files with employee names, job roles, and email addresses.
- By examining the company’s LinkedIn, they notice posts about cloud migration, hinting at AWS usage a detail often investigated in Ethical Hacking With Python .
- Finally, using Shodan, they detect an exposed IoT device connected to the corporate network.
This combination of passive and active techniques builds a detailed profile of the target, which attackers could exploit but ethical hackers use to strengthen defenses.
Countermeasures
Organizations must adopt proactive measures to reduce risks posed by footprinting. Some countermeasures include:
- Restricting information disclosure – Avoid publishing unnecessary details on websites, press releases, or job postings.
- Harden DNS servers – Disable zone transfers and monitor queries for unusual activity.
- Whois Privacy Protection – Use registrar services that hide ownership details.
- Email Security – Implement SPF, DKIM, and DMARC to prevent spoofing.
- Web Application Security – Regularly update CMS, patch vulnerabilities, and configure servers properly.
- Employee Awareness – Train staff to avoid oversharing on social media and recognize social engineering tactics.
By implementing these countermeasures, organizations can reduce the chances of attackers gathering exploitable data during the reconnaissance phase.
Role in Ethical Hacking Phases
Footprinting is the first phase of ethical hacking and sets the stage for subsequent steps. Without proper footprinting, scanning and enumeration may lack direction including assessments of the target’s Virtual Private Network . Ethical hackers rely on the intelligence gathered during footprinting to map attack surfaces and identify potential vulnerabilities. For example, knowing subdomains allows them to focus scanning efforts, while understanding technologies helps them choose the right exploits. Footprinting ensures that penetration testing is not a blind attempt but a strategic, informed process.
Conclusion
Footprinting is a foundational step in ethical hacking that involves systematically gathering information about a target. It can be performed through passive or active methods, leveraging tools like Nmap, Maltego, Whois, and Shodan. Ethical hackers conduct DNS, website, email, and social engineering footprinting to create a comprehensive picture of the target’s security environment. While attackers may use footprinting for malicious purposes, ethical hackers employ it to strengthen defenses and raise awareness about potential risks, which is a key focus of Cyber security training . By implementing countermeasures such as DNS hardening, web security practices, and employee training, organizations can significantly reduce their attack surface. Ultimately, footprinting is not just about gathering data it is about transforming intelligence into actionable strategies to build robust cybersecurity defenses.




