
- Introduction to Project Management
- Leadership and Team Management
- Time and Task Management
- Risk Assessment and Mitigation
- Budgeting and Financial Management
- Problem-Solving and Decision-Making
- Continuous Learning and Improvement
- Conclusion
Introduction to Project Management
Project management involves a combination of skills, tools, techniques, and methods to meet specific objectives within a defined time frame and budget. It encompasses the processes of planning, organizing, executing, and closing projects to achieve desired business outcomes efficiently. As organizations continue to rely more on project-driven practices, the demand for skilled project managers has significantly increased. Effective project management goes beyond technical expertise it also requires strong leadership abilities and sound strategic decision-making. Successful project managers need to demonstrate the ability to plan, coordinate, and motivate teams to ensure the project stays on track, similar to how Data Science Training equips individuals with the skills to manage data projects effectively. Key skills in project management include time management, risk management, communication, problem-solving, and team collaboration. A project manager must be adept at balancing scope, time, and cost while maintaining quality standards. Moreover, leadership skills are crucial for guiding teams, making tough decisions, and managing stakeholder expectations. With the growing complexity of projects, having the right skill set is essential for the timely and successful delivery of projects that align with organizational goals and objectives.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Data Science? Sign Up For Our Data Science Course Training Today!
Leadership and Team Management
Leadership is a crucial skill for project managers, as they are responsible for guiding and motivating teams to achieve project goals. Strong leadership fosters trust, improves team morale, and ensures that everyone remains focused on the project’s objectives. A successful project manager leads by example, providing clear direction and support, which helps teams stay aligned with the project’s vision, much like the Data Science Importance in Tech Industry drives alignment with business goals and technological advancements. Effective leadership also involves conflict resolution, decision-making, and offering guidance when needed. Project managers must have the ability to identify the individual strengths of their team members and assign tasks accordingly. By recognizing and leveraging each person’s skills, a project manager can enhance overall team performance. Additionally, a positive and inclusive work environment is essential for encouraging creativity, collaboration, and productivity.
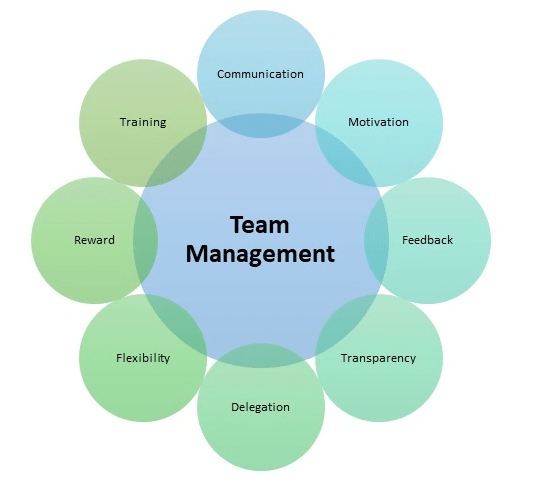
The project manager’s leadership style should foster open communication, where team members feel valued and heard, leading to better problem-solving and innovation. In summary, effective leadership in project management goes beyond task delegation; it is about inspiring teams, managing challenges, and creating an environment where people can thrive and contribute to the project’s success.
Time and Task Management
- Avoiding Multitasking: Focusing on one task at a time improves quality and efficiency. Multitasking can lead to errors, delays, and decreased productivity.
- Prioritization: Effective time and task management starts with prioritizing tasks based on urgency and importance. This ensures that critical tasks are addressed first, avoiding delays in project delivery.
- Setting SMART Goals: Setting Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART) goals helps to clarify the objectives and create a focused approach for task completion.
- Task Delegation: Delegating tasks based on expertise optimizes productivity, similar to how a Big Data Solution ensures efficient handling of tasks.
- Time Blocking: Time blocking involves setting aside specific periods to work on particular tasks. This method improves focus, reduces distractions, and enhances productivity by allocating time for different activities.
- Using Tools: Project management tools like Trello, Asana, or Microsoft To-Do allow managers to track tasks, set deadlines, and collaborate with teams. These tools enhance organization and ensure no tasks are missed.
- Regular Reviews: Conducting daily or weekly reviews helps assess progress, re-prioritize tasks, and address any challenges promptly. Regular check-ins ensure that tasks remain on track and the project stays within scope and deadlines.
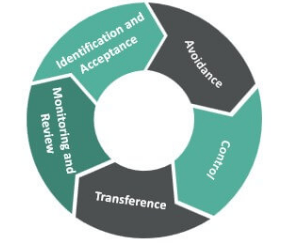
- Identifying Risks: The first step in risk management is identifying potential risks that could affect the project’s success. These can be technical, financial, operational, or external factors like market changes or regulatory shifts.
- Risk Analysis: Once risks are identified, it’s essential to analyze their potential impact on the project. This includes evaluating their probability of occurrence and the severity of their consequences, helping prioritize risks.
- Risk Prioritization: After analysis, prioritize risks based on their potential impact. Focus on high-probability, high-impact risks first, as they pose the greatest threat to the project’s success, much like how Data Science Training helps prioritize key factors for successful data analysis.
