
- Introduction
- Cloud Native
- Public Cloud
- What is Cloud Storage?
- Virtualization in Cloud Computing
- Cloud Computing Applications
- Challenges of Cloud Computing
- Conclusion
Introduction to Cloud Computing Platforms
Cloud computing platforms have revolutionized the way businesses and individuals store, access, and manage data. By offering on-demand services such as computing power, storage, and networking, these platforms eliminate the need for maintaining physical infrastructure, allowing organizations to scale rapidly and efficiently. Instead of investing in costly servers or on-premise storage, companies can now rent resources as needed, paying only for what they use.The primary advantage of cloud computing is its scalability. Cloud Computing Course , including Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud, enable organizations to quickly scale their resources up or down depending on demand. The ability to expand without worrying about infrastructure limitations is particularly valuable for businesses experiencing growth or needing to handle fluctuations in demand. Cloud computing platforms typically offer three key service models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).Cloud computing platforms have introduced new business possibilities, driving innovation across multiple industries and improving operational efficiency. With their flexibility, low upfront costs, and ease of management, they have become an essential tool for businesses worldwide.
Cloud Native
Cloud-native refers to a design and development methodology that enables applications to leverage the full potential of cloud environments. Cloud-native applications are built using microservices architecture, where each service operates independently and is designed to scale and fail independently. This approach contrasts with traditional monolithic applications, where the entire system is built as one large, tightly coupled unit.A core principle of Understanding the Cloud Native Applications applications is containerization. Containers allow applications to be packaged with their dependencies and deployed consistently across different environments. The use of containers simplifies deployment, scaling, and management, as containers are isolated and do not rely on specific hardware configurations.In cloud-native systems, orchestration tools like Kubernetes are essential for automating the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. Kubernetes facilitates load balancing, self-healing, and horizontal scaling by automatically adjusting the number of running container instances based on traffic or resource usage.
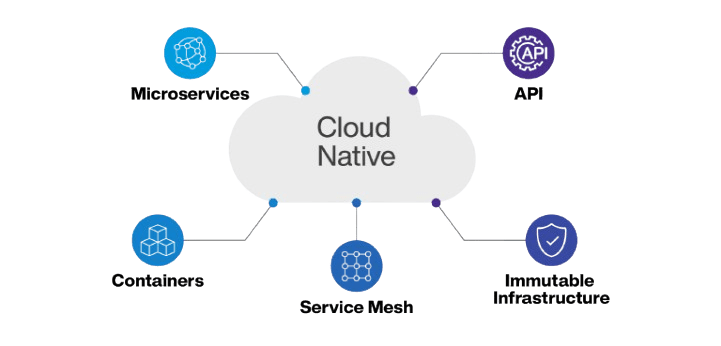
Cloud-native applications are designed for high availability and resilience, ensuring that services can be deployed across multiple cloud regions or data centers to reduce downtime. The cloud-native approach also emphasizes continuous integration (CI) and continuous delivery (CD) practices, allowing development teams to push new features or fixes quickly and reliably.Moreover, cloud-native architectures prioritize distributed computing, ensuring that workloads can be spread across multiple machines or even different clouds. This flexibility enables organizations to choose the best cloud providers, making cloud-native applications more portable and future-proof.Ultimately, cloud-native applications improve agility, speed up development cycles, and reduce operational overhead. Organizations adopting a cloud-native approach are better positioned to innovate and adapt to the rapidly changing technological landscape.
Advance your Cloud Computing career by joining this Cloud Computing Online Course now.
Public Cloud
- The public cloud refers to cloud computing resources such as servers, storage, and databases that are hosted by third-party cloud providers and made available to the public over the internet. Unlike private clouds, which are dedicated to a single organization, public clouds are shared among multiple users, offering cost efficiency and scalability. Public clouds are typically owned and operated by large cloud service providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
- One of the key benefits of the public cloud is its pay-as-you-go pricing model. Users are charged based on their actual usage of resources, which eliminates the need for significant upfront investment. This model makes the public cloud an attractive option for startups, small businesses, and enterprises that require flexibility and scalability without incurring heavy infrastructure costs.
