
- Introduction to Cloud Architecture
- Role and Responsibilities of a Cloud Architect
- Cloud Networking and Storage Management
- Essential Skills for Cloud Architects
- Choosing the Right Cloud Platform (AWS, Azure, GCP)
- Security and Compliance in Cloud Architecture
- Learning Cloud Computing Fundamental
- Hands-on Experience with Cloud Projects
- Career Paths and Job Market Trends
- Future Trends in Cloud Architecture
Introduction to Cloud Architecture
Cloud architecture refers to the design and management of cloud-based solutions. It involves selecting the appropriate cloud services, structuring the infrastructure, and overseeing the deployment and management of systems hosted on the cloud. The growing reliance on cloud computing across industries has led to the development of specialized professionals known as Cloud Architects, who are responsible for designing the structure of cloud solutions that are reliable, scalable, and secure. Professional cloud architect is more than selecting the right technology or services; it is about building efficient systems that meet business needs. This includes ensuring systems are scalable to handle varying loads, cost-effective, and meet strict security and compliance standards. In this guide, we will discuss the role of a Cloud Architect, the skills required, and how professionals can carve out a successful career in cloud computing. Additionally, we will dive into the essential concepts of cloud platforms, cloud security, and the trends shaping the future of cloud computing.
Role and Responsibilities of a Cloud Architect
Cloud Architects are responsible for the high-level design of cloud-based infrastructure, ensuring it meets the business’s needs while being scalable, cost-efficient, and secure. The role involves a wide range of activities:
- Requirement Gathering: The architect works with business stakeholders to understand application needs, user traffic, data storage, and security requirements.
- Infrastructure Design: They design the cloud architecture incorporating various cloud services, including computing, storage, Cloud Networking, and database management.
- Optimization: Cloud architects ensure the solutions are optimized for cost, performance, and scalability. They choose the appropriate cloud services and consider factors such as elastic scalability, high availability, and fault tolerance.
- Security Frameworks: Cloud architects integrate security best practices into the architecture, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data and systems. This includes encryption, firewalls, and identity and cost management.
- Compliance: The architect ensures that the design adheres to relevant regulatory frameworks such as HIPAA, GDPR, and SOC 2, depending on the industry.
- Cost Optimization: Cloud architects choose services that minimize costs while meeting performance requirements. They also monitor and manage cloud costs over time using tools like amazon web services Cost Explorer or Azure Cost Management.
- Cloud Economics: They design solutions focusing on cost-saving strategies such as auto-scaling, serverless architectures, and resource allocation adjustments.
- Working with DevOps and Development Teams: Cloud architects collaborate with developers, DevOps engineers, and IT operations to ensure smooth implementation and integration of the cloud infrastructure with applications.
- Client Interaction: They work with clients to explain technical concepts in non-technical terms and ensure that the solution fits the client’s requirements.
- Deployment: After designing the infrastructure, the architect assists in the deployment process, ensuring the solution is implemented correctly.
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting: Cloud architects monitor the performance of cloud systems, optimizing resource usage and troubleshooting any issues that arise during or after deployment.
Designing Cloud Solutions:
Ensuring Security and Compliance:
Cost Management:
Collaboration:
Implementation and Monitoring:
Cloud Networking and Storage Management
In addition to designing the network architecture, cloud architects must also focus on optimizing network traffic to ensure low latency and high throughput for cloud applications. This includes configuring and managing Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs), subnets, and routing tables to establish secure and efficient communication between cloud resources. Implementing load balancing strategies across multiple instances or availability zones helps distribute traffic evenly, preventing bottlenecks and ensuring consistent performance. Cloud architects must also leverage advanced tools like auto-scaling to automatically adjust resources based on traffic demands, ensuring the application remains responsive under varying loads.
