
- Introduction
- What is Artificial Intelligence?
- Types of Artificial Intelligence
- Artificial Intelligence Based on Capabilities
- Artificial Intelligence Based on Functionalities
- Advantages of AI
- Disadvantages of AI
- Conclusion
Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the modern world by blending technological innovation with human-inspired intelligence. From enhancing decision-making to transforming industries such as healthcare, transportation, finance, and entertainment, AI is now a critical force shaping daily life and future possibilities. To fully grasp its impact, it is essential to explore the different types and techniques of AI, categorized based on capabilities, functionalities, and learning approaches, often integrated into Data Science Training. AI types such as Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI), Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), and Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI) represent the stages of AI evolution, while functionalities like reactive machines, limited memory systems, theory of mind, and self-awareness highlight how AI systems interact and learn. Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of AI is equally important to harness its potential responsibly while addressing its challenges. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of AI’s definitions, types, strengths, limitations, and the profound role it plays in shaping our digital future.
Eager to Acquire Your Data Science Certification? View The Data Science Course Offered By ACTE Right Now!
What is Artificial Intelligence?
AI is a considerable technique that combines numerous educational disciplines, including computer science, psychology, linguistics, and mathematics. Massive quantities of information are used to create sensible robots in synthetic intelligence. The structures enhance project speed, accuracy, and effectiveness by using getting to know from beyond stories and getting to know to do human-like duties. Artificial Intelligence uses state-of-the-art algorithms and strategies to create machines that can make unbiased decisions. Deep getting to know and gadget getting to know is at the coronary heart of synthetic intelligence.
Industries that use of AI
Some sectors of enterprise that use AI are:
- Transportation (autonomous vehicles, site visitors manipulating buildings)
- Medical (scientific diagnosis, robot surgery)
- Banking (fraud detection, automated trading)
- Retail (stock manipulation, custom-designed recommendations)
- Entertainment (media produced by AI, warning material)
- E-trade (chatbots, patron insights)
Types of Artificial Intelligence
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) is profoundly influencing all aspects of human life, revolutionizing industries, reshaping economies, and transforming daily activities.
- From healthcare and education to transportation, entertainment, and business, AI is driving innovation and unlocking new possibilities that were once unimaginable.
- As this transformative technology continues to evolve at an accelerated pace, it becomes increasingly crucial to develop a thorough understanding of the various types of artificial intelligence and the unique characteristics that distinguish them.
- “In the context of Digital Transformation, AI can be broadly classified into several categories based on its capabilities, functionalities, learning approaches, and interaction with the environment. Each type reflects a different level of complexity, autonomy, and cognitive ability, ranging from simple task-specific systems to highly advanced machines capable of independent thought.
- Gaining a clear and comprehensive understanding of these classifications not only highlights the immense potential and current applications of AI but also prepares us to navigate the challenges and opportunities that future advancements will bring.
- Below are some of the key types of AI that are actively shaping the modern digital world and influencing the way we live and interact.
Artificial Intelligence Based on Capabilities
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly reshaping the modern world with its groundbreaking potential across industries. As AI evolves, it becomes essential to classify it based on its scope and abilities. Understanding these classifications helps us gauge where current technologies stand and what the future holds. AI systems vary widely, from those performing specific tasks to those aspiring to mimic or surpass human intelligence. Researchers categorize Artificial Intelligence into different types based on how capable and independent the systems are. These types show the progression from basic, narrow tasks to complex, human-like reasoning. They also offer insight into how AI might eventually transform decision-making, creativity, and innovation. Here, we explore the three primary types of AI based on their capabilities. Let’s dive into Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI), Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), and Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI).
Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI)
- AI specialized in performing a single task.
- Examples: Self-driving cars, chess-playing machines, speech recognition, e-commerce recommendations.
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
- AI with human-like cognitive abilities across a wide range of tasks.
- Status: Still under research and development.
Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI)
- Hypothetical AI that surpasses human intelligence in every field.
- Status: Not yet developed, currently a theoretical concept.
- AI systems that respond to specific inputs without memory or past experiences.
- Examples: IBM’s Deep Blue, Google’s AlphaGo.
- AI systems that learn from historical data for a short time to make decisions.
- Examples: Self-driving cars, chatbots, virtual assistants like Siri.
- AI that can understand human emotions, intentions, beliefs, and mental states.
- Examples: Early developments like MIT’s Kismet and Hanson Robotics’ Sophia (still in research).
- AI with consciousness, self-awareness, and the ability to understand its own internal states.
- Status: Purely theoretical at present, no real-world examples yet.