- Public clouds offer various service models, including Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS), catering to a wide range of needs. Advanced Infrastructure as a Service in Cloud Computing services enable organizations to store data, run applications, host websites, and more, all without having to manage or maintain physical hardware.
- Moreover, public cloud providers invest heavily in security and compliance, ensuring that their platforms meet the highest industry standards. With built-in encryption, secure access controls, and regular security audits, public cloud environments can be as secure—if not more secure than traditional on-premises infrastructure.
- Despite its numerous advantages, the public cloud also presents challenges. As the infrastructure is shared among multiple users, there is always a potential risk of data breaches or security vulnerabilities.
- Additionally, organizations may experience vendor lock-in, where it becomes difficult or costly to switch between cloud providers due to proprietary technologies and services. However, with careful planning and security measures, the public cloud remains a highly effective solution for many organizations worldwide.
- Definition: Virtualization refers to the process of creating virtual versions of physical resources, such as servers, storage devices, and networks. In cloud computing, virtualization allows multiple virtual machines (VMs) to run on a single physical server, improving resource utilization and scalability.
- Types of Virtualization: There are various types of virtualization, including hardware virtualization, software virtualization, and storage virtualization. Hardware virtualization involves creating virtual versions of hardware components like CPUs and memory, while software virtualization abstracts the underlying operating system and allows multiple OS instances to run on a single machine.
- Hypervisor Role: A hypervisor is software that enables the creation and management of VMs. There are two types of hypervisors: Type 1 (bare-metal) runs directly on the hardware, while Type 2 (hosted) runs on top of an existing operating system. The hypervisor manages the distribution of resources between the VMs and ensures their isolation from each other.
- Resource Allocation: Virtualization enables dynamic resource allocation, meaning that computing resources like memory and CPU cycles can be distributed across various VMs based on demand. Seamless Cloud Migration Guide ensures efficient use of available hardware.
- Scalability: Virtualization allows cloud environments to scale easily. As demand increases, more virtual machines can be spun up on existing hardware to handle the additional workload, providing near-instant scalability without needing to invest in new physical servers.
- Cost-Efficiency: Virtualization reduces the need for physical hardware, leading to lower capital expenses and operational costs. By consolidating workloads onto fewer physical servers, businesses can reduce power consumption, space requirements, and hardware maintenance.
- Cloud Impact: Virtualization is the cornerstone of cloud computing. It enables multi-tenant environments where multiple organizations can share the same physical infrastructure while maintaining isolation and security for each tenant.
- Downtime & Service Outages: While cloud providers offer high uptime guarantees, outages can still occur due to network issues, data center failures, or cyberattacks. Businesses must have contingency plans in place to ensure continuity during service disruptions.
- Vendor Lock-In: Cloud services often involve proprietary technologies, which can make it difficult to switch providers without significant effort and cost. This can create dependency on a specific provider’s infrastructure and services.
- Compliance Issues: Many organizations must adhere to strict regulatory frameworks governing data storage and processing. Ensuring compliance with laws like GDPR and HIPAA can be challenging when data is stored in the cloud.
- Cost Management: The pay-as-you-go pricing model of cloud services can lead to unexpected costs if usage exceeds projections. Organizations must monitor their cloud resource consumption to avoid budget overruns.
- Data Transfer Speed & Latency: Moving large amounts of data between on-premises systems and the cloud can introduce latency, especially for businesses with limited internet bandwidth.
- Limited Control & Flexibility: Cloud Resource Management With Resource Pooling users may have limited control over the underlying infrastructure, depending on the service model they choose. Organizations may face challenges when trying to implement custom configurations or specific features not supported by their cloud provider.
Become a Cloud Computing expert by enrolling in this Cloud Computing Online Course today.
What is Cloud Storage?
