
- Introduction to AWS Cloud Computing
- Advantages of AWS Cloud Services
- Scalability and Flexibility in AWS
- Security and Compliance Features
- Cost-Effectiveness of AWS
- AWS Reliability and High Availability
- Limitations and Drawbacks of AWS
- Common AWS Outages and Challenges
- Hidden Costs in AWS Pricing
- AWS vs Other Cloud Providers (Azure, GCP)
- Best Practices to Overcome AWS Limitations
- Conclusion
Introduction to AWS Cloud Computing
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is one of the most comprehensive and widely used cloud computing platforms, transforming how businesses and developers manage IT infrastructure. Launched in 2006 by Amazon, AWS introduced a new era of on-demand computing, enabling organizations to access powerful cloud-based resources without the need for physical hardware or data centers. Over the years, AWS has grown to become the leading cloud provider, offering an extensive suite of services that support businesses of all sizes, from startups to global enterprises. With its vast network of data centers spread across the world, AWS ensures high availability, scalability, and reliability, allowing companies to deploy applications seamlessly while maintaining optimal performance. Its cloud solutions have been instrumental in driving innovation across industries, supporting everything from web applications and enterprise software to artificial intelligence, big data analytics, and Internet of Things (IoT) applications. Beyond its technical capabilities, AWS has revolutionized the way businesses approach IT by offering flexible pricing models, eliminating the need for large upfront capital investments. This has allowed companies to scale their operations efficiently, paying only for the resources they use. Security and compliance are also at the core of AWS, with rigorous measures in place to protect data, meet industry regulations, and ensure business continuity. As cloud adoption continues to rise, AWS remains at the forefront of the industry, constantly evolving to meet the growing demands of modern businesses. Its commitment to innovation, reliability, and global reach has solidified its position as the preferred cloud computing solution for millions of organizations worldwide.
Advantages of AWS Cloud Services
- Global Reach: AWS operates in multiple regions worldwide, allowing users to deploy applications and services in various geographic locations to reduce latency and enhance performance.
- Comprehensive Service Offering: AWS offers over 200 fully-featured services, including computing power, storage, databases, machine learning, and analytics tools. This extensive service catalog enables businesses to build and deploy various applications.
- Flexible Pricing: AWS follows a pay-as-you-go pricing model, where users only pay for the resources they consume. This allows companies to reduce capital expenditures. AWS also offers reserved and spot instance pricing for cost optimization.
- Scalability and Reliability: AWS provides a highly scalable cloud infrastructure that automatically adjusts to demand. Services like Amazon EC2, Auto Scaling, and Elastic Load Balancing allow companies to scale their workloads seamlessly based on traffic.
- Security and Compliance: AWS offers a robust security model with features like Identity and Access Management (IAM), encryption, firewalls, and multi-factor authentication. AWS also complies with industry standards, including HIPAA, GDPR, and SOC certifications.
Scalability and Flexibility in AWS
Scalability and flexibility are two of AWS’s most substantial advantages. With AWS, businesses can rapidly scale their Infrastructure to meet changing demands without worrying about physical hardware limitations. Scalability and flexibility are two of AWS’s most substantial advantages. With AWS, businesses can rapidly scale their Infrastructure to meet changing demands without worrying about physical hardware limitations. AWS’s EC2 instances allow businesses to scale their computing power based on demand. By provisioning a variety of instance types, users can adjust resources according to their needs, ensuring that they only pay for what they use. AWS Auto Scaling automatically adjusts the number of EC2 instances or containers based on real-time traffic, ensuring consistent performance while optimizing costs. This feature is essential for dynamic workloads like e-commerce sites or web applications. ELB automatically distributes incoming traffic across multiple EC2 instances, ensuring high availability and fault tolerance. AWS offers storage solutions like Amazon S3 and EBS, which scale automatically based on data requirements. This flexibility allows businesses to store vast amounts of data without worrying about physical storage limits.