When it comes to cost management, Professional cloud architect must carefully assess the specific needs of each workload to determine the best storage solution. For instance, Amazon S3, Azure Blob Storage, and Google Cloud Platform Storage are popular object storage services for scalable, cost-effective storage with high durability. For high-performance workloads, block storage services such as Amazon EBS, Azure Managed Disks, or Google Persistent Disks are better suited for applications that require frequent read/write access. Additionally, cloud architects must also consider factors like data backup, disaster recovery strategies, and encryption to ensure data integrity, security, and compliance with industry regulations.
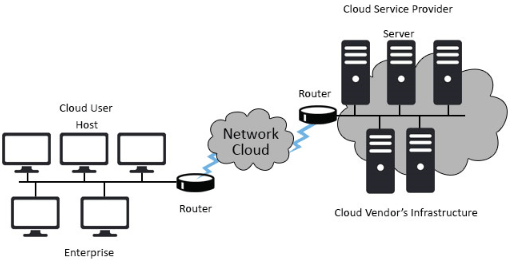
Essential Skills for Cloud Architects
- Technical Skills: Cloud Platforms Expertise: Familiarity with major cloud platforms such as amazon web services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is essential. Cloud architects must understand each platform’s services, including computing, storage, Cloud Networking, and databases.Infrastructure as Code (IaC) Proficiency in tools like Terraform,CloudFormation, or Azure Resource Manager (ARM) templates is important for automating cloud infrastructure deployment.
- Networking: Cloud architects must have an in-depth understanding of virtual networks, load balancing, DNS, firewalls, VPNs, and inter-region communications.Security and Compliance Knowledge of identity and access management (IAM), encryption, regulatory compliance (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA), and cost management.Containers and Microservices Expertise in containers (Docker), container orchestration (Kubernetes), and microservices architecture is becoming increasingly crucial in cloud-based deployments.Cloud Monitoring and Cost Management: The ability to monitor cloud resources, identify inefficiencies, and optimize costs using the built-in tools provided by cloud service providers.
- Analytical Skills: Problem Solving Cloud architects must be able to analyze business needs and translate them into cloud solutions that meet performance, security, and cost requirements.Scalability An architect must design scalable solutions to handle varying workloads, particularly for large enterprises identity and access management must foresee potential risks such as system downtime, security breaches, and cost overruns and implement strategies to mitigate them.
- Soft Skills: Communication Cloud architects need strong communication skills to interact with clients, stakeholders, and team members. They should be able to explain technical concepts in a way that is understandable to non-technical people.Collaboration is crucial to work well in a team environment with cross-functional teams. Cloud architects often collaborate with developers, operations teams, and business leaders.
Choosing the Right Cloud Platform (AWS, Azure, GCP)
Cloud architects often have to choose the right platform for their organization’s or client’s needs. The three major cloud providers, AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud Platform, each have strengths and weaknesses depending on the use case.
- AWS is the leader in cloud computing and has the largest market share. It offers a broad range of services, global availability, and flexibility, making it well-suited for complex and large-scale enterprise solutions.Web applications, big data, machine learning, and hybrid cloud solutions.
- Azure excels in hybrid cloud environments and integrates well with existing Microsoft products such as Windows Server, Active Directory, and SQL Server. It’s widely used by enterprises that already use Microsoft technologies. Enterprise applications, hybrid cloud solutions, and businesses that rely heavily on Microsoft products.
- GCP is known for its data analytics and machine learning capabilities. It offers a seamless experience for organizations that need high-performance computing and containerized applications.Big data, AI/ML, and containerized applications.The choice between amazon web services , Azure, and GCP often depends on existing infrastructure, team expertise, pricing, and specific business needs.
Security and Compliance in Cloud Architecture
Security is one of the most important aspects of cloud architecture. To secure applications and infrastructure, cloud architects must be proficient in implementing Identity and Access Management (IAM), data encryption, and firewalls. Compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, and other regulations is also critical.Zero Trust Security Models Implementing least-privilege access, continuous monitoring, and ensuring all users authenticate before accessing resources.Encryption data in transit and at rest using services like amazon web services KMS, Azure Key Vault, or Google Cloud Platform Key identity and access management.Audit and Logging Maintaining logs for all activities in the cloud infrastructure for accountability and auditing.
