
- What is Cloud Computing?
- Why Cloud Computing is a Lucrative Career Option
- Top Cloud Computing Job Roles
- Essential Cloud Computing Skills
- Cloud Certifications: AWS, Azure, Google Cloud
- How to Start a Career in Cloud Computing
- Hands-On Projects to Build Cloud Expertise
- Networking and Finding Cloud Computing Jobs
- Cloud Engineer vs Cloud Architect: Career Path Differences
- Salary Trends in Cloud Computing
- Common Challenges in Cloud Career Growth
- Future Prospects in Cloud Computing Careers.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics over the internet, also known as “the cloud.” Rather than owning their own Cloud Computing Course , businesses and individuals can rent access to these services from a cloud service provider. Cloud computing allows users to access their data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection, offering scalability, flexibility, and cost efficiency.
There are several key models in cloud computing:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. Examples include Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure. Platform as a Service (PaaS): Offers hardware and software tools over the internet, typically for application development. Examples include Google App Engine and AWS Elastic Beanstalk.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Provides access to software applications via the internet. Examples include Google Workspace (G Suite), Microsoft 365, and Salesforce. Cloud computing has become integral in enabling businesses to run applications, store data, and scale operations efficiently without maintaining physical infrastructure.
Why Cloud Computing is a Lucrative Career Option
Cloud computing has transformed how businesses operate, and as more organizations move their infrastructure to the cloud, there is an increasing demand for cloud professionals. This has made cloud computing a highly lucrative career option for several reasons:
- High Demand for Cloud Professionals: The widespread adoption of cloud technologies across industries has created a shortage of skilled cloud professionals, leading to a surge in demand for cloud engineers, architects, and specialists.
- Attractive Salaries: Given the high demand and specialized skill set, cloud computing jobs often come with attractive salaries. Professionals with expertise in cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud are particularly well-compensated.
- Job Flexibility and Remote Work: Firewall and Antivirus Software jobs are often flexible, with opportunities for remote work. Since cloud technologies enable decentralized infrastructure, many companies offer cloud computing positions that allow employees to work from anywhere.
- Rapid Technological Growth: The cloud industry is continuously evolving, offering professionals the opportunity to work with cutting-edge technologies like machine learning, artificial intelligence, and serverless computing.
- Career Growth Potential: The cloud computing industry is expected to continue growing, providing long-term career prospects and opportunities to climb the career ladder.
Master Cloud Computing skills by enrolling in this Cloud Computing Online Course today.
Top Cloud Computing Job Roles
Several key roles in cloud computing are in high demand across various organizations. Some of the top cloud computing job roles include:
- Cloud Engineer: Responsible for managing and maintaining cloud infrastructure, ensuring its availability, performance, and security.
- Cloud Architect: Designs and implements cloud solutions, ensuring that the architecture is scalable, cost-effective, and secure.
- Cloud Consultant: Provides expert advice to organizations on how to leverage cloud technologies, assisting with Data Security and implementation strategies.
- Cloud Security Engineer: Focuses on securing cloud infrastructure and applications, ensuring compliance with security standards and safeguarding data.
- Cloud Developer: Develops applications and software that run on cloud platforms, leveraging cloud services to build scalable and efficient solutions.
- Cloud DevOps Engineer: Combines development and operations expertise to automate processes and manage infrastructure using cloud technologies, often focusing on CI/CD pipelines.
- Cloud Sales Engineer: Works with customers to understand their cloud needs and helps in the sales process, demonstrating the value and capabilities of cloud solutions.
