
- Introduction to Cloud Migration
- Reasons for Cloud Migration
- Types of Cloud Migration Strategies
- Cloud Migration Trends and Future Outlook
- Tools for Cloud Migration
- Post-Migration Steps and Optimizations
- Environmental Impact of Cloud Migration
- Cloud Migration Challenges
- Best Practices for Cloud Migration
- Conclusion
Introduction to Cloud Migration
Cloud migration refers to the process of moving data, applications, and other business elements from on-premises infrastructure or legacy systems to a cloud environment (public, private, or hybrid). This shift enables organizations to leverage the scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency that cloud platforms offer. Cloud migration is often a part of digital transformation strategies, allowing businesses to modernize their IT infrastructure, enhance agility, and improve performance. Cloud migration involves several stages, including assessment, planning, execution, and optimization, and may involve rehosting, replatforming, or refactoring applications to ensure they run efficiently in the cloud.
Reasons for Cloud Migration
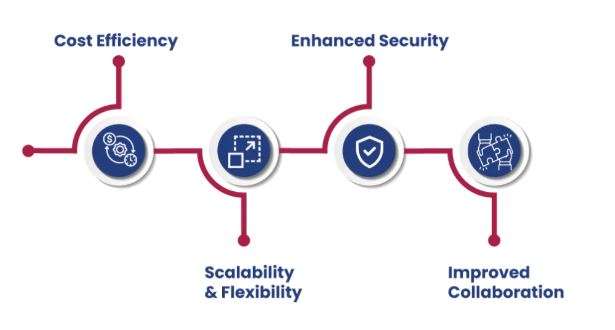
There are several key reasons why organizations migrate to the cloud, including:
- Cost Efficiency: Cloud computing offers a pay-as-you-go model, eliminating the need for significant upfront investments in hardware, reducing operational costs, and allowing businesses to scale resources as needed. A Cloud Computing Course can provide the skills and knowledge necessary to effectively implement and manage this flexible, cost-efficient model in your organization.
- Scalability and Flexibility: The cloud enables businesses to easily scale up or down based on demand, ensuring that resources are efficiently allocated without over-provisioning or under-utilizing.
- Enhanced Performance: Cloud providers offer high-performance computing resources that are often better than what many businesses can afford to maintain on-premises. With cloud services, organizations can take advantage of optimized data centers, faster processing power, and advanced technologies like AI and machine learning.
- Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity: The cloud provides built-in redundancy and backup options, allowing businesses to recover quickly from disasters and ensuring high availability of services even in case of failures.
- Collaboration and Accessibility: Cloud environments facilitate remote work and improve collaboration by making data and applications accessible from any location with an internet connection.
- Innovation and Agility: The cloud accelerates development cycles and fosters innovation by providing the latest technologies and services on demand. It supports agile methodologies by enabling quicker deployment and faster experimentation.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Cloud Computing? Sign Up For Our Cloud Computing Online Course Today!
Types of Cloud Migration Strategies
There are several strategies for migrating applications and data to the cloud, depending on the complexity of the workloads and the desired outcomes. The main strategies are:
Rehosting (Lift and Shift):
In this approach, applications and data are moved from on-premises environments to the cloud without significant changes to the architecture. It is the quickest and most straightforward migration strategy but may not fully leverage the cloud’s potential for optimization.- Example: Migrating a web server or database directly to an EC2 instance on AWS.
This strategy involves making minimal changes to an application to take advantage of cloud-native services or infrastructure while retaining the application’s core architecture.
- Example: Moving an application from an on-premises database to a managed cloud database service like Amazon RDS or Azure SQL Database.
Refactoring involves redesigning or re-architecting applications to optimize them for the cloud. This strategy allows organizations to fully leverage cloud-native features like auto-scaling, serverless computing, and microservices. Understanding Top Important Cloud Computing Terms is essential for mastering the concepts involved in refactoring and optimizing applications for the cloud environment.
- Example: Breaking a monolithic application into microservices and deploying it on Kubernetes in the cloud.
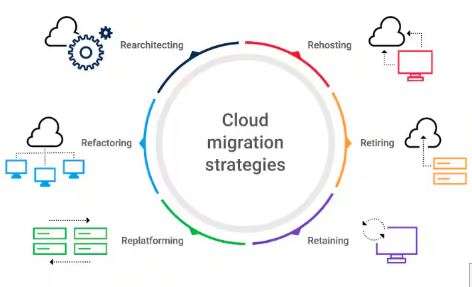
Repurchasing:
In this strategy, organizations replace legacy applications with cloud-based solutions, often through SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) applications.- Example: Switching from an on-premise CRM system to a cloud-based CRM like Salesforce.