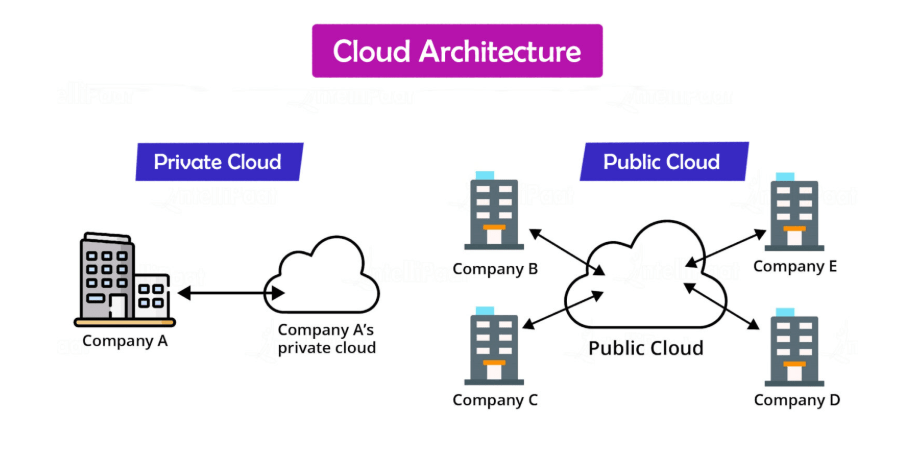
Learning Cloud Computing Fundamental
Before diving into specialized cloud platforms, it’s crucial to understand cloud computing fundamentals.Additionally, it is essential to understand cloud storage models (object storage, block storage, and file storage) and cloud networking (VPC, subnets, and routing). This includes learning about the types of cloud services:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): This provides virtualized computing resources over the Internet. amazon web services EC2 and Azure Virtual Machines are examples.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): This type of service provides a platform for customers to develop, run, and manage applications. Azure App Services and amazon web services Elastic Beanstalk are examples.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers software applications over the Internet, typically on a subscription basis. Google Workspace and Microsoft 365 are examples.
Hands-on Experience with Cloud Projects
Theoretical knowledge provides a solid foundation, but to truly excel as a Professional cloud architect, hands-on experience is crucial. Deploying real-world cloud projects helps bridge the gap between theory and practical application. Engaging in cloud labs, hackathons, or working on personal cloud projects allows you to experiment with different cloud services, troubleshoot real challenges, and understand the nuances of cloud architecture. This practical exposure not only builds confidence but also enhances problem-solving skills, making you better equipped to design and implement robust, scalable, and cost-effective cloud solutions in a professional setting.
Career Paths and Job Market Trends
Cloud architecture is a growing field, with demand increasing for experienced professionals. Cloud architects can advance to roles such as Cloud Engineering Manager, Enterprise Architect, or Chief Technology Officer (CTO). The job market for cloud architects remains robust, with many companies migrating to the cloud or optimizing their cloud infrastructure.Salary Expectations for Cloud Architects Salaries for cloud architects vary based on experience, location, and cloud platform expertise:
- Entry-level: $90,000 – $120,000 per year.
- Mid-level: $120,000 – $150,000 per year.
- Senior-level: $150,000 – $200,000+ per year.
Future Trends in Cloud Architecture
Cloud architecture is evolving rapidly. Future trends include Serverless computing Reducing the need for managing infrastructure. AI and machine learning More cloud architectures incorporate AI/ML capabilities. Edge computing Processing data closer to where it is generated, reducing latency. Multi-cloud strategies Organizations use services from multiple cloud providers for better flexibility and redundancy. Professional cloud architects will continue to play a critical role in shaping the future of technology, focusing on creating more scalable, efficient, and secure cloud environments.





