
- Introduction
- Security and Privacy Concerns
- Data Availability and Reliability
- Compliance and Legal Issues
- Vendor Lock-in
- Cost Management in Cloud
- Performance Optimization Challenges
- Managing Cloud Complexity
- Conclusion
Introduction
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses manage their IT infrastructure, offering numerous benefits such as scalability, cost-efficiency, and flexibility. However, as more organizations transition to the cloud, they face a range of security, performance, and operational challenges. From concerns about data privacy and compliance to the complexities of managing multiple cloud services, these hurdles require careful planning and strategic solutions. A Cloud Computing Course can provide the knowledge and tools needed to navigate these challenges and implement effective strategies for managing cloud environments securely and efficiently. This article delves into the key challenges organizations face when adopting cloud computing and explores the solutions that can help mitigate these risks, ensuring that businesses can harness the full potential of the cloud while maintaining security, compliance, and optimal performance. Additionally, it highlights best practices for cost management, performance optimization, and minimizing vendor lock-in, providing businesses with a comprehensive guide to navigating the cloud landscape successfully. By understanding these challenges and implementing the right strategies, companies can maximize the benefits of cloud computing while safeguarding their critical data and resources.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Cloud Computing? Sign Up For Our Cloud Computing Online Course Today!
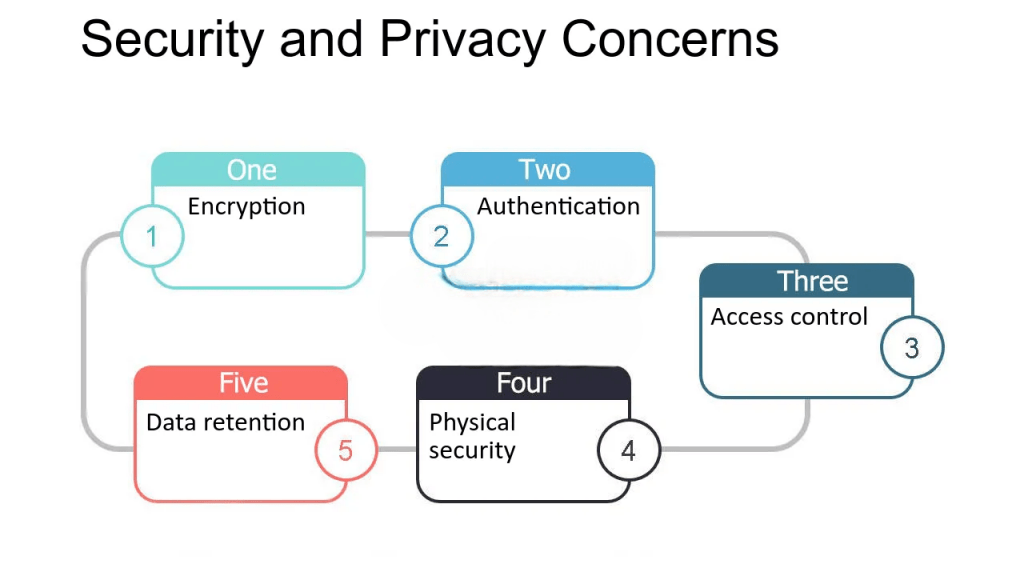
Security and Privacy Concerns
One of the primary concerns when adopting cloud computing is security and privacy. Storing sensitive data and running critical applications on external servers raises concerns about unauthorized access, data breaches, and compliance with privacy regulations. Cloud environments introduce new challenges that organizations need to address to safeguard their data.
-
Challenges:
- Data Breaches: Cloud service providers host data for multiple customers (multi-tenancy), which increases the risk of data breaches. While providers implement strong security measures, vulnerabilities in shared environments could still be exploited.
- Data Sovereignty: Data may be stored in various regions or countries, and organizations must ensure compliance with data protection regulations (such as GDPR or HIPAA) that govern where and how data can be stored and accessed. Understanding the Top 10 Reasons to do a SMAC Certification can help professionals gain the expertise to manage data security and compliance in a cloud environment, ensuring adherence to global data protection standards.
- Access Control: Ensuring that only authorized users can access sensitive data is crucial. Implementing proper identity and access management (IAM) practices, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), is necessary to mitigate unauthorized access.
- Insider Threats: Employees or contractors with access to cloud services may inadvertently or maliciously cause data breaches or leaks, making it essential to have tight access controls and continuous monitoring. Solutions:
- Encryption: Use strong encryption methods for data at rest and in transit.
- Access Management: Implement robust IAM policies, including role-based access controls (RBAC) and MFA.