Retiring:
This strategy involves decommissioning outdated or unused applications during migration. Organizations assess their applications and decide to stop using those that are no longer needed or relevant.- Example: Discontinuing legacy applications that no longer serve a business function.
Retaining:
In some cases, organizations decide to leave certain applications on-premises and not migrate them to the cloud, either because they are not suitable for the cloud or due to regulatory requirements.- Example: Keeping legacy systems that require compliance with strict data residency rules.
Cloud Migration Trends and Future Outlook
As cloud adoption continues to grow, several key trends are shaping the future of cloud migration. Multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies are becoming more popular, allowing organizations to distribute workloads across multiple cloud providers for greater flexibility, cost optimization, and redundancy. The rise of edge computing is also influencing migration strategies, as businesses seek to process data closer to end-users for reduced latency and improved performance. From Developer To AWS Cloud Specialist The AWS Certification Learning Paths can help individuals gain the necessary skills to effectively implement edge computing solutions within AWS, optimizing performance and reducing latency in cloud migration strategies. Additionally, automation and AI-driven migration tools are making cloud transitions more efficient by reducing manual effort, identifying optimization opportunities, and ensuring seamless workload portability. As businesses continue to evolve, cloud migration will remain a critical component of digital transformation strategies, with increasing emphasis on security, governance, and sustainability.
To Explore Cloud Computing in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Cloud Computing Online Course To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Tools for Cloud Migration
AWS Migration Hub:
AWS Migration Hub provides a central location to track migration progress across multiple AWS and partner migration tools. It offers insight into the status of your migration and simplifies planning.
Azure Migrate:
Azure Migrate is a comprehensive tool for migrating on-premises servers, applications, and data to Microsoft Azure. It provides assessment and migration tools for planning and executing migrations.
Google Cloud Migration Tools:
Google Cloud provides several tools, such as Migrate for Compute Engine, to facilitate the migration of virtual machines from on-premises or other clouds to Google Cloud.
CloudEndure (AWS):
CloudEndure is an AWS service that offers disaster recovery and migration solutions. It automates the migration process by replicating workloads in real-time to the cloud. Understanding Why And How To Pursue a Career In AWS can help professionals gain the necessary skills to effectively use services like CloudEndure, ensuring smooth migrations and robust disaster recovery strategies in cloud environments.
Velostrata:
Velostrata (now part of Google Cloud) is a migration tool that simplifies the process of migrating applications and data to the cloud, especially for virtual machines.
Carbonite:
Carbonite offers cloud migration and backup solutions that help businesses migrate critical workload. Decide whether to rehost, replatform, or refactor depending on the nature of each workload.
Ensure Data Security and Compliance:
Implement strong security measures, such as encryption, access control, and multi-factor authentication (MFA), to protect sensitive data during the migration process. Ensure compliance with all relevant regulations.
Monitor and Optimize:
After migrating to the cloud, continuously monitor your cloud infrastructure for performance, security, and cost optimization. Use cloud-native tools like AWS CloudWatch or Azure Monitor to track resources.
Train Teams and Update Processes:
Ensure that your IT teams are well-trained in cloud technologies and processes. Update existing workflows and processes to align with cloud-based operations.
Post-Migration Steps and Optimizations
Once the migration is complete, there are several important steps and optimization efforts to ensure the cloud environment is functioning efficiently:
- Testing and Validation:After migration, thoroughly test all applications, systems, and services to ensure they are working as expected in the cloud. Validate performance, functionality, and security.
- Cost Optimization: Analyze cloud resource usage and adjust the environment to avoid over-provisioning. Leverage auto-scaling, use appropriate storage classes, and eliminate unused resources to optimize costs.
- Performance Tuning: Continuously monitor and optimize the performance of cloud services. Identify bottlenecks, reduce latency, and enhance resource allocation to improve efficiency.
- Disaster Recovery and Backup: Implement a disaster recovery plan and configure automated backups to ensure data resilience in the cloud environment. A Cloud Computing Course can teach you the best practices for designing and implementing disaster recovery strategies, as well as configuring automated backup solutions to safeguard critical data.
- Ongoing Support and Management: Set up a support and management framework to handle ongoing maintenance, troubleshooting, and security updates. Leverage cloud monitoring tools to maintain cloud environments and improve automation.
- Feedback and Continuous Improvement: Solicit feedback from teams and stakeholders on the cloud environment and make adjustments as needed. Focus on continuous improvement, keeping the cloud infrastructure aligned with business goals. to the cloud while ensuring data protection and security.
- Downtime and Disruption: Migration can cause temporary downtime or disruptions in service. Minimizing downtime during migration is critical to ensure business continuity. Understanding The The Top In-demand cloud skills can help professionals develop the expertise needed to manage migrations efficiently, reducing disruptions and ensuring a seamless transition to the cloud.
