
- Introduction to Cloud Security
- Key Threats and Challenges in Cloud Security
- Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Cloud Security Best Practices
- Encryption and Data Protection in the Cloud
- Compliance and Regulatory Standards
- Cloud Security Tools and Solutions
- Future Trends in Cloud Security
- Conclusion
Introduction to Cloud Security
As more businesses and organizations transition to cloud environments, the importance of securing cloud-based systems, applications, and data grows significantly. Cloud computing offers a variety of benefits, such as cost-efficiency, scalability, and flexibility. However, with these advantages come significant security risks and challenges that require dedicated strategies and tools to protect cloud resources from threats. Cloud security ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data and applications hosted in the cloud. Cloud Computing Course encompasses policies, technologies, and services designed to protect cloud environments from malicious attacks, data breaches, and unauthorized access.Cloud security has become a critical consideration for both cloud service providers and their customers. It involves securing a wide range of resources, including computing infrastructure, storage systems, applications, and even entire business operations. Given the distributed nature of the cloud, cloud security requires a combination of technical controls and strong governance practices. This article delves into the key threats and challenges in cloud security, as well as best practices and solutions for effectively securing cloud environments.
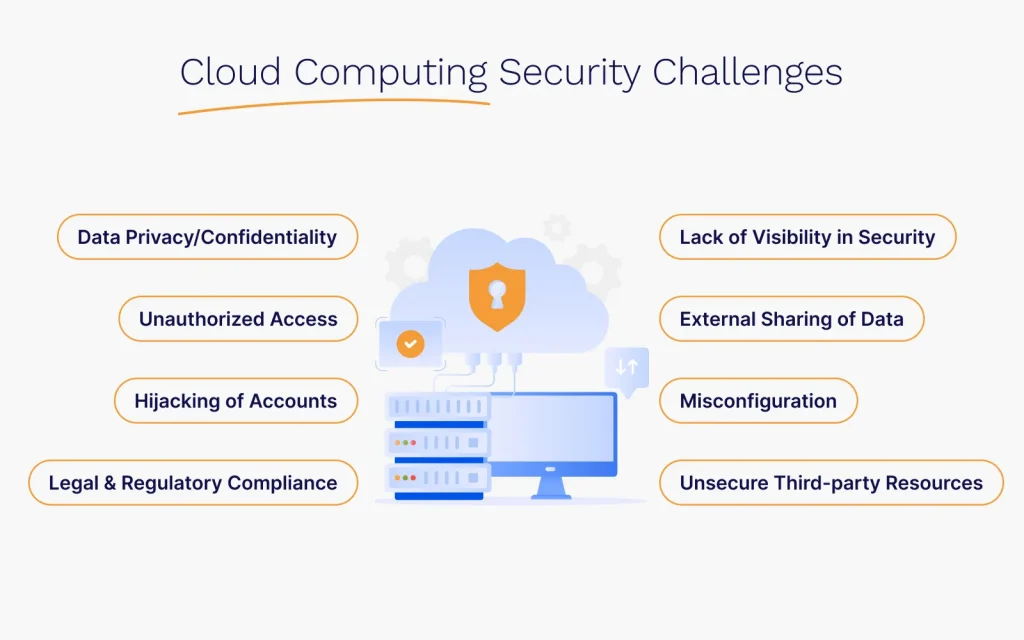
Key Threats and Challenges in Cloud Security
While cloud computing provides numerous benefits, it also exposes organizations to various security risks. Understanding these threats is crucial for developing effective security strategies. Below are some of the most common threats and challenges in cloud security:
- Data Breaches: Data breaches are one of the most significant threats to cloud security. Sensitive data can be exposed due to misconfigured cloud storage, weak access controls, or vulnerabilities in cloud applications. Cloud providers implement strong security measures, but customers are also responsible for ensuring Azure Advisor data is protected, which includes configuring their resources securely and encrypting data before uploading it to the cloud.
- Insecure APIs: Many cloud services offer application programming interfaces (APIs) to facilitate integration with third-party applications. However, poorly designed or insecure APIs can expose cloud resources to attacks. Hackers can exploit API vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access to cloud systems, compromising sensitive data and potentially affecting the entire environment.
