
- What is ETL?
- ETL vs ELT
- Extract: Data Sources and Techniques
- Transform: Cleansing and Formatting
- Load: Target Systems and Methods
- ETL Tools Overview
- ETL in Data Warehousing
- Common ETL Challenges
- Scheduling and Automation
- Error Handling and Logs
- Best Practices in ETL Design
- Real-Life ETL Scenarios
What is ETL?
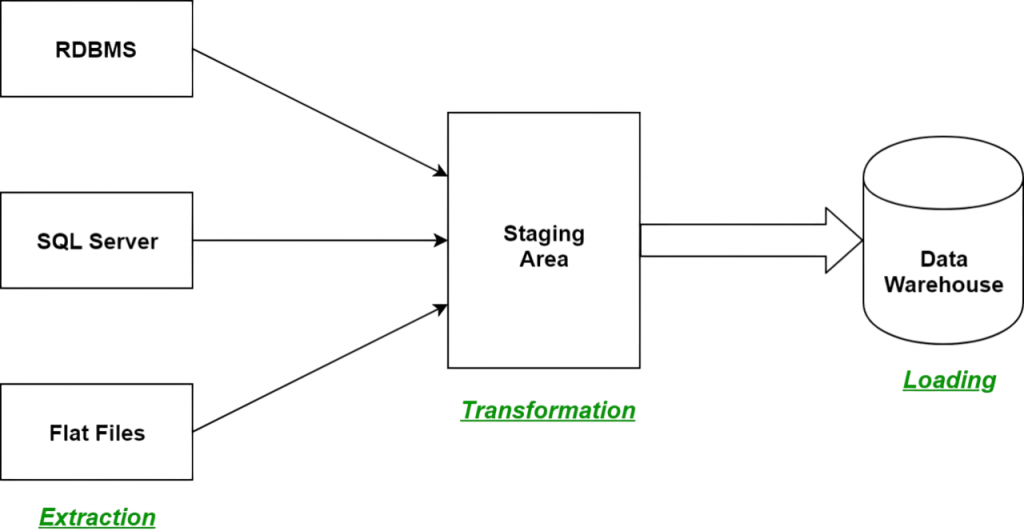
ETL stands for Extract, Transform, Load. It is a process used in data warehousing and data integration that involves collecting data from multiple sources, transforming it into a clean, usable format, and loading it into a target system such as a database or data warehouse. The ETL process is crucial for turning raw data into meaningful insights and is widely used in business intelligence, analytics, and reporting a key component often covered in an AWS Course . It enables organizations to centralize their data, ensure consistency, and improve decision-making.ETL plays a foundational role in organizing and structuring big data. It ensures that disparate sources such as databases, APIs, flat files, and cloud services are unified into a single repository where data scientists and analysts can run queries, generate reports, and build models. The steps are typically automated and scheduled to keep the data updated in real-time or near real-time.
ETL vs ELT
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) and ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) are two approaches to data integration. While they perform similar functions, they differ in the sequence and execution of the transformation process.
ETL performs data transformation before loading it into the target system. This approach works best with traditional relational databases and on-premise data warehouses. It allows more control over transformation and supports structured, validated data within a Cloud Databaseenvironment.
ELT on the other hand, loads raw data directly into the target system and performs transformation inside the data warehouse. This approach is better suited for modern cloud platforms like BigQuery or Snowflake that are optimized for large-scale processing.
| Feature | ETL | ELT |
|---|---|---|
| Transformation | Before loading | After loading |
| Performance | Depends on external tools | Utilizes power of DWH |
| Storage | Transformed before storage | Raw data stored first |
| Use Cases | Legacy systems, structured data | Big data, cloud DWH |
| Tools | Informatica, Talend, SSIS | BigQuery, Snowflake, ADF |
Choosing between ETL and ELT depends on the architecture, scalability needs, and the nature of the data processing involved.
Do You Want to Learn More About AWS? Get Info From Our AWS certification Training Today!
Extract: Data Sources and Techniques
Cloud systems like AWS S3, relational databases like Oracle and MySQL, NoSQL databases like MongoDB, and diverse file formats like CSV and JSON are just a few of the many sources of data that are gathered during the extract phase. Data from online services like REST APIs can also be pulled by it, and processed efficiently using the Python Map Function. There are three types of extraction methods: streaming extraction, which uses tools like Apache Kafka to collect data in real-time; incremental extraction, which only obtains new or updated data; and full extraction, which loads all data often during the initial run. In addition to maintaining data accuracy and consistency, a successful extraction procedure lessens the burden on source systems. To extract data from multiple sources, convert it into a format that can be used, and then load it into a target system, such as a data warehouse, an ETL data pipeline is necessary. To guarantee data accuracy, consistency, and availability for analysis and reporting, organisations depend on a well-designed ETL data pipeline. An ETL data pipeline facilitates better decision-making across company operations and increases efficiency by automating data flows.
Would You Like to Know More About AWS? Sign Up For Our AWS certification Training Now!
Transform: Cleansing and Formatting
The process of transforming unstructured data into an orderly, clean format that is prepared for analysis is called transformation. This includes a number of crucial processes, such as data cleansing (removing duplicates and correcting errors), data normalisation (converting data into consistent formats, such as dates or currencies), data aggregation (summarising information by calculating totals or averages), data mapping (matching data from various sources to a common structure), and business rule application to make the data useful for decision-making.
- These procedures aid in preparing the data for analysis and ensuring its accuracy and dependability.
- Scripts, SQL, or specialised ETL tools are frequently used for this activity.