- Mitigation Strategies: Develop mitigation strategies for each identified risk. These strategies aim to reduce the likelihood of a risk occurring or minimize its impact if it does arise.
- Contingency Planning: In case a risk occurs, contingency plans outline specific actions to take, helping ensure that the project stays on course even when unexpected issues arise.
- Monitoring Risks: Continuously monitor risks throughout the project lifecycle. This allows for early detection of any emerging issues, enabling proactive adjustments.
- Communication: Effective communication with stakeholders and team members about risks ensures that everyone is aware of potential challenges and is prepared to respond efficiently.
- Identifying the Problem: The first step in problem-solving is clearly identifying the issue at hand. Effective project managers assess the situation, gather information, and define the problem’s root cause to address it accurately.
- Analyzing the Situation: Once the problem is identified, analyzing it from different perspectives helps to understand its implications on the project. This analysis includes evaluating potential impacts, constraints, and available resources.
- Generating Solutions: Brainstorming solutions offers broader perspectives, like Using Big Data and AI to Fight COVID19 Pandemic explores varied strategies.
- Evaluating Alternatives: After generating solutions, evaluating their feasibility, cost, time, and resource requirements is crucial. Comparing the pros and cons of each option ensures that the best solution is chosen for the project.
- Making the Decision: Based on evaluation, project managers must make an informed decision. This decision should align with project goals, available resources, and stakeholder interests.
- Implementing the Solution: Once the decision is made, effective implementation is essential. Clear action plans, resources, and communication channels ensure the solution is executed smoothly.
- Reviewing Outcomes: After implementing the solution, project managers should review the outcomes to assess its effectiveness, identify areas for improvement, and apply lessons learned to future projects.
To Explore Data Science in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Data Science Course Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Risk Assessment and Mitigation
Budgeting and Financial Management
Budget management and financial planning are crucial skills for project managers to ensure that projects are completed within financial constraints and deliver profitability. Project managers are responsible for preparing accurate budget estimates at the beginning of a project, carefully forecasting costs, and allocating resources efficiently. Monitoring expenses throughout the project lifecycle is key to avoiding overspending and keeping the project on track financially. Project managers must regularly track costs, compare actual spending to the budget, and identify any variances that could impact the project’s financial health, all of which are key elements in a Project Report Format. When discrepancies arise, they must be proactive in adjusting plans or reallocating resources to minimize financial risks. Skills in financial forecasting, cost-benefit analysis, and expense tracking are vital for maintaining control over the project’s budget. Tools like QuickBooks, FreshBooks, and Microsoft Project offer practical features to assist with managing project budgets, tracking expenses, and generating financial reports. Effective financial control ensures that the project stays within its financial limits while delivering the expected value, ultimately contributing to its overall success and profitability.
Looking to Master Data Science? Discover the Data Science Masters Course Available at ACTE Now!
Problem-Solving and Decision-Making
Continuous Learning and Improvement
The project management field is continuously evolving with the introduction of new methodologies, tools, and best practices. To stay competitive and relevant, good project managers prioritize ongoing learning and development. Earning certifications is one of the most effective ways to stay updated and enhance professional skills. Some of the most respected certifications include Project Management Professional (PMP), Certified ScrumMaster (CSM), PRINCE2 Practitioner, and Agile Certified Practitioner (PMI-ACP). These certifications help project managers deepen their knowledge and demonstrate expertise in various methodologies, much like a well-crafted Business Plan showcases strategic understanding and direction. In addition to formal certifications, continuous learning also involves staying current with industry trends and participating in workshops, conferences, or webinars. Adopting new project management technologies and tools further strengthens a project manager’s capabilities. Another critical aspect of growth is seeking feedback and conducting post-project reviews. These reflections provide valuable insights into areas of improvement, helping project managers refine their skills and enhance their performance for future projects. By embracing a culture of lifelong learning, project managers can effectively navigate an ever-changing business environment.
Preparing for a Data Science Job Interview? Check Out Our Blog on Data Science Interview Questions & Answer
Conclusion
Building project management capabilities is crucial for ensuring successful project delivery and achieving business objectives. Key capabilities such as communication, leadership, time management, risk analysis, and financial management enable project managers to effectively meet project goals delivering projects on time, within budget, and to a high standard of quality. Mastery of technical tools and software also enhances efficiency and allows project managers to streamline processes. Moreover, flexibility and the ability to manage stakeholder expectations are critical in navigating the complexities of modern projects, much like how Data Science Training prepares individuals to adapt and manage data challenges effectively. A project manager who adapts to changing circumstances, anticipates challenges, and collaborates with diverse stakeholders is more likely to drive successful outcomes. By continuously improving their skills and staying updated with new methodologies and technologies, project managers can remain competitive. This ongoing development not only boosts their performance but also helps organizations achieve greater efficiency, foster innovation, and enhance overall success. In today’s fast-paced business environment, strengthening project management capabilities is key to driving long-term organizational growth.