- Auditing and Monitoring: Continuously monitor cloud environments and implement logging for detecting and responding to potential threats.
Data Availability and Reliability
Cloud environments offer the promise of high availability, but ensuring that services remain accessible and reliable poses significant challenges. Disruptions such as network failures, software bugs, or outages can have a major impact on business operations. Key challenges include service downtime, where unexpected outages or maintenance can disrupt access to data and applications despite high uptime SLAs. Data durability is another concern, as organizations must ensure their data is properly replicated and backed up to prevent loss, with disaster recovery strategies implemented alongside the provider’s redundancy features. The AWS Career Guide can help professionals understand how to leverage AWS tools and services to ensure data durability and implement effective disaster recovery solutions. Additionally, performance degradation can occur even when cloud services are running, with issues like high latency, resource contention, or slow network speeds affecting application performance. To address these challenges, organizations can deploy applications and data across multiple availability zones or cloud regions, implement regular backups and automatic data replication for redundancy, and continuously monitor performance metrics such as latency, bandwidth, and uptime to ensure optimal service functioning.
To Explore Cloud Computing in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Cloud Computing Online Course To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Compliance and Legal Issues
Compliance with regulations is a significant concern when moving to the cloud. Organizations must ensure that they meet legal requirements, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS, when storing sensitive data in the cloud.
-
Challenges:
- Data Sovereignty: Cloud service providers may store data in multiple regions, and local laws may dictate that certain types of data must remain within specific countries or regions.
- Regulatory Compliance: Each industry (e.g., healthcare, finance) has specific compliance requirements for data storage and processing. Cloud environments must be configured to meet these standards.
- Auditing and Reporting: Cloud providers may not offer sufficient visibility or tools for compliance auditing, requiring additional steps from organizations to ensure that they are meeting legal obligations. A Cloud Computing Course can equip professionals with the skills to implement effective compliance and auditing strategies, ensuring adherence to legal and regulatory requirements in the cloud. Solutions:
- Know Your Provider’s Compliance: Understand the compliance certifications your cloud provider holds and verify that they meet industry-specific requirements.
- Data Encryption and Access Controls: Encrypt sensitive data and implement strict access controls to ensure that only authorized users can access regulated data.
- Regular Audits: Perform regular audits of your cloud infrastructure to ensure that you are adhering to compliance and regulatory standards.
Vendor Lock-in
Vendor lock-in occurs when a company becomes overly reliant on a specific cloud provider’s tools, APIs, or services, making it challenging and costly to switch to another provider. This dependency can create long-term issues, especially when an organization wants to migrate or diversify its cloud services. Key challenges include the use of proprietary technologies by cloud providers, which lack direct equivalents in other platforms, making data migration or workload transitions complex and costly. Additionally, migrating to a different provider often involves significant expenses in terms of time, effort, and resources, including transferring data, rewriting code, and retraining staff. Understanding What does a AWS solution architect do can help organizations navigate this process efficiently, as they design and implement cloud architectures that minimize migration challenges and optimize resource allocation. Vendor lock-in also limits flexibility, preventing businesses from taking advantage of potentially better pricing, services, or features offered by other providers. To mitigate these risks, organizations can adopt a multi-cloud strategy, distributing workloads across different providers to reduce dependence on a single vendor. Utilizing standardized APIs and open-source technologies like Kubernetes and Docker can also minimize reliance on proprietary services, while building cloud-agnostic architectures ensures that applications and systems can be easily ported between cloud environments, reducing vendor-specific dependencies.
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Cloud Computing by Enrolling in Our Cloud Computing Masters Course.
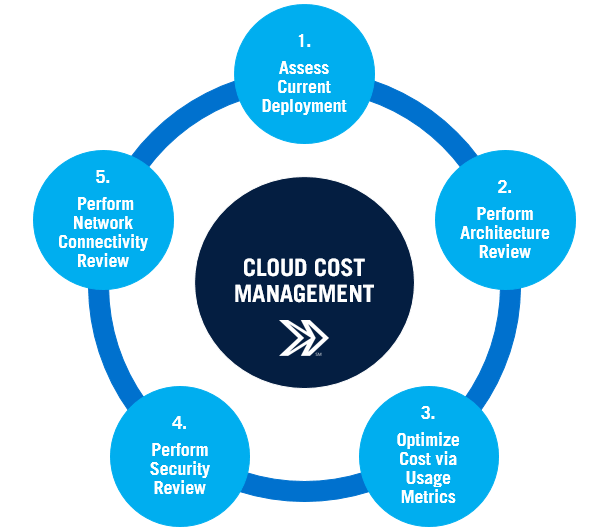
Cost Management in Cloud
While cloud computing offers cost efficiencies compared to traditional IT infrastructure, it also introduces challenges in managing costs. Without proper oversight, cloud costs can quickly spiral out of control, especially with pay-as-you-go pricing models and variable resource usage.