- Account Hijacking: Account hijacking occurs when malicious actors gain control over an organization’s cloud service accounts through phishing attacks, credential theft, or exploiting weak login credentials. Once an attacker gains control over an account, they can perform unauthorized actions such as deleting data, deploying malware, or extracting sensitive information.
- Misconfiguration and Human Error: Cloud environments are often complex; mistakes when configuring cloud resources can lead to security vulnerabilities. Common misconfigurations include leaving cloud storage buckets open to the public, misapplying access control policies, or failing to patch software vulnerabilities.
- Insider Threats: Insider threats are a significant concern in cloud environments, as employees or contractors with legitimate access to cloud resources can misuse their privileges to cause harm. Whether through negligence or malicious intent, insider threats can result in data leaks, security breaches, or sabotage.
- Data Loss: Organizations may suffer permanent data loss without a reliable backup strategy or disaster recovery plan. Cloud providers typically offer data backup and redundancy features, but customers must configure and manage these solutions effectively.
- Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks: Denial-of-service attacks (DoS) are designed to overwhelm cloud services with excessive traffic, rendering them unavailable to Understanding Grid Computing.Distributed DoS (DDoS) attacks, where the traffic is generated from multiple sources, are particularly difficult to mitigate and require specialized defenses.
- Vendor Lock-In: Vendor lock-in occurs when an organization becomes too dependent on a single cloud service provider’s infrastructure, tools, and services. Vendor lock-in can result in a lack of flexibility and complicate the organization’s security posture, especially if the new provider has different security features or configurations.
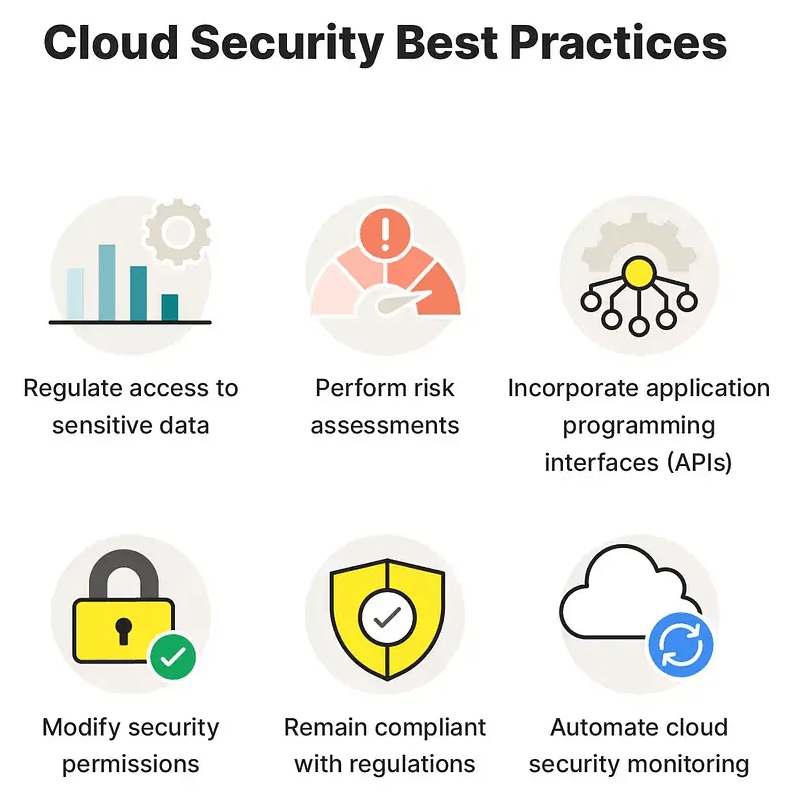
- Implement Strong Authentication and Access Control: Proper identity and access management (IAM) policies are essential for protecting cloud resources. Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) to strengthen login security and prevent unauthorized access. Enforce the principle of least privilege, ensuring that users have only the permissions necessary to perform their job functions. Additionally, I regularly review and update access policies to ensure they remain appropriate as roles evolve.
