
- Introduction to Quality Planning
- Defining Quality Objectives
- Quality Assurance vs Quality Control
- Tools for Quality Planning
- Continuous Improvement Strategies
- Quality Audits and Reviews
- Documentation and Reporting
- Conclusion
Introduction to Quality Planning
Quality planning is a critical component of project management that defines how quality standards will be achieved and maintained throughout a project. It involves setting clear, measurable quality objectives aligned with project requirements, customer expectations, and regulatory standards. Quality planning ensures that deliverables consistently meet defined criteria, contributing to successful project outcomes and organizational goals. A key aspect of quality planning is identifying potential risks that could impact quality and establishing preventive measures to mitigate them, a process that can be enhanced through Data Science Training. It also includes developing processes, procedures, and quality assurance activities to monitor and control quality throughout the project life cycle. Techniques such as root cause analysis, quality audits, and continuous improvement methods are often incorporated to maintain high standards. Additionally, selecting the right tools and metrics such as control charts, checklists, or benchmarking helps in tracking quality performance and identifying deviations early. Effective quality planning reduces the need for costly rework, boosts customer satisfaction, ensures compliance, and enhances overall project efficiency. It lays a solid foundation for delivering reliable and high-value outcomes.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Data Science? Sign Up For Our Data Science Course Training Today!
Defining Quality Objectives
Quality objectives are specific, quantifiable goals that define the level of desired quality for a project. They serve as benchmarks for performance, ensuring that deliverables meet customer expectations, regulatory requirements, and organizational standards. These objectives are essential for guiding project execution and evaluating outcomes against predefined quality standards, especially when integrating Personalized Smart Learning for Modern Education to tailor approaches and enhance results. Examples of quality objectives include achieving a 98% customer satisfaction rate, reducing defects by 15%, or ensuring 100% compliance with safety regulations. These targets not only define expectations but also provide a clear direction for teams to follow throughout the project lifecycle.
To ensure clarity and effectiveness, organizations use the SMART criteria when setting quality objectives. This means the objectives must be Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. SMART goals help teams understand exactly what needs to be done, how to measure progress, and by when results should be achieved. Quality objectives play a crucial role in aligning teams, supporting data-driven decision-making, and maintaining focus on quality outcomes. They ensure that performance is not only tracked but also continuously improved, contributing to overall project success.
Quality Assurance vs Quality Control
- Definition: QA focuses on improving processes to prevent defects, while QC identifies and corrects defects in the final product.
- Objective: QA enhances development processes to avoid mistakes; QC ensures the final product meets quality standards.
- Focus: QA ensures process quality; QC checks product specs Group Tabs in Chrome help organize both efficiently.
- Methods: QA uses audits, training, and process standards; QC involves inspections, testing, and reviews.
- Timing: QA is continuous throughout the project; QC typically occurs after production or at specific stages.
- Responsibility: QA is the responsibility of the entire team; QC is usually handled by specialized testers or inspectors.
- Goal: QA aims to build quality into the process; QC ensures the final product meets the required standards.
- Quality Function Deployment (QFD): QFD helps translate customer needs into specific product or service requirements, ensuring alignment with quality standards.
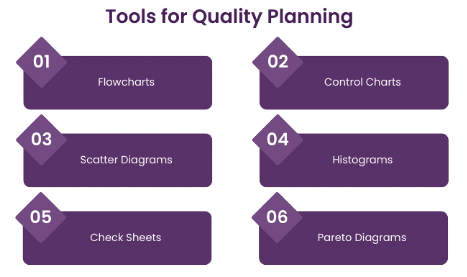
- Flowcharts: Flowcharts visually map processes and identify potential areas for improvement, supporting better planning and process design.
- Cause-and-Effect Diagram (Fishbone): This tool helps identify root causes of quality issues, ensuring that preventive measures are incorporated during the planning phase key for both Program Manager vs. Project Manager roles.
- Control Charts: Control charts track process performance over time, allowing teams to set quality benchmarks and measure consistency during production.
- Pareto Analysis: By applying the 80/20 rule, Pareto analysis helps prioritize quality issues, focusing on the most significant problems that will have the greatest impact.
- Checklists: Checklists ensure that all required quality standards are considered and met, helping to reduce errors during the planning process.
