
- Introduction to CI/CD
- Understanding Continuous Integration (CI)
- Understanding Continuous Delivery (CD)
- Key Components of a CI/CD Pipeline
- Setting Up a CI/CD Pipeline
- Popular CI/CD Tools and Platforms
- Benefits of Implementing CI/CD
- Challenges in CI/CD Adoption
- Emerging Trends in CI/CD Ecosystems
- Conclusion
Introduction to Cloud Computing
CI/CD stands for Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery, a set of software development practices that aim to improve delivery speed, efficiency, and quality. These techniques automate every phase of the software development process, from writing code to testing and deploying the application. The goal is to deliver new features and bug fixes quickly, reliably, and continuously. Traditional software development methodologies often involve lengthy development cycles, resulting in delayed software rollouts. With CI/CD and Devops Training , developers can frequently push code changes, which are automatically tested, integrated, and delivered in short, manageable cycles. This continuous flow of changes lowers the risk of errors by catching issues early in the process and ensures that the software remains up-to-date and bug-free. By enabling rapid and reliable updates, CI/CD enhances collaboration between development and operations teams, reduces time-to-market, and leads to higher-quality software. As a result, CI/CD has become a core part of modern software development, empowering teams to release software more frequently and with greater confidence.
Understanding Continuous Integration (CI)
The Role of Continuous Integration
Continuous Integration (CI) frequently merges developers’ code changes into a central repository. These changes are automatically tested and validated to ensure new features or bug fixes don’t break the existing codebase. Best ci/cd tools used by programmers include Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab CI/CD, CircleCI, Travis CI, and Azure DevOps. These tools help automate testing, deployment, and monitoring, ensuring efficient and reliable software development workflows.
How CI Works
In a CI environment, developers commit their code to a shared repository daily. The CI server is responsible for pulling the latest code version from the repository, building the application, and running automated tests to check for errors. This ensures that the code is always in a deployable state.
Benefits of CI in the Development Process
- Early Detection of Errors: CI ensures that errors are caught early in the development cycle, reducing the time spent fixing issues.
- Faster Feedback: Developers get immediate feedback about their code’s quality, allowing them to address issues sooner.
- More Reliable Builds: Since the code is continuously integrated, conflicts or broken builds are less likely.
Ready to Pursue Your Devops Certificate? View The Devops Course Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Understanding Continuous Delivery (CD)
Continuous Delivery (CD) extends CI by ensuring that the application is always in a deployable state. After successfully integrating and testing the code, it’s automatically prepared for release to a staging or production environment. CD aims to automate the process from code commit to deployment, enabling developers to release software quickly and safely.
Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud)
EC2 instances come in various configurations based on the amount of CPU, memory, and storage you need. Using The right AWS EC2 instance types can help you manage, monitor, and optimize these instances effectively.
Continuous Delivery vs. Continuous Deployment
While “Continuous Delivery” and “Continuous Deployment” are often used interchangeably, they have distinct meanings. Continuous Delivery refers to automatically preparing software for release, but the actual deployment to production is usually a manual step. In contrast, Continuous Deployment automates this final step, deploying code to production without manual intervention.
The CD Workflow
The CD process involves taking code that has passed automated tests and packaging it for deployment to a staging or production environment. It includes:
- Automated deployment to testing environments.
- Configuration management and infrastructure provisioning.
- Monitoring and feedback loops for deployed services.
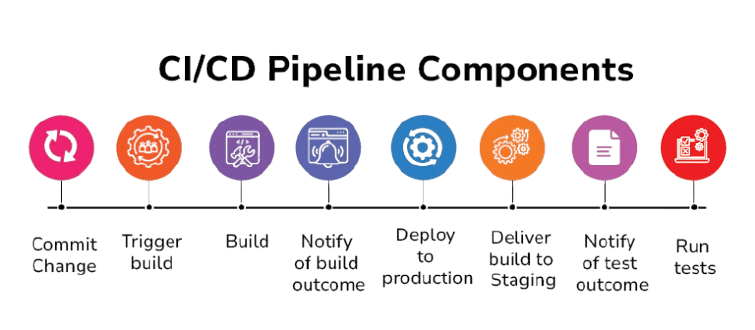
Key Components of a CI/CD Pipeline
A CI/CD pipeline comprises several essential components that work together to ensure seamless software development, testing, and deployment.
