
- Introduction to Public Cloud
- Key Characteristics of Public Cloud
- Public Cloud vs Private Cloud vs Hybrid Cloud
- Benefits of Using Public Cloud
- Challenges and Limitations of Public Cloud
- Top Public Cloud Providers (AWS, Azure, GCP)
- Conclusion
Introduction to Public Cloud
The public cloud is a computing model where computing resources such as servers, storage, and applications are provided over the internet by third-party cloud service providers. These services are made available to the general public, allowing businesses and individuals to rent computing resources on demand. Public cloud services are hosted on a shared infrastructure that is managed and maintained by cloud providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
Unlock your potential in Cloud Computing with this Cloud Computing Online Course .
In the public cloud model, users access these resources via the internet and pay only for the resources they use, typically following a pay-as-you-go pricing model. This eliminates the need for businesses to invest in or manage their hardware, offering significant cost savings. The Cloud Computing Course is scalable, flexible, and easily accessible, making it an attractive solution for a variety of industries looking to streamline operations and increase efficiency.Public cloud services include a wide range of offerings, such as virtual machines, storage services, databases, analytics tools, networking, and developer tools. These services can be used for anything from hosting websites and applications to running complex data processing tasks and machine learning workloads.
Key Characteristics of Public Cloud
- On-Demand Self-Service: Users can provision and manage resources as needed, without requiring human intervention from the cloud provider. This allows for flexibility and autonomy in resource management.
- Scalability: Public cloud services are highly scalable, allowing users to easily adjust their computing resources up or down based on demand. This elasticity ensures that businesses can handle spikes in usage without over-provisioning or under-provisioning resources.
- Multi-Tenancy: Multiple customers share the same physical infrastructure but are logically isolated from each other. Each customer’s data and applications are kept secure and separate, ensuring privacy and security.
- Resource Pooling: Cloud providers pool their resources and allocate them dynamically to meet the needs of users. This allows providers to optimize resource usage, reduce costs, and deliver services at scale.
- Pay-as-You-Go Pricing: Users are billed based on the resources they use, allowing for more predictable costs and eliminating the need for large upfront investments in hardware. Ansible Tower is particularly advantageous for businesses with fluctuating demands.
- Accessibility and Availability: Public cloud resources are typically available 24/7, with high levels of reliability. Cloud providers often guarantee uptime through Service Level Agreements (SLAs).
- Managed by Cloud Providers: Cloud providers handle all aspects of resource management, including hardware, software updates, security, and maintenance, allowing users to focus on their core business activities.
- Security and Privacy Concerns: Storing data in a public cloud can raise concerns about unauthorized access, data breaches, and privacy. Although cloud providers implement strong security measures, organizations must also implement their security protocols to ensure data is protected.
- Compliance and Regulatory Challenges: Public cloud environments may not always meet the specific compliance requirements of certain industries, such as finance or healthcare. Organizations must ensure that the cloud provider meets the necessary legal and regulatory standards (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
- Latency Issues: Depending on the location of the cloud data center, users may experience latency issues when accessing cloud-based applications or data. For critical applications requiring real-time processing, Cloud Computing Course may be a concern.
- Vendor Lock-In: Switching between cloud providers can be difficult and costly due to proprietary technologies, services, and APIs. Organizations may become dependent on a particular cloud provider’s services, making it harder to migrate to another provider.
- Limited Control: With public cloud services, users have limited control over the underlying infrastructure. The cloud provider manages the hardware and network resources, which can be restrictive for businesses needing custom configurations.
- Cost Management: Although the public cloud offers cost efficiency, organizations may struggle to manage costs effectively. Unused resources or misconfigured services can lead to unexpected expenses. Proper monitoring and resource management are essential.
- Reliability of Service: While cloud providers strive for high availability, occasional outages or service disruptions can affect business operations. Organizations must ensure that they have adequate backup and disaster recovery plans in place.
- Public cloud services are widely used to host websites, web applications, and mobile apps, providing scalability and flexibility to handle fluctuating user traffic.
- Many organizations use the public cloud to back up critical data and Edge Computing With Aws Greengrass. Cloud-based backup solutions are cost-effective and provide quick recovery in case of an emergency.
- Public cloud storage services like AWS S3, Azure Blob Storage, and Google Cloud Storage offer businesses an easy way to store, manage, and analyze large volumes of data without the need for on-premise infrastructure.
- The public cloud is ideal for running large-scale analytics workloads. Services like Google BigQuery, AWS Redshift, and Azure Synapse Analytics allow businesses to store and process massive datasets in real time.
- Public cloud platforms provide powerful tools and frameworks for building and deploying AI and machine learning models. Providers like AWS, Azure, and GCP offer pre-built machine learning models and managed services for training and deploying custom models.
- Public cloud platforms are crucial for supporting remote work by offering collaboration tools, secure access to enterprise applications, and cloud-based desktops.
- Public cloud platforms support DevOps practices by offering tools for continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD), automating the software development lifecycle.
Learn how to manage and deploy cloud services by joining this Cloud Computing Online Course today.