During the data integration process, Cloud Data Ingestion and ETL transformation techniques are essential for transforming unstructured data into a comprehensible format. Organisations can guarantee high-quality and consistent data for analysis by implementing several ETL transformation techniques, such as filtering, aggregating, and data cleansing. Gaining proficiency in efficient ETL transformation techniques methods facilitates precise, data-driven decision-making and data pipeline optimisation.
Load: Target Systems and Methods
Loading moves transformed data into the target storage system. The destination could be:
- Data Warehouses: Amazon Redshift, Snowflake, Google BigQuery
- Data Lakes: Azure Data Lake, AWS Lake Formation
- Relational Databases: PostgreSQL, SQL Server, Oracle
- BI Tools: Tableau, Power BI, Qlik Types of Loading:
- Full Load: In a Serverless Computing environment, it overwrites existing data with new data efficiently, without the need to manage underlying infrastructure.
- Incremental Load: Adds only new or changed records.
- Batch Load: Loads data in scheduled intervals.
- Real-Time Load: Continuous ingestion for up-to-date analytics.
Efficient loading ensures that analytical systems have up-to-date data with minimal latency.
ETL Tools Overview
ETL tools simplify the design, execution, and monitoring of ETL processes. Common ETL tools include:
- Informatica PowerCenter: Enterprise-grade platform with strong transformation capabilities.
- Apache NiFi: Open-source tool for building data pipelines with a graphical UI.
- Microsoft SSIS: Integrates seamlessly with SQL Server, ideal for Microsoft environments.
- Talend Open Studio: Offers both free and paid versions, great for SMEs.
- Apache Airflow: Python-based orchestration tool to manage complex workflows.
These tools come with features like job scheduling, monitoring, error handling, and connectors to various data sources topics commonly explored in an AWS Course .
ETL in Data Warehousing
Because ETL makes sure that data is reliable, consistent, and accessible, it is essential to data warehousing. Data from several transactional systems is combined and arranged into dimensional models, such as snowflake or star schemas. Before the data reaches the end users, ETL applies business rules and gets the data ready for usage in BI tools and dashboards. Data warehouses would be disorganised and unreliable without ETL, which might result in bad choices and resource waste.
Common ETL Challenges
ETL processes are powerful but not without challenges:

- Scalability: As data volume grows, ETL pipelines can become bottlenecks.
- Data Quality: Incomplete or incorrect data can cause analysis errors a challenge highlighted in case studies like How AWS Powers Netflix, where data accuracy is critical for reliable streaming analytics.
- Performance: Slow jobs can delay reporting and decision-making.
- Complexity: Multiple dependencies and transformations complicate maintenance.
- Monitoring & Logging: Lack of visibility makes it hard to detect failures.
- Data Governance: Tracking lineage and applying compliance policies.
- Schedulers: Tools like Apache Airflow, Cron, Azure Data Factory.
- Triggers: File drop, database event, or API call.
- Dependencies: Ensuring tasks run in the correct order.
- Monitoring: Alert systems to flag job failures or performance issues.
- Design modular workflows for easier testing and maintenance.
- Use parameterization to make scripts reusable.
- Enable incremental loads to optimize performance.
- Track data lineage for governance and auditing.
- Validate inputs/outputs at each stage.
- 1. Retail Analytics:
A global retailer extracts data from online and in-store POS systems. The data is transformed to include calculated KPIs like average basket size and customer retention, and loaded into a data warehouse used by business analysts.
- 2. Healthcare:
A hospital network integrates patient data from EMR systems and wearable devices. ETL ensures that patient history, diagnosis codes, and vitals are standardized for analysis and compliance.
- 3. Banking:
A financial institution aggregates transaction records, applies fraud detection rules during transformation, and updates dashboards for real-time monitoring a practical scenario often discussed in an AWS Course .
- 4. Marketing Campaigns:
An agency pulls social media, CRM, and ad performance data into a central store. Transformation includes lead scoring and segmentation for targeted campaigns.
- 5. Logistics:
A shipping company consolidates package tracking data from sensors and partner systems. The data is transformed and loaded into a real-time dashboard for customers and support teams.These examples highlight how ETL is critical for operational excellence, regulatory compliance, and strategic insight.
Conclusion
ETL remains a vital component in modern data architecture. It enables organizations to bring order to chaos by transforming raw, scattered data into valuable insights. With the shift toward cloud and real-time systems, ETL processes are evolving but continue to underpin data analytics, reporting, and business intelligence. A well-designed ETL strategy supported by powerful tools and guided by best practices can make data the most valuable asset of any organization.
Mitigating these issues requires good architecture, automated testing, and clear documentation.
Gain Your Sample resume in AWS Training by Enrolling in Our AWS Sample resume Now!
Scheduling and Automation
ETL pipelines are typically scheduled to run at specific intervals or triggered by events.
Key components include:Automation enhances reliability, reduces human error, and ensures timely data availability.
Error Handling and Logs
In order to preserve data integrity and facilitate speedy recovery in the event of issues, effective error handling is crucial. This entails applying retry logic to automatically repeat unsuccessful actions and using try-catch blocks to handle problems during data conversions practices often required in the Top 7 DevOps Job Roles. While alarms and notifications notify the team right away if a job fails, logging systems capture timestamps and success and failure messages. Audit logs also aid with traceability and data lineage tracking. When combined, these error handling and logging procedures are essential for system maintenance, troubleshooting, and regulatory compliance.
Preparing for AWS Job? Have a Look at Our Blog on AWS interview questions and answers To Acte Your Interview!
Best Practices in ETL Design
To build a robust ETL architecture, follow these best practices:
Implementing these practices helps ensure scalable, reliable, and secure ETL processes.