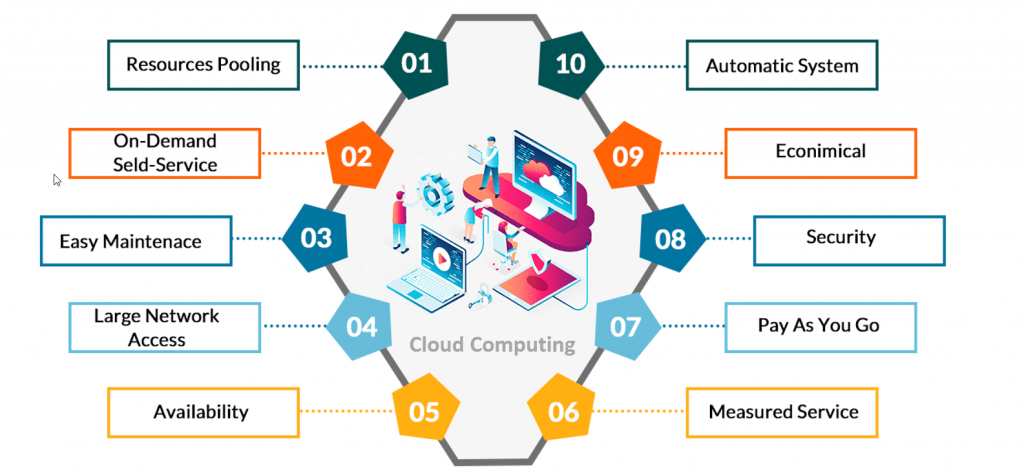
Essential Cloud Computing Skills
To pursue a career in cloud computing, individuals need a combination of technical skills, problem-solving abilities, and a good understanding of cloud platforms. Some essential cloud computing skills include Cloud Platform Knowledge Proficiency in popular cloud platforms such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). Cloud Architecture Understanding how to design scalable, reliable, and secure cloud systems that meet business needs. Networking Strong knowledge of cloud networking concepts, including virtual networks, Cloud Computing Course, load balancing, and DNS. Security Proficiency in cloud security practices, including data encryption, identity and access management (IAM), and compliance requirements. Automation and Scripting Knowledge of automation tools (like Terraform, Ansible, or AWS CloudFormation) and programming/scripting languages (Python, Shell, Bash) to automate cloud deployments. Containers and Orchestration Familiarity with containerization technologies like Docker and Kubernetes to manage applications in the cloud. DevOps Familiarity with DevOps practices and tools such as Jenkins, GitLab, and CI/CD pipelines to automate software deployment and integration. Database Management Understanding cloud databases such as Amazon RDS, Azure SQL Database, and NoSQL databases like DynamoDB or MongoDB. Troubleshooting Ability to diagnose and troubleshoot cloud-related issues in applications, infrastructure, and services.
Cloud Certifications: AWS, Azure, Google Cloud
Cloud certifications are highly regarded in the industry as they validate a professional’s knowledge and expertise in cloud technologies. Here are some popular cloud certifications:
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate: This certification demonstrates expertise in designing and deploying scalable, secure, and cost-efficient cloud systems on AWS.
- Microsoft Certified: Azure Solutions Architect Expert: This certification proves the ability to design and implement solutions on Microsoft Azure.
- Google Cloud Professional Cloud Architect: A certification for those who design and manage Data Classification using Google Cloud.
- AWS Certified DevOps Engineer: Focuses on the skills needed to operate in a DevOps environment on AWS, including automation and monitoring.
- Microsoft Certified: Azure DevOps Engineer Expert: Proves the skills required to design and implement DevOps practices in Azure environments.
- Certified Kubernetes Administrator (CKA): For professionals who want to demonstrate their ability to manage and orchestrate containers using Kubernetes, a key technology in cloud computing.
- Learn the Fundamentals: Begin by understanding the basic concepts of cloud computing, including the various service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS) and cloud deployment models (public, private, hybrid).
- Choose a Cloud Platform: Pick a cloud platform to focus on (AWS, Azure, GCP). Each has its own ecosystem, and specializing in one will give you a deeper understanding of its services and offerings.
- Get Hands-On Experience: Work on cloud projects, set up virtual machines, databases, and other services to gain practical experience. Most Cloud Security Service offer free-tier services to practice on.
- Earn Certifications: Obtain certifications for the cloud platform you’re focusing on. Certifications demonstrate your expertise to potential employers and give you an edge in the job market.
- Network with Cloud Professionals: Attend Cloud Expertise meetups, webinars, and conferences. Join online communities and forums to learn from others and expand your network.
- Stay Updated: Cloud computing is a rapidly evolving field, so staying current with the latest developments, tools, and best practices is essential.
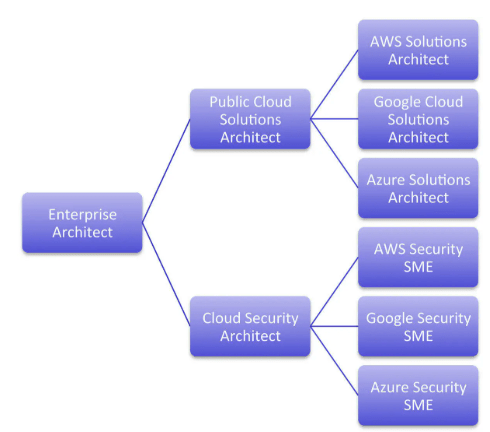
- Cloud Engineer: A cloud engineer focuses on the hands-on management, maintenance, and implementation of cloud infrastructure. They work with cloud services, networking, storage, and security to ensure the efficient operation of applications in the cloud. Expertise in cloud platforms, automation tools, networking, and infrastructure management. Typically begins as a junior cloud engineer, moving up to a senior cloud engineer or DevOps engineer.