-
Challenges:
- Unpredictable Costs: Cloud costs can fluctuate based on usage, and without careful management, organizations may end up with unexpected charges, especially for storage, data transfer, or computing power.
- Over-Provisioning: Without proper monitoring, businesses may provision more resources than needed, leading to higher costs. The Cloud Computing Career Guide can help professionals understand the best practices for resource management and monitoring, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency in cloud environments.
- Underutilized Resources: Cloud services are highly scalable, and resources can be dynamically adjusted, but organizations often fail to decommission unused resources, leading to unnecessary expenses.
- Cost Monitoring Tools: Utilize cloud provider tools like AWS Cost Explorer, Azure Cost Management, and Google Cloud Pricing Calculator to monitor and optimize spending.
- Auto-Scaling: Implement auto-scaling to adjust resources based on demand, ensuring that you’re only paying for what you need.
- Budgets and Alerts: Set budgets and create alerts to notify stakeholders when usage is approaching budget limits.
Performance Optimization Challenges
Cloud computing offers significant potential for optimized performance, but ensuring that applications run efficiently in the cloud requires continuous attention and expertise. Key challenges include resource allocation, where over-provisioning or under-provisioning can lead to poor application performance or inefficient use of cloud resources. Network latency is another issue, as applications may experience delays if cloud services are located far from end users or if network bandwidth is insufficient. Additionally, balancing cost and performance can be difficult, especially in cloud environments with elastic scaling and variable pricing. To address these challenges, organizations can implement strategies such as right-sizing resources, continuously monitoring application performance, and adjusting cloud resources to meet demand without over-provisioning. For latency-sensitive applications, edge computing can be used to process data closer to the user, reducing delays. Understanding the Top 10 Reasons to Learn AWS can help you leverage AWS edge computing solutions to optimize application performance and enhance user experience by reducing latency. Utilizing performance monitoring tools like CloudWatch, Datadog, and New Relic helps track application performance and identify potential bottlenecks, ensuring optimal performance in the cloud.
Managing Cloud Complexity
As organizations migrate more workloads to the cloud, managing the complexity of cloud architectures becomes increasingly challenging. The cloud ecosystem is vast, with many tools, services, and configurations to keep track of.
-
Challenges:
- Multiple Cloud Services: With multiple services and tools available across different providers, organizations may struggle to integrate and manage various components efficiently.
- Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Environments: Managing a mix of on-premises infrastructure, private clouds, and public cloud services can create operational complexity.
- Continuous Monitoring: As cloud environments scale, it becomes more difficult to monitor the health and performance of all resources in real time.
- Cloud Management Platforms (CMP): Use cloud management platforms like VMware vRealize, CloudHealth, or RightScale to centralize management across hybrid or multi-cloud environments.
- Automation and Orchestration: Automate routine tasks like provisioning, scaling, and monitoring with tools like Terraform, Ansible, or Kubernetes to reduce complexity and improve efficiency.
- Governance and Policies: Establish clear cloud governance policies, including tagging strategies, resource management rules, and security protocols, to ensure consistent cloud usage and compliance across teams. A Cloud Computing Course can provide the necessary knowledge to implement effective governance practices, ensuring your cloud environment is secure, efficient, and compliant.
Are You Preparing for Cloud Computing Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Cloud Computing Interview Questions & Answer to Boost Your Preparation!
Solutions:Conclusion
In conclusion, while cloud computing offers immense opportunities for businesses to enhance their operations, it also presents several challenges that must be addressed to ensure success. Security and privacy concerns, data availability and reliability, cost management, vendor lock-in, and compliance issues are just some of the key hurdles organizations must navigate. However, with the right strategies in place such as robust encryption, continuous monitoring, multi-cloud approaches, and strong compliance practices businesses can mitigate these risks effectively. By optimizing resource allocation, ensuring performance efficiency, and maintaining flexibility in cloud architectures, companies can maximize the value of their cloud investments. Ultimately, successful cloud adoption requires ongoing vigilance, planning, and a proactive approach to risk management. With these considerations, businesses can not only safeguard their data and maintain regulatory compliance but also unlock the full potential of cloud computing to drive innovation and growth.