- Encrypt Data at Rest and in Transit: Encryption is a fundamental component of cloud security. Encrypt sensitive data at rest (when stored in the cloud) and in transit (when transmitted between systems). Cloud service providers offer encryption options, but it’s crucial to implement additional layers of encryption on your data before uploading it to the cloud. Additionally, ensure that encryption keys are stored securely and are managed in a centralized location.
- Regularly Monitor and Audit Cloud Resources: Continuous monitoring and auditing of cloud resources can help detect security issues before they become serious problems. Utilize cloud-native security tools like AWS CloudTrail or Azure Security Center to track changes and monitor unusual activities. Auditing logs helps maintain visibility into users’ actions and behaviors, allowing you to promptly identify and respond to potential threats.
- Regularly Update and Patch Systems: Ensure that cloud applications and Optimize Your Cloud with Azure Resource Manager Masteryare regularly updated and patched to protect against known vulnerabilities. Many cloud providers manage infrastructure updates for you, but applications and services deployed in the cloud may still require regular patching. A comprehensive patch management strategy helps reduce the risk of exploitation due to unpatched vulnerabilities.
- Secure APIs and Services: Secure all APIs and services using authentication mechanisms such as OAuth, API keys, and JSON Web Tokens (JWT). Limit the scope of API access, ensure that APIs are rate-limited to prevent abuse, and monitor for abnormal API calls that could indicate a security breach. Additionally, HTTPS should always encrypt communications between APIs and clients.
- Back Up Data Regularly: Data backup and recovery should be part of your overall cloud security strategy. Ensure backups are performed regularly, Optimize It With Azure Migration Tools, and tested to verify their integrity. Cloud providers typically offer backup services and disaster recovery options, but organizations should ensure these features are appropriately configured and aligned with their data retention and recovery policies.
- Educate Employees on Cloud Security: Human error remains a significant factor in cloud security breaches. Conduct regular employee training on cloud security best practices, such as recognizing phishing attempts, using strong passwords, and reporting suspicious activities. Foster a culture of security awareness to help reduce the risk of security incidents caused by negligence.
- Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) Tools: These tools help monitor and manage security configurations across cloud environments to prevent misconfigurations.
- Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASB): CASBs provide visibility and control over cloud applications, ensuring compliance and preventing unauthorized access.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): IDPS tools monitor cloud systems for suspicious activity and provide alerts or automated responses to potential threats.
- AI and Machine Learning for Threat Detection: Artificial intelligence and machine learning will increasingly play a role in detecting security threats in real time, analyzing vast amounts of data for anomalies and potential risks.
- Zero Trust Security: Zero trust models, where all users and devices are considered untrusted by default, will become more prevalent in cloud environments to prevent insider threats and unauthorized access.
- Quantum Cryptography: As quantum computing advances, quantum cryptography may offer new methods for encrypting data in the cloud, providing stronger protection against future threats.
Start your journey in Cloud Computing by enrolling in this Cloud Computing Online Course .
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a crucial element of cloud security, helping organizations control who can access their cloud resources and what actions they are authorized to perform. Effective IAM is vital for reducing the risk of unauthorized access and ensuring that only authorized users can interact with sensitive data or perform specific tasks. In cloud environments, user authentication and authorization play a significant role. Strong authentication methods, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), are necessary to verify users’ identities. IAM tools offer mechanisms to manage user credentials, create strong password policies, and enforce periodic password changes to further enhance security.Another key IAM feature is Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), which is commonly used to manage access in cloud environments. RBAC assigns users to predefined roles based on their job responsibilities, each with specific permissions. By ensuring that users only have the minimum necessary access required for Cloud Computing Course, organizations can mitigate the risk of privilege escalation and unauthorized access. Additionally, Single Sign-On (SSO) is a widely adopted IAM feature that allows users to authenticate once and gain access to multiple applications or services without needing to log in repeatedly. SSO simplifies the user experience and strengthens security by reducing the reliance on multiple passwords, which can become a vulnerability if not properly managed.