Version Control System (VCS)
A VCS, such as Git, stores the source code and tracks changes. It ensures the code is versioned and provides an audit trail for every change.
Version Control System (VCS)
A VCS, such as Git, stores the source code and tracks changes. It ensures the code is versioned and provides an audit trail for every change.
Build Automation Tools
Build automation tools like Maven, Gradle, and Ant to automate software compilation, packaging, and versioning. These tools integrate with the CI server to create reproducible builds. devops tools for database automation streamline the process by automating infrastructure provisioning, configuration management, and deployment, ensuring consistency across environments.
Deployment Automation
Deployment tools like Kubernetes, Docker, and Ansible automate deploying applications to various environments. These tools ensure consistency and can be scaled as needed.
Setting Up a CI/CD Pipeline
Tools and Technologies for CI/CD
Setting up a CI/CD pipeline involves choosing the right tools for your organization. Popular tools for CI processes include Jenkins, GitLab CI, CircleCI, and Travis CI, and for deployment automation, Kubernetes, Docker, and Ansible.
Building the Pipeline: Step-by-Step Guide
- Set up version control: Start by creating a repository for your code (e.g., GitHub or Bitbucket).
- Integrate the CI server: Connect the repository to a CI server (e.g., Jenkins) to automate build processes.
- Automate testing: Implement automated unit, integration, and end-to-end tests.
- Deploy to staging environments: Set up deployment pipelines for staging and production environments.
- Monitor and improve: Continuously monitor the pipeline and collect feedback to refine and improve the process.
- Keep builds small and frequent – commit small incremental changes to reduce complexity and simplify debugging.
- Automate everything – automate build, test, and deployment processes to ensure consistency and reduce manual errors.
- Implement comprehensive testing – use a mix of unit, integration, and acceptance tests to catch issues early.
- Utilize effective version control – leverage systems like Git to manage changes and enable seamless integration and rollback.
- Ensure environment consistency – use containerization and configuration management to maintain uniformity across development, staging, and production environments through Devops Training.
- Have robust rollback strategies – prepare automated rollback mechanisms to quickly revert to a stable version when issues arise.
- Monitor continuously – implement monitoring and logging to receive real-time feedback on performance and identify problems early.
- Integrate security (DevSecOps) – embed security practices throughout the pipeline including automated security scans and vulnerability assessments.
- Foster cross-functional collaboration – encourage communication between development, operations, and security teams to streamline the pipeline.
- Document and iterate – regularly document processes and continuously refine the CI/CD pipeline based on feedback and evolving best practices.
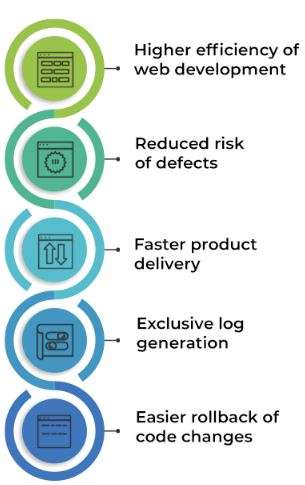
- Faster Release Cycles CI/CD allows for frequent and rapid software releases by automating repetitive tasks. Developers can push new code changes as soon as they’re ready, reducing the time to market for new features and bug fixes.
- Improved Code Quality CI/CD automates the testing process, ensuring that errors and bugs are detected early. Continuous testing increases the software’s overall quality and stability.
- Enhanced Collaboration CI/CD fosters collaboration among team members as changes are shared and integrated continuously. Teams can work on different features simultaneously without causing conflicts in the codebase.
- Reduced Manual Errors Automation reduces human error, ensuring that builds, tests, and deployments are consistent and reliable.
- In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, CI/CD pipelines are continuously evolving to meet the demands of modern software development. Organizations are shifting towards agile practices that not only focus on rapid deployment but also prioritize robustness, security, and scalability.
- One emerging trend is the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into CI/CD processes. These technologies enable predictive analysis of code changes and help identify potential issues before they escalate, leading to smarter testing and faster remediation. Jenkins pipeline , as a widely used automation tool, can leverage AI/ML capabilities to optimize build processes, detect anomalies, and enhance overall software delivery efficiency.
