- Overview of Data Scientist and Data Analyst
- Required Technical Skills
- Required Soft Skills
- Educational Background
- Tools and Technologies Used
- Salary Comparison
- Career Pathways
- Industry Demand
Overview of Data Scientist and Data Analyst
Data Scientists and Data Analysts are both crucial roles in the data ecosystem, but they serve different purposes and require distinct skill sets. A Data Analyst primarily focuses on interpreting existing data to help organizations make informed decisions. They clean, organize, and analyze data sets, often using tools like Excel, SQL, and visualization software such as Tableau or Power BI. Their work typically involves generating reports, identifying trends, and providing actionable insights to support business strategies. Data Analysts play a vital role in answering specific business questions by working with structured data and summarizing findings in a clear, understandable manner. On the other hand, Data Scientists, with Data Science Training, have a broader and more advanced scope. They not only analyze data but also build predictive models and algorithms using statistical methods and machine learning techniques. Data Scientists work with large volumes of structured and unstructured data, leveraging programming languages like Python or R, and tools such as TensorFlow or Hadoop. Their goal is to uncover hidden patterns, create data-driven products, and solve complex problems that go beyond descriptive analytics. They often collaborate with business leaders to design experiments and develop strategies that can improve business outcomes. In essence, while Data Analysts focus on descriptive and diagnostic analytics to explain what happened and why, Data Scientists dive deeper into predictive and prescriptive analytics, forecasting future trends and suggesting actions. Both roles require strong analytical skills, but Data Scientists generally need more advanced programming and statistical knowledge. Together, they help organizations harness the full power of data to drive smarter decision-making and innovation.
Interested in Obtaining Your Data Science Certificate? View The Data Science Course Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Required Technical Skills
Both Data Scientists and Data Analysts require a strong foundation in technical skills, though the specifics vary based on their roles. For Data Analysts, proficiency in data manipulation and visualization tools is essential. They typically need to be skilled in SQL for querying databases and extracting relevant information. Knowledge of spreadsheet software like Microsoft Excel is fundamental for data cleaning and basic analysis. Visualization tools such as Tableau, Power BI, or Google Data Studio are critical for presenting data insights clearly to stakeholders. Data Analysts should also understand basic statistics to interpret trends and patterns accurately, which is a common focus in A Day in the Life of a Data Scientist. Additionally, familiarity with scripting languages like Python or R can enhance their ability to automate repetitive tasks and perform more advanced analyses. Data Scientists, however, require a deeper and broader technical skill set. Strong programming skills in Python or R are crucial, as these languages are widely used for data manipulation, statistical modeling, and machine learning. Knowledge of machine learning frameworks and libraries such as scikit-learn, TensorFlow, or PyTorch is important for building predictive models. Data Scientists must be comfortable working with big data technologies like Hadoop, Spark, or cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) to process large-scale datasets. Expertise in statistical analysis, probability, and linear algebra forms the mathematical backbone for developing algorithms.
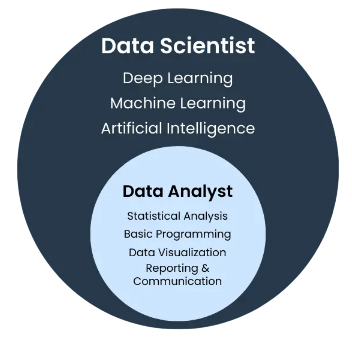
Additionally, Data Scientists need experience with data wrangling, feature engineering, and model evaluation techniques to ensure robust and accurate results. Familiarity with version control systems like Git and containerization tools such as Docker can also be beneficial for collaborative projects. Overall, while both roles share foundational skills in data handling and analysis, Data Scientists require a more advanced and technical toolkit to address complex, predictive, and prescriptive analytics challenges.
Required Soft Skills
- Communication: Both roles require strong communication skills to explain complex data findings clearly to non-technical stakeholders. Data Scientists often communicate more technical insights, while Data Analysts focus on translating data into actionable business recommendations.
- Critical Thinking: Data Scientists need advanced critical thinking to design experiments, develop models, and interpret ambiguous results. Data Analysts use critical thinking to analyze data trends and validate findings for decision-making.
- Problem-Solving: Data Scientists often tackle open-ended problems that require innovative approaches and creativity, frequently utilizing Top Data Science Programming Languages to develop effective solutions.
- Collaboration: Both roles demand collaboration, but Data Scientists frequently work with cross-functional teams including engineers, product managers, and researchers. Data Analysts mostly collaborate with business units to align data insights with business needs.
