- Introduction to Computer Vision
- History and Evolution of Computer Vision
- How Does Computer Vision Work?
- Key Concepts in Computer Vision
- Popular Computer Vision Algorithms
- Applications of Computer Vision in Real Life
- Tools and Frameworks for Computer Vision
- Role of AI and Deep Learning in Computer Vision
Introduction to Computer Vision
Computer vision is a dynamic field within artificial intelligence (AI) that focuses on enabling computers to interpret and understand visual information from the world, much like the human eye and brain. It involves the development of sophisticated algorithms and models that allow machines to process, analyze, and extract meaningful insights from images and videos. By mimicking human vision capabilities, computer vision systems can recognize objects, detect patterns, track movements, and even make decisions based on visual inputs. This technology has become increasingly vital across multiple industries, emphasizing the importance of Data Science Training. In healthcare, computer vision aids in diagnosing diseases through medical imaging, such as X-rays and MRIs. In the automotive sector, it powers self-driving cars by enabling real-time object detection and navigation. Retail businesses use it for customer behavior analysis and inventory management, while in security, it supports facial recognition and surveillance systems. With the rise of AI and the growing demand for automation, computer vision is now a cornerstone of modern intelligent systems. The integration of deep learning techniques has significantly enhanced its accuracy and capabilities, making it possible to solve complex visual tasks that were once thought to be exclusive to human intelligence. As technology advances, the impact of computer vision will only continue to expand.
Interested in Obtaining Your Data Science Certificate? View The Data Science Course Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
History and Evolution of Computer Vision
The history of computer vision dates back to the 1960s, when researchers first began exploring how computers could interpret images. Early efforts focused on basic image processing and pattern recognition, often limited by the computational power of the time. Initial projects included recognizing simple shapes and analyzing scanned documents. In the 1980s and 1990s, computer vision research expanded with advanced algorithms for edge detection, object recognition, and motion tracking, showing Why Data Science Matters & How It Powers Business Value. During this period, traditional techniques like Harris corner detection, SIFT (Scale-Invariant Feature Transform), and HOG (Histogram of Oriented Gradients) played a crucial role in enabling machines to extract meaningful features from images. The major breakthrough came in the 2010s with the rise of deep learning.
In 2012, AlexNet, a deep convolutional neural network, won the ImageNet competition by a wide margin, demonstrating the power of deep learning in image classification. This marked the beginning of a new era where deep learning models like ResNet, YOLO, and Mask R-CNN began to outperform traditional methods. Today, computer vision is integral to cutting-edge technologies such as facial recognition, autonomous vehicles, medical imaging, and augmented reality. It continues to evolve rapidly, driven by advancements in AI, larger datasets, and more powerful computing resources.
How Does Computer Vision Work?
- Image Acquisition: The process starts with capturing images or videos using cameras, sensors, or other imaging devices. This raw visual data serves as the input for further analysis.
- Preprocessing: Images are enhanced, resized, and filtered to improve their quality and make them suitable for analysis. This step may involve noise reduction, contrast adjustment, and normalization.
- Feature Extraction: Key attributes such as edges, textures, colors, and shapes are identified to distinguish objects within an image. These features are crucial for accurate detection and classification.
- Object Detection and Classification: Machine learning and deep learning models like CNNs detect and classify objects, highlighting Machine Learning Vs Deep Learning.
- Post-Processing and Decision Making: The extracted information is interpreted and used for specific applications such as facial recognition, autonomous driving, or medical diagnostics.
- Model Training and Optimization: To improve accuracy, models are trained using large annotated datasets and fine-tuned through techniques like transfer learning, hyperparameter tuning, and cross-validation.
- Deployment and Monitoring: Once optimized, computer vision systems are integrated into real-world applications. Continuous monitoring and updates ensure they perform accurately under various conditions and environments.
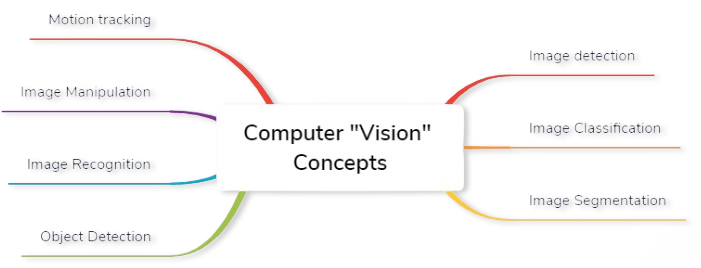
- Feature Extraction: Identifying key patterns or characteristics within an image, such as corners, edges, or textures, to help in recognition tasks.
- Object Detection: Locating and identifying objects within an image or video stream, often using techniques like YOLO (You Only Look Once) or Faster R-CNN.
- Facial Recognition: Identifying and verifying individuals based on facial features, widely used in security, surveillance, and authentication systems, is an application often explored in Data Science Training.
- Pose Estimation: Determining the orientation and position of a person or object in an image, often used in motion capture, augmented reality, and human-computer interaction.
- Segmentation: Dividing an image into meaningful parts to separate objects from the background. This includes semantic segmentation (labeling each pixel by category) and instance segmentation (distinguishing individual objects).
- Optical Character Recognition (OCR): Extracting text from images, commonly used for scanning documents, license plates, and translating handwritten or printed text into digital form.
- Image Captioning: Automatically generating descriptive text for images by combining computer vision and natural language processing, useful in accessibility tools and content generation.