Gain in-depth knowledge of Cloud Computing by joining this Cloud Computing Online Course now.
Cloud Security Best Practices
Cloud security best practices are critical for organizations seeking to protect their cloud environments and data. These best practices can be used to mitigate the most common threats and challenges associated with cloud security:
Encryption and Data Protection in the Cloud
Azure Service Fabric offers several powerful features and capabilities that set it apart from other orchestrators and platforms. Below are some of the most notable features:Encryption is a fundamental aspect of cloud security, as it protects sensitive data from unauthorized access both when stored (at rest) and when being transmitted (in transit). It serves as a critical safeguard in case of data breaches, ensuring that even if attackers gain access to encrypted data, they cannot read it without the decryption key. Data encryption at rest is essential for protecting stored information, such as database files or backups, in the The Future of Mobile Cloud Computing. While cloud providers offer encryption services, it is recommended to implement your own encryption solution for sensitive data, particularly if compliance requirements demand strict control over data encryption. In addition, data encryption in transit is equally important for securing information transmitted between users and cloud services or between different cloud resources. To protect sensitive data from interception by attackers, it is crucial to always use secure protocols like HTTPS or TLS, ensuring that data remains encrypted during transmission.
Take charge of your Cloud Computing career by enrolling in ACTE’s Cloud Computing Master Program Training Course today!
Compliance and Regulatory Standards
Cloud security is closely tied to compliance with various regulations and standards that govern data protection. Organizations in regulated industries like healthcare, finance, and government must ensure their cloud security practices meet the relevant legal and regulatory requirements. For instance, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), enacted by the European Union, protects individuals’ privacy and mandates that organizations operating in or doing business with the EU comply with its data processing, storage, and security provisions. This includes encrypting personal data and implementing access controls to prevent unauthorized access. Similarly, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is a U.S. regulation that requires the protection of healthcare-related data. Cloud providers servicing healthcare organizations must meet HIPAA’s privacy, security, and data protection standards, including encrypting electronic health records (EHR) and other sensitive Cloud Deployment Models. Additionally, the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) outlines a set of security requirements for organizations that store, process, or transmit payment card information, mandating practices like encryption and secure storage to safeguard cardholder data.
Cloud Security Tools and Solutions
Various cloud security tools are available to help organizations protect their cloud environments. These include:
Want to ace your Cloud Computing interview? Read our blog on Cloud Computing Interview Questions and Answers now!
Future Trends in Cloud Security
As cloud adoption continues to grow, cloud security will increasingly evolve to tackle emerging threats and challenges driven by the expanding attack surface and more complex environments. With organizations migrating critical workloads to the cloud, cybersecurity measures must adapt to safeguard against advanced threats, such as data breaches, insider threats, and increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks. Cloud providers are investing heavily in next-gen security tools, including AI-powered threat detection, encryption advancements, and identity and access management solutions, to proactively address vulnerabilities. Additionally, the growing reliance on hybrid and multi-cloud environments will push for better integration of security policies and tools across diverse platforms, ensuring a unified and resilient defense against evolving cyber risks. As regulatory compliance becomes more stringent, organizations will need to implement more robust security frameworks and practices to meet legal and industry standards while maintaining flexibility and scalability in A Basic Guide to Computer Networks.Some future trends include:
Conclusion
Cloud security is an essential concern for businesses leveraging cloud computing technologies. Organizations can safeguard their data, applications, and infrastructure by understanding the key threats and challenges associated with cloud environments and following best practices for securing cloud resources. While maintaining compliance with relevant regulations, leveraging tools such as IAM, encryption, and monitoring solutions ensures that cloud environments remain secure, resilient, and trustworthy in the face of evolving threats. As cloud technology evolves, staying informed and adapting to new trends will be crucial for maintaining robust Cloud Computing Course . Additionally, fostering a culture of security awareness within the organization is vital for mitigating human error risks. Collaborating with trusted cloud service providers and ensuring they meet stringent security standards further enhances protection. Finally, organizations must continuously evaluate and update their cloud security strategies to address emerging vulnerabilities and threats effectively.