- Cloud Architect: A cloud architect designs the overall cloud strategy and architecture for an organization. Role of Cloud in The Internet of Things ensure that the cloud infrastructure aligns with business goals and that it is scalable, secure, and cost-efficient. Strong design skills, deep knowledge of cloud services, leadership, and communication skills. Career Path Cloud architects often have years of experience in engineering or IT operations and move into architecture roles.
- Cloud Engineer: $80,000 – $130,000 per year.
- Cloud Architect: $120,000 – $180,000 per year.
- Cloud Security Engineer: $100,000 – $150,000 per year.
- Cloud Consultant: $90,000 – $150,000 per year.
- Cloud Developer: $85,000 – $140,000 per year.
- Keeping Up with Rapid Technological Changes: Cloud technologies evolve rapidly, requiring continuous learning and adaptation.
- Gaining Practical Experience: Without hands-on experience, it can be challenging to gain in-depth knowledge, especially for beginners.
- Staying Competitive: With so many cloud professionals in the field, it can be difficult to stand out without a specialization or advanced certifications.
- Cloud Security Concerns: As more organizations move to the cloud, security becomes an increasing concern. Cloud professionals must constantly stay updated on security best practices and threat mitigation.
Learn the fundamentals of Cloud Computing with this Cloud Computing Online Course .
How to Start a Career in Cloud Computing
Starting a career in cloud computing typically involves the following steps:
Hands-On Projects to Build Cloud Expertise
Working on hands-on projects is one of the best ways to build cloud computing expertise. Some project ideas include, Build a Web Application on AWS/Azure/GCP Set up a simple web application and deploy it to the cloud using the platform’s services (e.g., AWS EC2, Azure App Services, GCP Compute Engine). Automate Infrastructure with Terraform Use Terraform to create and manage cloud infrastructure in a repeatable and automated way. Set Up a CI/CD Pipeline Use Jenkins, GitLab, or AWS CodePipeline to automate the deployment process of an application to the cloud. Create a Serverless Application Build a serverless app using AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, or Google Cloud Functions to handle event-driven workflows. Containerize Applications Using Docker and Kubernetes Containerize an application and deploy it on a Kubernetes cluster in the cloud to understand container orchestration.
Want to lead in Cloud Computing? Enroll in ACTE’s Cloud Computing Master Program Training Course and start your journey today!
Networking and Finding Cloud Computing Jobs
Networking is crucial for landing a cloud computing job. Some strategies to find opportunities include LinkedIn: Build a professional LinkedIn profile that showcases your cloud skills, certifications, and hands-on projects. Follow Address Resolution Protocol leaders and join relevant groups. Job Portals Use job boards like Indeed, Glassdoor, and specialized tech job boards like Stack Overflow Jobs or AngelList to find cloud computing positions. Cloud Provider Communities Join cloud-specific forums and user groups for AWS, Azure, or GCP, where you can connect with others and learn about job openings. Cloud Certifications Highlight your cloud certifications and any hands-on experience in your resume. Certifications are highly valued by employers in the cloud domain. Online Networking Attend cloud computing webinars, meetups, and conferences to network with professionals in the field.
Cloud Engineer vs Cloud Architect: Career Path Differences
The roles of Cloud Engineer and Cloud Architect differ in terms of responsibility, scope, and career trajectory:
Salary Trends in Cloud Computing
Cloud computing professionals are highly compensated due to the specialized skills required. While salaries can vary based on location, experience, and job role, here are some average salary ranges:
Salaries are higher in major tech hubs such as Silicon Valley, New York, and Seattle but also vary with experience and the specific cloud platform expertise.
Common Challenges in Cloud Career Growth
While cloud computing offers lucrative opportunities, professionals may face challenges such as:
Preparing for Cloud Computing interviews? Visit our blog for the best Cloud Computing Interview Questions and Answers!
Future Prospects in Cloud Computing Careers
The future of cloud computing is bright, with increasing reliance on cloud services across industries. Some key trends that will shape cloud computing careers include, Growth of Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud: More organizations are adopting multi-cloud strategies, increasing the demand for professionals who can manage multiple cloud environments. AI and Machine Learning in the Cloud The integration of AI and machine learning into cloud platforms will create new career opportunities in AI/ML cloud services. Cloud-Native Technologies The rise of serverless computing and containerization (e.g., Kubernetes) will continue to redefine how cloud services are deployed. Cloud Security With growing concerns around data privacy and security, there will be a high demand for professionals specializing in Cloud Computing Course . The continued expansion of cloud technologies offers a wealth of career opportunities for professionals with the right skills and certifications.