- As development teams handle increasingly complex systems, incorporating AI-driven tools ensures higher-quality releases and reduces the manual effort involved in debugging. Another key development is the rise of DevSecOps, where security is embedded into every stage of the CI/CD pipeline.
- Automated security scans, vulnerability assessments, and compliance checks are becoming integral parts of the workflow. This shift towards proactive security measures minimizes risks and fortifies applications against potential breaches.
- Furthermore, with the widespread adoption of cloud-native technologies, CI/CD tools are being optimized for multi-cloud and hybrid environments, allowing seamless integration across various platforms.
- Enhanced monitoring and real-time analytics also provide actionable insights, facilitating continuous improvement and faster iterations. As the industry continues to embrace these innovations, the future of CI/CD will likely focus on greater automation, improved collaboration between cross-functional teams, and more adaptive pipelines that can respond dynamically to changing business needs.
- Embracing these trends not only improves software quality but also fosters a culture of continuous innovation and operational excellence. The evolution of CI/CD is unstoppable.
Thrilled to Achieve Your Devops Certification? View The Devops Online Course Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Best Practices for CI/CD Implementation
Popular CI/CD Tools and Platforms
Jenkins is one of the most popular open-source CI/CD tools. It offers various plugins for integrating multiple build and deployment tools, making it highly customizable for different use cases. GitLab CI/CD is a part of the GitLab platform that provides integrated CI/CD pipelines. It supports Git repositories, auto-deployments, and monitoring tools. CircleCI automates the entire software delivery pipeline, enabling teams to deploy faster and more reliably. It integrates with GitHub, Bitbucket, and Docker. Travis CI is a cloud-based CI tool that integrates well with GitHub repositories. It allows developers to automate testing and deployment workflow often featured in devops for cloud-based CI/CD practices. Bamboo, developed by Atlassian, provides CI/CD automation alongside integration with other Atlassian tools like Jira and Bitbucket.
Are You Considering Pursuing Devops Master’s Degree? Enroll For Devops Masters Course Today!
Benefits of Implementing CI/CD
Challenges in CI/CD Adoption
Implementing CI/CD requires a culture shift. It’s essential to foster a mindset that embraces automation, continuous improvement, and collaboration. Selecting the right tools and setting up the necessary infrastructure can be complex, particularly for organizations with legacy systems or complicated deployment pipelines. While CI/CD aims to reduce errors, failures can still occur. Automated rollback strategies are essential to mitigate risks during production deployments. Devops vs Agile comes into play when considering deployment approaches—while Agile focuses on iterative development, DevOps emphasizes seamless integration and operations. Integrating CI/CD into legacy systems may require significant modifications to existing workflows, making the transition more challenging for older applications.
Ensuring security and compliance within CI/CD pipelines can be a challenge, as automated deployments must align with industry regulations and best practices. Teams may also face resistance to change, requiring strong leadership and effective training programs to encourage adoption. Monitoring and optimizing CI/CD processes demand continuous effort, as performance bottlenecks, test flakiness, and infrastructure costs can impact efficiency.
Finally, achieving true CI/CD maturity requires ongoing refinement and optimization. Organizations must continuously evaluate their pipeline, incorporate feedback, and adapt to new technologies to stay competitive. Overcoming these challenges demands a combination of technical expertise, strategic planning, and a commitment to fostering a DevOps culture.
Emerging Trends in CI/CD Ecosystems
Getting Ready for Devops Job Interview? Check Out Our Blog on Devops Interview Questions & Answer
Conclusion
As software development advances, CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery) will become an increasingly central component of the software delivery process. New technologies such as AI and machine learning will further improve CI/CD pipelines by automating more sophisticated tasks and providing enhanced predictive capabilities, such as detecting potential problems before they arise or optimizing deployment tactics. CI/CD revolutionizes the software development life cycle by creating a culture of continuous improvement and integrating Devops Training to enhance collaboration and efficiency. With processes automated for testing, code integration, and deployment, the likelihood of human mistakes is reduced, resulting in better-quality releases. Additionally, CI/CD facilitates collaboration across developers, operations teams, and other stakeholders, enhancing overall communication and process. As DevOps methodologies evolve, CI/CD remains a keystone of contemporary software development, enabling teams to produce and deploy software quicker with reliability and quality.