- Attention to Detail: High attention to detail is crucial for both roles to ensure data accuracy and the validity of insights. Data Scientists especially need this when developing models or algorithms that impact critical decisions.
- Curiosity: A natural curiosity drives Data Scientists to explore new data sources, test hypotheses, and develop novel solutions. Data Analysts use curiosity to uncover patterns and trends that inform business strategies.
- Time Management: Managing multiple projects and deadlines is essential for both roles. Data Scientists may balance research and production tasks, while Data Analysts often juggle reporting and ad hoc analysis.
- Degree Requirements: Data Scientists typically hold advanced degrees such as a Master’s or Ph.D. in fields like computer science, statistics, mathematics, or engineering. Data Analysts usually require a bachelor’s degree in areas such as business, economics, mathematics, or information technology.
- Mathematics and Statistics: Both roles need a strong foundation in mathematics and statistics. However, Data Scientists delve deeper into advanced topics like linear algebra, calculus, and probability theory, while Data Analysts focus on basic statistical concepts and descriptive analytics.
- Programming Knowledge: Data Scientists are expected to have proficient programming skills in languages like Python, R, and SQL, often complemented by knowledge of big data tools, all of which are typically covered in Data Science Training.
- Machine Learning and AI: Data Scientists study machine learning algorithms, artificial intelligence, and data modeling extensively as part of their education. This is less emphasized for Data Analysts, who focus more on data visualization and reporting techniques.
- Domain Expertise: Data Analysts often have education aligned with specific business domains like marketing, finance, or healthcare to better interpret data in context. Data Scientists, while also needing domain knowledge, prioritize technical and analytical education.
- Research Experience: Graduate-level education for Data Scientists frequently includes research projects or theses that involve complex data analysis, fostering strong analytical skills. Data Analysts might have less formal research training but more practical data handling experience.
- Certifications and Continuing Education: Both roles benefit from certifications such as Google Data Analytics or Microsoft Certified: Data Analyst Associate for Analysts, and advanced certifications in data science, machine learning, or cloud platforms for Scientists.
- Average Salary Levels: Data Scientists generally command higher average salaries than Data Analysts due to the advanced technical skills and responsibilities involved. Median salaries for Data Scientists often range from $100,000 to $150,000, while Data Analysts typically earn between $60,000 and $90,000 annually.
- Experience Impact: Salary growth is significant in both roles with experience. Senior Data Scientists with extensive experience and specialized skills can earn well above $160,000, whereas senior Data Analysts may see salaries reach up to $100,000 or slightly more.
- Education Influence: Data Scientists usually have higher educational qualifications such as Master’s or Ph.D., which contribute to higher starting salaries, especially in fields like Big Data vs Data Science.
- Industry Variation: Industries like finance, technology, and healthcare tend to offer higher salaries for both roles due to the critical importance of data in these sectors. Data Scientists in these industries often see a larger salary premium.
- Company Size: Larger corporations and tech giants typically offer more competitive salaries for Data Scientists and Data Analysts compared to small or medium-sized businesses.
- Geographic Location: Salaries vary widely based on location. Urban tech hubs like Silicon Valley, New York, and Seattle tend to offer higher compensation for both roles compared to smaller cities or rural areas.
- Specialization Premium: Data Scientists with expertise in machine learning, AI, and big data tools often command the highest salaries. Data Analysts with advanced skills in data visualization and business intelligence tools also receive salary boosts but usually less than specialized Data Scientists.
To Earn Your Data Science Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Data Science Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Data Science Course Training Today!