Cloud storage is a service that allows individuals and organizations to store data remotely on servers, which can be accessed via the internet. Unlike traditional storage methods—such as local hard drives or on-premises servers cloud storage allows data to be stored offsite, often in data centers that span multiple locations, ensuring high availability and data redundancy. One of the primary advantages of cloud storage is its accessibility. Cloud storage platforms enable users to access their files from any location with an internet connection, using a variety of devices such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops. Whether you’re working remotely or on the go, cloud storage ensures that your data is always available. Popular cloud storage providers include Google Drive, Dropbox, and Amazon S3. Cloud Computing Course platforms offer different storage tiers, ranging from basic free plans to premium offerings with higher storage capacities. Cloud storage is commonly used for file backup, collaboration, and data sharing, making it an essential tool for both individuals and businesses. Cloud storage platforms also come with advanced features such as automatic file synchronization, real-time collaboration, and version control, allowing teams to work together efficiently. For businesses, cloud storage offers secure data storage with built-in encryption and access management features, helping to ensure compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA. However, cloud storage is not without its challenges. Organizations must consider factors such as data security, compliance, and cost when selecting a cloud storage provider. In particular, concerns about data breaches and unauthorized access can be a barrier for some businesses, particularly those handling sensitive or confidential information. Nonetheless, the Amazon Cloudfront and Its Benefits storage such as scalability, flexibility, and ease of access make it a popular solution for storing data in the digital age.
Virtualization in Cloud Computing
Ready to excel in Cloud Computing? Enroll in ACTE’s Cloud Computing Master Program Training Course and begin your journey today!
Cloud Computing Applications
Cloud computing allows healthcare providers to store large amounts of patient data securely and access it remotely. Cloud-based electronic health record (EHR) systems enable doctors to update and retrieve patient information in real-time, improving the quality of care and reducing errors. Cloud-based learning management systems (LMS) such as Moodle and Google Classroom enable students and instructors to collaborate, share materials, and track progress. Cloud Technologies also facilitates scalable online exams and virtual classrooms, making education more accessible to a broader audience. Cloud computing supports the banking industry by offering secure and efficient methods for data storage, processing transactions, and managing financial records. Blockchain solutions powered by cloud technology are increasingly being used to enhance transparency, reduce fraud, and streamline cross-border payments. Cloud platforms enable online retailers to scale their infrastructure quickly in response to demand.
Services like AWS Elastic Load Balancing and Azure Storage allow businesses to manage customer orders, track inventory, and handle high traffic volumes during peak shopping seasons. Cloud computing offers media companies the ability to store and stream large files efficiently. Platforms like Netflix and Spotify use cloud infrastructure to deliver high-quality content to millions of users worldwide. Hybrid Cloud Hypervisors for Scalability also enables collaboration among artists and filmmakers, allowing them to work remotely and share resources. Cloud computing ensures that businesses can continue operating even in the face of disasters. By storing critical data offsite and having access to cloud-based backup solutions, organizations can maintain continuity and minimize downtime. Cloud computing supports manufacturing by offering supply chain management tools, inventory tracking, and predictive maintenance systems. Cloud analytics help manufacturers optimize production processes, reduce waste, and forecast demand more accurately.
Are you getting ready for your Cloud Computing interview? Check out our blog on Cloud Computing Interview Questions and Answers!
Challenges of Cloud Computing
Storing data on remote servers raises concerns about unauthorized access, data breaches, and surveillance. Organizations must carefully assess the security measures implemented by cloud providers to protect their data.
Conclusion
Cloud computing platforms have transformed the way businesses operate by offering scalable, flexible, and cost-efficient solutions for managing data and infrastructure. From enhancing collaboration to supporting innovations across industries like healthcare, finance, and e-commerce, the impact of cloud technology is profound. However, challenges such as security concerns, downtime, and vendor lock-in remain significant considerations. Despite these obstacles, Cloud Computing Course continues to empower businesses and individuals to achieve greater efficiency and agility in a connected, data-driven world. Cloud computing also fosters innovation by enabling rapid deployment of new applications and services, driving competitive advantages. It allows businesses to access cutting-edge technologies such as AI, machine learning, and big data analytics without heavy upfront investments. As cloud platforms evolve, their ability to provide even more tailored, secure, and efficient solutions will continue to shape the future of digital transformation across industries.