Public Cloud vs Private Cloud vs Hybrid Cloud
| Cloud Model | Deployment | Access | Examples | Best for |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public Cloud | The infrastructure is owned, operated, and maintained by a third-party provider and shared with multiple users. | Services are available over the internet, with resources allocated dynamically based on demand. | AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud | Small to medium-sized businesses, startups, and companies with dynamic workloads that require scalability and Virtualization in Cloud Computing. |
| Private Cloud | The cloud infrastructure is dedicated to a single organization, hosted on-premises or by a third-party provider. | Resources are not shared with external organizations, offering greater control over data security and privacy. | VMware Private Cloud, Microsoft Azure Stack, Google Cloud Anthos (for on-premise private cloud) | Large enterprises, government agencies, or organizations with strict security and compliance requirements. |
| Hybrid Cloud | Combines public and private clouds, allowing data and applications to be shared between them. | Greater flexibility, with the ability to run applications and store data across multiple environments. | AWS Outposts, Azure Arc, Google Cloud Anthos | Enterprises that need to balance flexibility with data security and have a mix of sensitive and non-sensitive workloads. |
Benefits of Using Public Cloud
Public cloud providers offer a pay-as-you-go pricing model, eliminating the need for large capital expenditures. This enables businesses to only pay for the resources they use, which can significantly reduce operational costs. Public cloud services can easily scale up or down to meet fluctuating demand. Whether it’s increasing storage capacity, processing power, or network bandwidth, the public cloud offers immense flexibility. With the on-demand nature of the public cloud, businesses can deploy new applications, test new ideas, and respond to market changes more quickly.
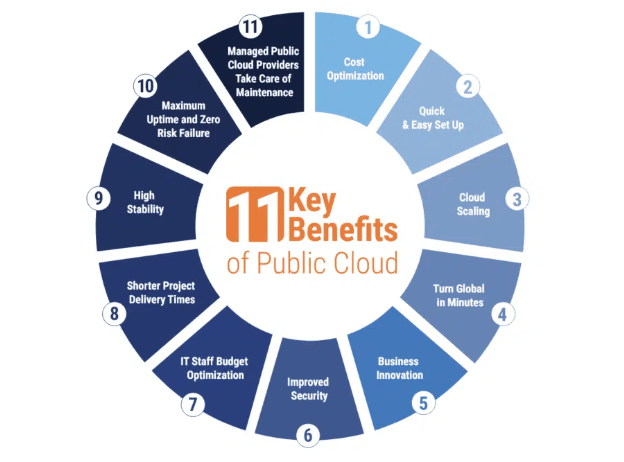
This agility fosters innovation and accelerates time-to-market for products. Leading public cloud providers offer high levels of redundancy and uptime guarantees, ensuring that resources are available when needed. Many public Practices and Tools in Devops provide geographically distributed data centers for disaster recovery and failover protection. Public cloud providers manage infrastructure and software, handling maintenance, updates, and security, which allows businesses to focus on core activities without the burden of managing IT infrastructure. Public cloud services are available in multiple regions around the world, making it easier for businesses to serve global markets and deliver low-latency services to customers. While security is a shared responsibility between the provider and the user, major public cloud providers invest heavily in securing their infrastructure. Features like encryption, multi-factor authentication, and identity and access management (IAM) help protect sensitive data and applications.
Aspiring to lead in Cloud Computing? Enroll in ACTE’s Cloud Computing Master Program Training Course and start your path to success!
Challenges and Limitations of Public Cloud
Use Cases and Applications of Public Cloud
Preparing for Cloud Computing interviews? Visit our blog for the best Cloud Computing Interview Questions and Answers!
Top Public Cloud Providers (AWS, Azure, GCP)
AWS is the leading public cloud provider, offering a broad range of services, including computing, storage, networking, and database solutions. AWS also provides specialized services like machine learning, IoT, and analytics. AWS has a vast global network of data centers and is known for its scalability, flexibility, and a robust ecosystem of third-party integration. Azure is a major player in the public cloud space, particularly favored by enterprises due to its strong integration with Microsoft products like Windows Server, SQL Server, and Active Directory.

Azure offers a wide range of Ansible Playbooks Explained Guide, including AI, machine learning, and blockchain. Azure is known for its hybrid capabilities, allowing businesses to seamlessly integrate on-premise systems with the cloud. Google Cloud excels in services related to big data, AI, and machine learning, leveraging its expertise in search and analytics. GCP provides strong offerings for Kubernetes and containerized applications, along with highly scalable compute resources and storage services. GCP is often chosen for its advanced data analytics tools and global network infrastructure.
Conclusion
The public cloud has revolutionized the way businesses and individuals access computing resources, offering unparalleled flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency. By leveraging the services of major cloud providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud, organizations can reduce infrastructure costs, improve operational agility, and accelerate innovation. The key benefits of public cloud—such as on-demand self-service, pay-as-you-go pricing, and global reach—make it an attractive solution for businesses of all sizes. However, it is important for organizations to carefully consider the challenges associated with Cloud Computing Course , such as security and privacy concerns, vendor lock-in, and regulatory compliance. By understanding these challenges and taking proactive measures to address them, businesses can fully unlock the potential of the public cloud and ensure that their cloud adoption is secure, cost-effective, and aligned with their long-term strategic goals. Ultimately, the public cloud remains a powerful tool for organizations looking to streamline operations, scale efficiently, and innovate in today’s fast-paced digital landscape. Whether hosting web applications, running big data analytics, or supporting remote work, the public cloud offers the resources and flexibility to meet a wide array of business needs.