- Benchmarking: Benchmarking compares project processes to industry best practices, providing a reference for setting realistic quality goals.
- Purpose: Quality audits and reviews are conducted to verify compliance with established standards and identify areas where improvements can be made.
- Process Reviews: Process reviews examine workflows to detect inefficiencies or deviations, providing recommendations to enhance overall process effectiveness.
- Product Reviews: These reviews evaluate products or deliverables against predefined quality standards to ensure they meet customer expectations and regulatory specifications.
- Corrective Measures: Audits and reviews help identify non-conformities, leading to corrective actions that address issues and prevent future occurrences in Project Management.
- Building Trust: Regular audits and reviews reinforce an organization’s commitment to quality, boosting confidence among stakeholders by demonstrating adherence to high-quality standards.
- Internal Audits: These audits are carried out by internal teams to assess whether processes are in line with quality objectives and internal guidelines, helping to pinpoint areas for improvement.
- External Audits: External audits are performed by independent third parties to confirm that an organization complies with industry standards, regulations, and legal requirements, offering an impartial evaluation.
To Explore Data Science in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Data Science Course Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Tools for Quality Planning
Continuous Improvement Strategies
Continuous improvement is a key principle of quality planning, focusing on the ongoing enhancement of processes, products, and services. Central to this is Kaizen, a Japanese philosophy that promotes small, incremental improvements through employee involvement and feedback. This approach fosters a culture of constant refinement at all levels of an organization. Lean Six Sigma integrates lean principles, which eliminate waste, with Six Sigma methods, which focus on reducing defects, thus optimizing both process efficiency and quality. The combination, enhanced by Data Science Training, leads to more effective operations and improved outcomes. The PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle is another critical tool in continuous improvement. It involves planning changes, implementing them, checking their results, and acting on those results to refine processes continuously. Additionally, Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is employed to identify the underlying causes of quality issues, enabling organizations to implement solutions that prevent recurrence. By embedding continuous improvement into their culture, organizations can enhance efficiency, lower costs, and consistently deliver higher-quality products and services. This iterative approach drives long-term success and competitiveness.
Are You Considering Pursuing a Master’s Degree in Data Science? Enroll in the Data Science Masters Course Today!
Quality Audits and Reviews
Documentation and Reporting
Accurate documentation and reporting play a crucial role in quality planning, ensuring transparency, traceability, and accountability throughout the project. Quality Management Plans (QMP) define the project’s quality standards, processes, and metrics, providing a roadmap for maintaining quality throughout the project lifecycle. Test reports capture the results of quality inspections, highlighting any defects or deviations from the expected standards, serving as a basis for corrective actions. Similarly, issue logs track quality-related problems, documenting their resolution and ensuring that corrective measures are taken to prevent recurrence using effective Conflict Management Strategies. Compliance reports verify adherence to industry regulations, legal requirements, and internal policies, offering assurance that the project aligns with external standards. Comprehensive and well-organized documentation enhances communication among stakeholders, ensuring everyone is informed about the quality performance and any issues that arise. It also serves as a record for future reference, enabling teams to learn from past projects and improve processes. Effective documentation and reporting ultimately support informed decision-making, project success, and continuous quality improvement.
Go Through These Data Science Interview Questions & Answer to Excel in Your Upcoming Interview.
Conclusion
Quality planning is a crucial aspect of project management, ensuring that deliverables meet or exceed stakeholder expectations. By defining clear quality objectives and aligning them with project goals, organizations can establish a framework for consistent, high-quality results. Utilizing practical tools such as quality management plans, process audits, and performance metrics helps streamline processes and maintain quality standards throughout the project lifecycle. Incorporating continuous improvement strategies, like Kaizen or Lean Six Sigma, further strengthens the planning process by identifying areas for optimization and driving ongoing enhancements, especially when supported by Data Science Training. This approach not only ensures that quality is maintained but also fosters innovation and efficiency. Effective quality planning contributes to higher customer satisfaction by ensuring the final product or service aligns with their needs and expectations. It also minimizes risks by addressing potential issues early in the process and enables teams to implement proactive corrective actions. Ultimately, quality planning drives long-term business success by enhancing performance, building stakeholder trust, and sustaining operational excellence.