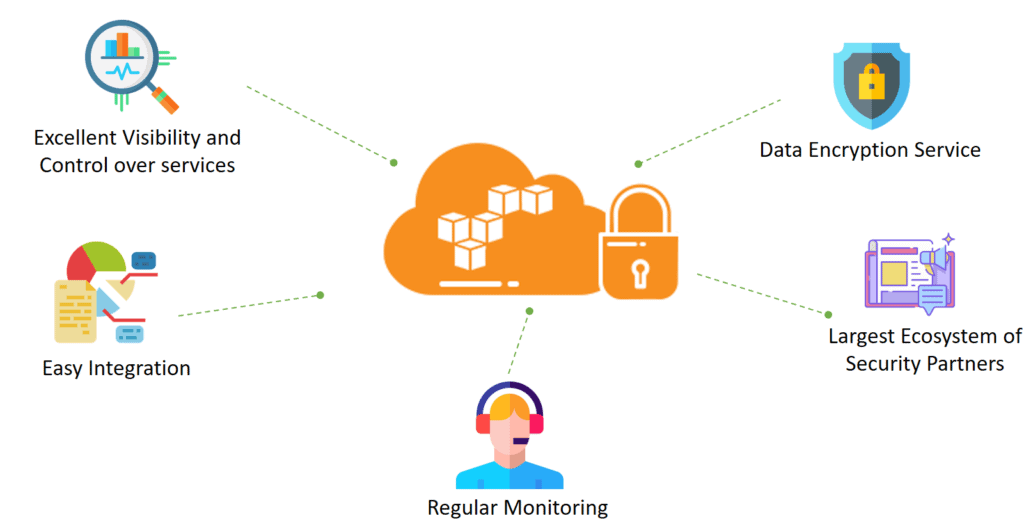
Security and Compliance Features
AWS strongly emphasizes security, offering a comprehensive set of features to protect data, applications, and workloads.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): AWS IAM lets you control user access to AWS resources. You can create and manage users, roles, and permissions to ensure only authorized personnel can access critical resources.
- Encryption: AWS offers encryption features for both data in transit (e.g., SSL/TLS) and data at rest (e.g., Amazon S3 encryption, Amazon RDS encryption). This ensures that sensitive information is always protected.
- Security Monitoring and Auditing: AWS provides tools like AWS CloudTrail and Amazon GuardDuty for monitoring, logging, and auditing activity within your AWS environment. CloudTrail logs every API request to AWS services, while GuardDuty uses machine learning to detect threats in your cloud infrastructure.
- Compliance Certifications: AWS complies with numerous regulatory standards, including HIPAA, SOC 1, 2, and 3, and PCI-DSS, making it suitable for industries such as finance, healthcare, and government.
Cost-Effectiveness of AWS
AWS’s cost model is designed to be both flexible and cost-effective, allowing businesses to pay only for the resources they use. With AWS, there are no upfront costs or long-term contracts. You pay for the computing, storage, and other services based on actual usage, ensuring cost efficiency. For users who need predictable workloads, AWS offers Reserved Instances, which allow customers to reserve computing capacity for one or three years at a discounted rate. AWS also offers Spot Instances, where users can bid for unused EC2 capacity at a significantly lower price. This offers potential cost savings for flexible workloads. AWS provides a free tier for new users, which includes limited access to some of its services. This allows businesses to experiment and build applications without incurring additional costs.
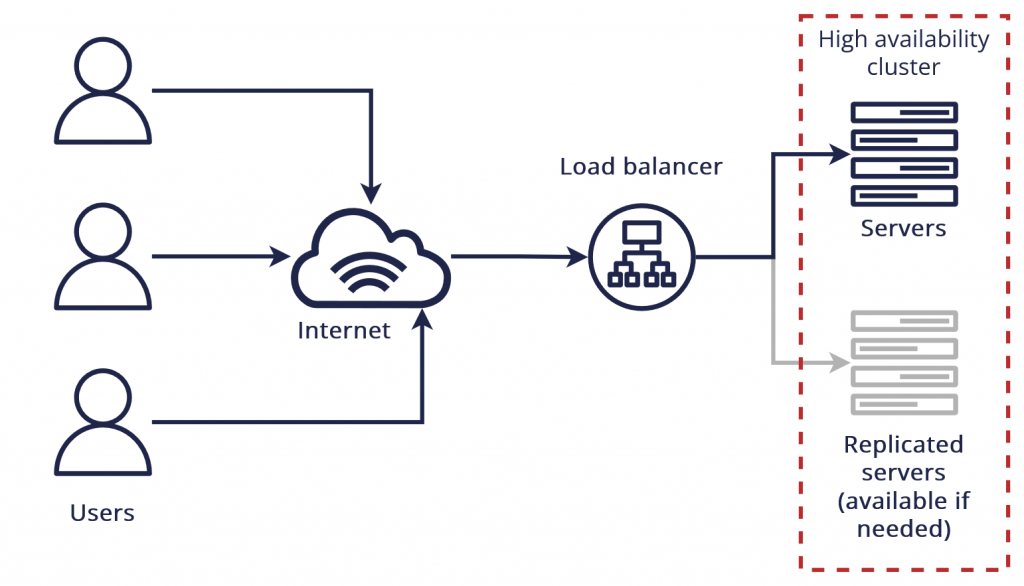
AWS Reliability and High Availability
- Multi-AZ and Multi-Region Deployment: AWS allows users to deploy their applications across multiple Availability Zones (AZs) within or across various regions. This multi-zone architecture ensures high availability and disaster recovery capabilities, enabling seamless failover in case of failure.
- Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) helps ensure your application’s availability by evenly distributing incoming traffic across multiple EC2 instances.
- AWS Fault-Tolerant Services: AWS services such as Amazon RDS, S3, and EC2 have built-in fault tolerance and redundancy. If an issue exists in one available zone, the service is automatically switched to another.
Limitations and Drawbacks of AWS
While AWS is a powerful cloud platform, it has its limitations. AWS’s pricing model can be complex and challenging, especially for new users. Understanding the costs of different services and resources may require significant time and effort. AWS offers a broad range of services, each with unique configurations and use cases. New users may find navigating AWS’s ecosystem and managing services overwhelming. Due to the proprietary nature of AWS’s services, migrating away from AWS can be challenging and costly, especially if your Infrastructure becomes deeply integrated with AWS services.
Common AWS Outages and Challenges
While AWS is known for its reliability, there have been instances of service outages that have affected customers globally.
- Major Outages: AWS has faced several high-profile outages, such as the 2017 S3 outage that took down many websites and services worldwide. Such outages highlight the need for businesses to have disaster recovery plans.
- Service Dependencies: Many AWS services are interconnected, so an issue in one service, such as S3 or EC2, can cause a ripple effect that impacts other services. This can lead to system downtime and service disruption.
- Regional Failures: AWS services are spread across multiple regions, but problems with specific areas can affect services globally. Therefore, companies must use multi-region strategies to ensure fault tolerance.
Hidden Costs in AWS Pricing
While AWS offers cost-effective pricing, there are hidden costs that businesses may overlook.Transferring data between different AWS regions or out of AWS can incur additional charges. These data transfer costs can add up quickly if not carefully managed. While Amazon S3 offers low storage costs, storing large amounts of data or frequently accessing data can result in higher-than-expected costs. AWS offers different levels of support plans, including Basic, Developer, Business, and Enterprise support, which can incur additional costs based on the service level.
AWS vs Other Cloud Providers (Azure, GCP)
When comparing AWS to other major cloud providers such as Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform (GCP), there are several differences:
- Service Offering: While AWS is the largest cloud provider, Azure and GCP are close contenders, each excelling in different areas. Azure is strong in hybrid cloud solutions and enterprise integrations, while GCP is known for its big data and machine learning services.
- Market Share: AWS holds the largest market share, but Azure and GCP are growing rapidly, particularly in the enterprise space, where Microsoft has a strong presence.
- Pricing: AWS typically offers a more complex pricing model than Azure and GCP, which might have more straightforward pricing for specific use cases.
Best Practices to Overcome AWS Limitations
Use AWS’s cost management tools like AWS Cost Explorer to track and optimize usage. Consider Reserved Instances for predictable workloads and Spot Instances for flexible tasks. Leverage AWS training resources and certifications to become proficient in AWS services and understand best practices. Use multiple Availability Zones (AZs) and regions for high availability and disaster recovery. Use AWS Cloud Watch and AWS Lambda for automation to monitor services and respond to issues proactively.
Conclusion
AWS remains a dominant force in the cloud computing industry, offering a vast range of services that cater to businesses of all sizes. Its scalability, flexibility, security, and cost-effectiveness make it an attractive choice for organizations looking to migrate to the cloud. However, AWS is not without its challenges, such as complex pricing structures, potential service outages, and vendor lock-in concerns. To maximize the benefits of AWS, businesses should adopt best practices, such as optimizing costs through reserved and spot instances, leveraging multi-region deployments for high availability, and continuously monitoring usage to prevent unexpected charges. While AWS leads the market, organizations should also consider alternative cloud providers like Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform, depending on their specific needs. By understanding both the advantages and limitations of AWS, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals, ensuring a robust, scalable, and cost-efficient cloud infrastructure.