- Data Transfer and Bandwidth Constraints: Migrating large amounts of data to the cloud can be time-consuming, especially when dealing with bandwidth limitations. Ensuring efficient data transfer without overloading network resources is key.
- Compatibility and Integration Issues: Applications and systems designed for on-premises infrastructure may not be fully compatible with cloud environments. Migration often requires significant re-engineering or reconfiguration to ensure smooth integration with cloud services.
- Security and Compliance: Migrating sensitive data to the cloud raises security concerns. Ensuring compliance with industry regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS, is essential during migration.
- Cost Management: Migration projects can become costly if not properly managed. Unforeseen expenses like additional storage, network usage, or cloud service configurations can affect the overall budget.
- Skills Gap: Cloud migration often requires specialized knowledge of cloud platforms and migration tools. Organizations may need to upskill their IT staff or hire cloud specialists to ensure a successful migration.
- Define Clear Objectives – Identify business goals, cost savings, scalability, and security needs.
- Assess Current Infrastructure – Conduct a cloud readiness assessment to analyze workloads, dependencies, and risks.
- Choose the Right Cloud Strategy – Decide between public, private, hybrid, or multi-cloud based on requirements.
- Select the Right Migration Approach – Consider Rehosting (Lift and Shift), Refactoring, Rearchitecting, Rebuilding, or Replacing based on application complexity.
- Prioritize Workloads – Migrate workloads in phases, starting with non-critical applications. Understanding the differences between Edge Computing Vs Cloud Computing can help you make informed decisions on where to place workloads, ensuring optimal performance and resource utilization based on your specific needs.
- Ensure Security & Compliance – Implement security best practices, encryption, IAM, and compliance frameworks (GDPR, HIPAA, etc.).
- Optimize Cost Management – Use cost calculators, reserved instances, and auto-scaling to optimize cloud spending.
- Automate & Use Infrastructure as Code (IaC) – Leverage Terraform, CloudFormation, or Ansible to automate deployments.
- Implement a Robust Data Migration Plan – Choose between online, offline, or hybrid data transfer methods (AWS Snowball, Azure Data Box, etc.).
- Monitor & Optimize Performance – Use cloud-native monitoring tools like AWS CloudWatch, Azure Monitor, or Google Cloud Operations Suite.
Are You Considering Pursuing a Master’s Degree in Cloud Computing? Enroll in the Cloud Computing Masters Course Today!
Environmental Impact of Cloud Migration
Cloud migration not only provides businesses with enhanced operational efficiency but also contributes to sustainability efforts. Traditional on-premises data centers consume significant amounts of energy and require constant cooling, leading to high carbon emissions. Cloud providers, on the other hand, invest in energy-efficient data centers powered by renewable energy sources, reducing the overall environmental impact. Migrating to the cloud can help organizations lower their carbon footprint by optimizing resource usage, reducing hardware waste, and leveraging shared infrastructure. Additionally, cloud-based analytics enable businesses to monitor and manage their sustainability goals more effectively, ensuring greener and more responsible IT operations.
Cloud Migration Challenges
While cloud migration provides many benefits, the process can be complex and presents several challenges that organizations need to address:
Best Practices for Cloud Migration
Want to Learn About Cloud Computing? Explore Our Cloud Computing Interview Questions & Answer Featuring the Most Frequently Asked Questions in Job Interviews.
Conclusion
Cloud migration is a transformative process that has become essential for businesses aiming to enhance their operational efficiency and scalability. By transferring data, applications, and other business processes from on-premises infrastructure to cloud platforms, organizations can tap into the many advantages that cloud environments offer. These include greater flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and the ability to scale resources on demand. The cloud also enables businesses to increase collaboration and accessibility, as employees can work from virtually any location, leveraging cloud-based applications and data. However, cloud migration also introduces challenges, such as ensuring data security, managing compliance requirements, and avoiding disruptions during the transition. A Cloud Computing Course can help you understand these challenges and equip you with the skills needed to address security, compliance, and minimize disruptions during the migration process. These challenges make it crucial for businesses to approach cloud migration with careful planning and strategic decision-making. In conclusion, cloud migration offers significant long-term benefits for organizations, such as improved performance, reduced costs, and increased business agility. It allows businesses to adopt a more innovative and flexible approach to technology, which is vital in a fast-evolving digital world. However, migrating to the cloud is not a one-size-fits-all solution, and businesses must assess their specific needs, risks, and resources before making the shift. Proper preparation, including choosing the right cloud provider, ensuring data protection, and planning for a seamless transition, is key to maximizing the benefits of cloud migration. When done correctly, cloud migration can empower organizations to stay competitive, adapt to market changes, and drive long-term success.