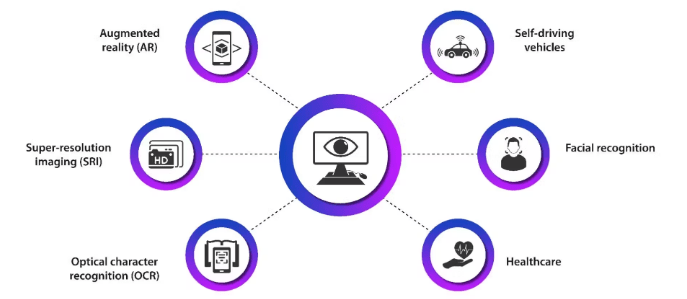
- Healthcare: Computer vision is used in medical imaging to detect diseases such as cancer, fractures, and infections through X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans, improving diagnostic accuracy and speed.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars rely on computer vision for lane detection, traffic sign recognition, obstacle avoidance, and pedestrian tracking to navigate roads safely.
- Agriculture: Drones and sensors use computer vision to monitor crop health, detect pests, and optimize irrigation, leading to higher yields and reduced resource use.
- Manufacturing: Automated inspection systems detect defects in products on production lines, ensuring consistent quality control and reducing manual labor an application discussed in Top Data Science Books for Beginners & Advanced Data Scientist.
- Smart Cities and Surveillance: Computer vision helps in traffic management, crowd monitoring, and public safety by analyzing video feeds in real time.
- Facial Recognition: Widely used in security systems, smartphones, and surveillance, facial recognition identifies individuals by analyzing facial features for access control and monitoring.
- Retail and E-commerce: Vision-based systems track customer behavior, manage inventory through image recognition, and enhance shopping experiences with virtual try-ons and automated checkouts.
To Earn Your Data Science Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Data Science Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Data Science Course Training Today!
Key Concepts in Computer Vision
Popular Computer Vision Algorithms
Computer vision relies on a wide range of algorithms that enable machines to interpret visual data effectively. These algorithms are foundational to tasks like object detection, image classification, face recognition, and motion tracking. One of the most well-known algorithms is the Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), which automatically extracts spatial hierarchies of features from images. CNNs form the backbone of many modern computer vision applications due to their high accuracy and efficiency. Variants like ResNet, VGGNet, and Inception have further improved performance in deep learning-based image recognition, often implemented using Top Data Science Programming Languages. For object detection, algorithms such as YOLO (You Only Look Once), SSD (Single Shot Detector), and Faster R-CNN are widely used. These models not only classify objects in an image but also localize them with bounding boxes, making them essential in autonomous driving, surveillance, and robotics. In the area of image segmentation, U-Net and Mask R-CNN are popular, especially in medical imaging, where pixel-level accuracy is crucial. SIFT (Scale-Invariant Feature Transform) and ORB (Oriented FAST and Rotated BRIEF) remain useful for feature matching and image stitching in traditional computer vision tasks. Together, these algorithms power a vast array of real-world applications and continue to evolve with advancements in AI and deep learning.
Are You Considering Pursuing a Master’s Degree in Data Science? Enroll in the Data Science Masters Course Today!
Applications of Computer Vision in Real Life
Tools and Frameworks for Computer Vision
Computer vision development has been significantly accelerated by the availability of powerful tools and frameworks that simplify the process of building, training, and deploying models. These tools provide pre-built functions, optimized libraries, and flexible environments for both beginners and experts. OpenCV (Open Source Computer Vision Library) is one of the most widely used libraries, offering hundreds of algorithms for image processing, face detection, object tracking, and more. It supports multiple languages including Python, C++, and Java, making it versatile for various applications a key consideration in comparing Python vs R vs SAS. TensorFlow and PyTorch are leading deep learning frameworks extensively used in computer vision. They provide modules for building convolutional neural networks (CNNs), handling large datasets, and training models on GPUs. TensorFlow’s Keras API is user-friendly for rapid prototyping, while PyTorch offers dynamic computation graphs preferred for research and development. Other tools like Detectron2 (by Facebook AI) and YOLO (You Only Look Once) models are specialized for real-time object detection. MATLAB is also used in academic and industrial settings for its rich visualization and image processing capabilities. These frameworks and tools not only make development faster but also enable the creation of scalable and production-ready computer vision solutions, fostering innovation across industries like healthcare, automotive, and retail.
Preparing for Data Science Job? Have a Look at Our Blog on Data Science Interview Questions & Answer To Ace Your Interview!
Role of AI and Deep Learning in Computer Vision
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and deep learning have revolutionized the field of computer vision, enabling machines to interpret and understand visual data with unprecedented accuracy. Traditionally, computer vision relied on manual feature extraction and rule-based algorithms, which were limited in their ability to generalize across different tasks and environments. With the advent of deep learning particularly convolutional neural networks (CNNs) the landscape changed dramatically. Deep learning models automatically learn hierarchical features from raw images, eliminating the need for manual intervention, a concept thoroughly covered in Data Science Training. These models excel in tasks such as object detection, facial recognition, image classification, and semantic segmentation. AI-driven systems powered by deep learning can now surpass human-level performance in specific vision tasks, making them invaluable in industries like healthcare, automotive, retail, and surveillance. For example, in healthcare, AI models analyze medical images for early disease detection. In autonomous vehicles, deep learning helps in real-time object recognition and decision-making. Continuous advancements in model architectures, such as transformers and generative models, are further pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. In essence, AI and deep learning have not only enhanced the capabilities of computer vision but have also made it scalable and adaptable to real-world challenges, driving innovation across various sectors.