Educational Background
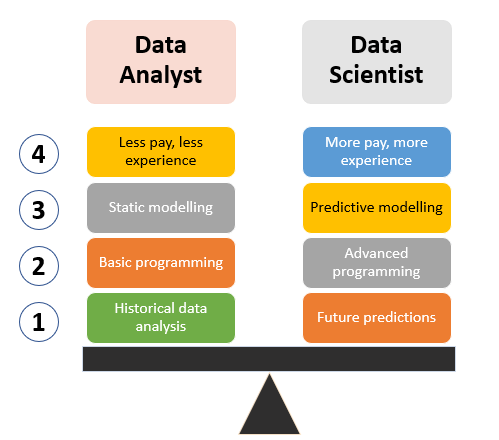
Tools and Technologies Used
Data Scientists and Data Analysts rely on a diverse set of tools and technologies to extract value from data, each tailored to the complexity and goals of their work. Data Analysts primarily use tools focused on data querying, visualization, and reporting. SQL is indispensable for accessing and manipulating structured data stored in relational databases. For data visualization and dashboard creation, tools like Tableau, Power BI, and Google Data Studio are widely used because they help translate complex datasets into easy-to-understand visual stories. Analysts often use Excel for quick data cleaning, basic analysis, and ad hoc calculations. Additionally, scripting languages like Python and R are increasingly common among Data Analysts to automate repetitive tasks, perform statistical tests, and enhance data processing capabilities, opening up numerous Python Career Opportunities. In contrast, Data Scientists work with more advanced and often large-scale tools designed for predictive modeling, machine learning, and big data processing. Programming languages such as Python and R serve as the core platforms for data science, offering extensive libraries like scikit-learn, TensorFlow, Keras, and PyTorch for machine learning and deep learning projects. Big data technologies such as Apache Hadoop and Apache Spark enable Data Scientists to handle and analyze massive datasets efficiently. Cloud computing platforms including AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud provide scalable infrastructure and tools for data storage, processing, and deployment of models. Version control systems like Git facilitate collaboration and code management. Additionally, containerization tools like Docker allow Data Scientists to create reproducible and portable environments for their projects. Together, these tools empower Data Analysts and Data Scientists to transform raw data into meaningful insights and predictive models, supporting smarter business decisions and innovation.
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Data Science by Enrolling in Our Data Science Masters Course.
Salary Comparison
Career Pathways
Career pathways for Data Scientists and Data Analysts often begin with foundational roles but can diverge significantly based on skills, interests, and industry demands. For Data Analysts, entry-level positions typically involve handling data cleaning, reporting, and basic analysis using tools like Excel, SQL, and visualization software. With experience, Data Analysts can advance to senior analyst roles, specializing in areas such as business intelligence, data visualization, or operations analysis. Many also transition into data engineering or analytics management, where they oversee data workflows and lead teams responsible for delivering data-driven insights. Upskilling in programming languages and machine learning, including understanding Machine Learning Vs Deep Learning, can open doors for Data Analysts to transition into Data Science roles, expanding their scope to predictive modeling and advanced analytics. Data Scientists usually start their careers in junior or associate positions, working alongside experienced scientists to develop models, conduct experiments, and analyze complex datasets. Progression involves gaining expertise in machine learning, big data technologies, and domain-specific knowledge. Mid-level Data Scientists often take on project leadership roles, designing end-to-end data science solutions and collaborating closely with stakeholders across business units. Senior Data Scientists or Lead Scientists typically influence company strategy, mentor junior staff, and innovate with cutting-edge AI and data techniques. From here, career options include moving into specialized areas such as AI research, machine learning engineering, or chief data officer (CDO) roles that combine technical leadership with business strategy. Both career paths emphasize continuous learning due to the fast-evolving data landscape. Certifications, advanced degrees, and real-world project experience play key roles in career advancement, enabling professionals to adapt and thrive in an increasingly data-driven world.
Want to Learn About Data Science? Explore Our Data Science Interview Questions & Answer Featuring the Most Frequently Asked Questions in Job Interviews.
Industry Demand
The demand for Data Scientists and Data Analysts has surged across industries, driven by the increasing reliance on data-driven decision-making and technological advancements. In the United States, the Bureau of Labor Statistics projects a 35% growth in employment for data scientists from 2022 to 2032, significantly outpacing the national average for all occupations. Industries such as finance, healthcare, retail, and technology are at the forefront of this demand. In finance, institutions like JPMorgan Chase and Goldman Sachs employ data scientists to enhance risk assessment, detect fraud, and optimize trading strategies. Healthcare organizations leverage data analytics for predictive modeling, patient care optimization, and operational efficiency, all of which are enhanced through Data Science Training. Retail giants like Amazon and Walmart utilize data science for personalized recommendations, inventory management, and customer behavior analysis. Technology companies, including Google and Meta, integrate data science to improve user experiences and develop AI-driven products. In India, the data analytics sector is experiencing rapid growth, with projections indicating the creation of 11 million job openings by 2026. This expansion is fueled by the adoption of AI, machine learning, and big data technologies across various sectors. Key industries driving this demand include finance, healthcare, e-commerce, and government sectors, all seeking professionals skilled in data analysis, predictive modeling, and machine learning. As organizations continue to recognize the value of data, the need for skilled Data Scientists and Analysts is expected to remain strong, offering promising career opportunities in the foreseeable future.