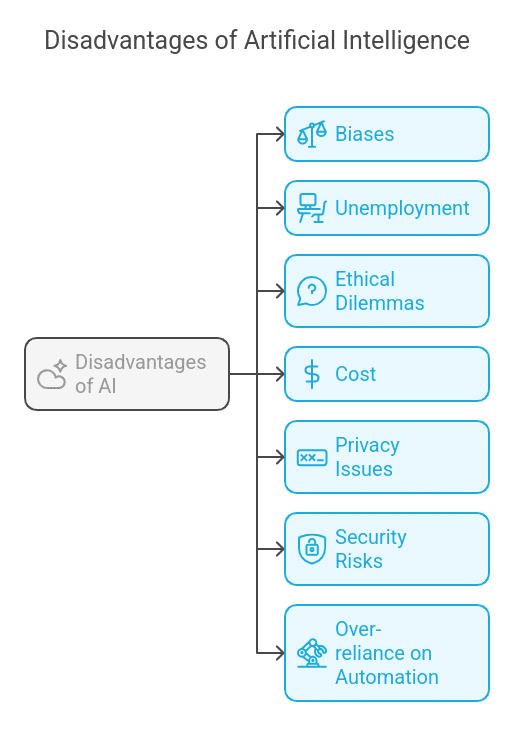
- Despite its blessings, AI has numerous drawbacks that pose demanding situations throughout specific industries. One predominant difficulty is process displacement, as automation powered through AI can update human employees in diverse sectors, leading to unemployment and financial disruption.
- Many ordinary and repetitive duties are currently being dealt with through AI, lowering the need for human labor in manufacturing, customer support, and records entry.
- Another significant drawback is the decline in Emotional Intelligence and creativity. AI can follow algorithms and review documents. It cannot, however, represent human emotions, intuition, or innovative thought.
- As a result, AI performs noticeably worse in fields that need empathy, such as social work, counseling, and the arts and literary professions.
- High costs and the need for valuable resources provide further difficulties because AI architectures can be costly to build, install, and maintain.
- Businesses require a significant amount of processing power and qualified experts to work with AI technology, which prevents smaller businesses from using it.
- Lastly, AI structures are vulnerable to loss of transparency and unpredictability, as deep mastering fashions feature “black boxes,” making it challenging to recognize how they attain conclusions.
- This can create acceptance as accurate with issues, especially in essential regions like healthcare and finance. While AI brings many blessings, addressing those negative aspects is vital for accountable and truthful AI development.
Excited to Obtaining Your Data Science Certificate? View The Data Science Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Artificial Intelligence Based on Functionalities
Artificial Intelligence (AI) can be classified in multiple ways depending on how it operates and evolves. One of the most fundamental ways is based on its functionalities — essentially, how an AI system responds, learns, and interacts with the environment. Understanding these types helps clarify how far AI has come and what future developments might look like. Functionality-based classification reflects the level of advancement an AI system has achieved. It ranges from simple, reactive systems to theoretical, self-aware machines. Each type represents a critical stage in AI’s evolution. Some forms are already a part of our daily lives, while others remain aspirational goals for researchers. “The journey from reactive AI to self-aware AI defines the roadmap of AI innovation, with Data science Training playing a crucial role in this evolution. Let’s explore these types in detail.
Reactive Machines
Limited Memory
Theory of Mind
Self-Awareness
Interested in Pursuing Data Science Master’s Program? Enroll For Data Science Master Course Today!
Advantages of AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) improves decision-making, accuracy, and efficiency in various industries. Automation is one of the most significant advantages since AI can perform time-consuming and repetitive tasks with little human assistance, increasing output and reducing operating costs. AI-driven chatbots and digital assistants improve customer service by offering impromptu answers and tailored exchanges. AI Chatbots tools, along with AI-powered chatbots and digital assistants, enhance customer support by presenting spontaneous responses and personalized interactions Another key gain is recorded processing and analysis, wherein AI can quickly manage significant quantities of records and discover styles that people might overlook. This results in higher decision-making, as AI-pushed insights assist agencies in optimizing techniques in regions like marketing, finance, and healthcare. AI also reduces errors and increases accuracy, particularly in economic forecasting, manufacturing, and scientific diagnosis. As demonstrated by Netflix, Amazon, and Spotify’s advising systems, which examine user behavior to provide tailored material, AI also improves personalization. AI also fosters innovation by enabling advancements in autonomous cars, robots, and smart cities. Artificial intelligence (AI) is a helpful tool in today’s virtual world since it increases productivity, enhances customer experiences, and advances technology.
Preparing for a Data Science Job Interview? Check Out Our Blog on Data Science Interview Questions & Answer
Disadvantages of AI
Conclusion
Artificial intelligence has transformed industries and lifestyles by enhancing efficiency, automation, and decision-making. It could completely transform the financial industry, healthcare, manufacturing, and many other sectors, riding innovation and progress. With its capacity to manage vast quantities of facts and carry out complicated tasks, AI complements productivity and creates new possibilities for growth. However, at its advantages, AI offers demanding situations, activity displacement, moral concerns, and high implementation costs. To ensure the accountable improvement of AI, it’s essential to promote the stability of technological development through Data Science Training, moral considerations, transparency, and human oversight. While AI can’t update human creativity and emotional intelligence, it could function as an effective device to reinforce human capabilities. Moving forward, non-stop research, regulations, and collaboration among generation builders and policymakers could be vital in shaping AI to take advantage of society and minimize its risks. AI isn’t always the future – it’s already shaping the present, and how we use it will determine its long-term effect on humanity.


